Abstract
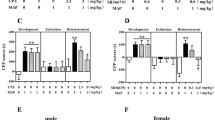
Drug addiction is a chronically relapsing disorder in humans; yet, the underlying mechanism remained unclear. Recent studies suggested that the histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 1 (HINT1) may play significant roles in diverse neuropsychiatric diseases including drug addiction. In our present study, we used different batches of mice to establish the different stages of methamphetamine (METH)-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) to explore the dynamic changes throughout the process of addiction in different brain regions, including prefrontal cortex (PFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), corpus striatum (CPu), and hippocampus (Hip). We found that in NAc of the METH group mice, the HINT1 expression level initially increased after acquisition phases, and then dropped to the normal level after extinction phase, and again increased after reinstatement phase. However, there was no statistical difference in the HINT1 expression level in other three encephalic regions (PFC, CPu, and Hip). Therefore, the HINT1 protein, particularly in the NAc, plays a vital role in the METH-induced CPP. However, the precise mechanisms will require further investigation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RM, Everett CV, Nelson AM, Gulley JM, Zahniser NR (2007) Low and high locomotor responsiveness to cocaine predicts intravenous cocaine conditioned place preference in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86:37–44
Barbier E, Zapata A, Oh E, Liu Q, Zhu F, Undie A, Shippenberg T, Wang JB (2007) Supersensitivity to amphetamine in protein kinase-C interacting protein/HINT1 knockout mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1774–1782
Baron M (2001) Genetics of schizophrenia and the new millennium: progress and pitfalls. Am J Hum Genet 68:299–312
Cunningham CL, Gremel CM, Groblewski PA (2006) Drug-induced conditioned place preference and aversion in mice. Nat Protoc 1:1662–1670
Dang YH, Liu ZW, Chen F, Guo K, Wang JB (2014) Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 and human diseases. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 36:454–460
Fang J, Wang X, He B (2014) Association between common genetic variants in the opioid pathway and smoking behaviors in Chinese men. Behav Brain Funct 10:2
Garzon J, Rodriguez-Munoz M, Sanchez-Blazquez P (2012) Direct association of mu-opioid and NMDA glutamate receptors supports their cross-regulation: molecular implications for opioid tolerance. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 5:199–226
Homer BD, Solomon TM, Moeller RW, Mascia A, DeRaleau L, Halkitis PN (2008) Methamphetamine abuse and impairment of social functioning: a review of the underlying neurophysiological causes and behavioral implications. Psychol Bull 134:301–310
Hyman SE (2005) Addiction: a disease of learning and memory. Am J Psychiatry 162:1414–1422
Jackson KJ, Chen Q, Chen J, Aggen SH, Kendler KS, Chen X (2011) Association of the histidine-triad nucleotide-binding protein-1 (HINT1) gene variants with nicotine dependence. Pharmacogenomics J 11:251–257
Jackson KJ, Wang JB, Barbier E, Damaj MI, Chen X (2013) The histidine triad nucleotide binding 1 protein is involved in nicotine reward and physical nicotine withdrawal in mice. Neurosci Lett 550:129–133
Karam CS, Ballon JS, Bivens NM, Freyberg Z, Girgis RR, Lizardi-Ortiz JE, Markx S, Lieberman JA, Javitch JA (2010) Signaling pathways in schizophrenia: emerging targets and therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31:381–390
Kauer JA (2004) Learning mechanisms in addiction: synaptic plasticity in the ventral tegmental area as a result of exposure to drugs of abuse. Annu Rev Physiol 66:447–475
Kelley AE, Berridge KC (2002) The neuroscience of natural rewards: relevance to addictive drugs. J Neurosci 22:3306–3311
Kelley AE, Andrzejewski ME, Baldwin AE, Hernandez PJ, Pratt WE (2003) Glutamate-mediated plasticity in corticostriatal networks: role in adaptive motor learning. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:159–168
Klein DA, Gulley JM (2009) Reduced sensitivity to the locomotor-stimulant effects of cocaine is associated with increased sensitivity to its discriminative stimulus properties. Behav Pharmacol 20:67–77
Klein MG, Yao Y, Slosberg ED, Lima CD, Doki Y, Weinstein IB (1998) Characterization of PKCI and comparative studies with FHIT, related members of the HIT protein family. Exp Cell Res 244:26–32
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2010) Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:217–238
Li H, Zhang Y, Su T, Santella RM, Weinstein IB (2006) Hint1 is a haplo-insufficient tumor suppressor in mice. Oncogene 25:713–721
Liu Q, Puche AC, Wang JB (2008) Distribution and expression of protein kinase C interactive protein (PKCI/HINT1) in mouse central nervous system (CNS). Neurochem Res 33:1263–1276
Mandt BH, Schenk S, Zahniser NR, Allen RM (2008) Individual differences in cocaine-induced locomotor activity in male Sprague-Dawley rats and their acquisition of and motivation to self-administer cocaine. Psychopharmacology 201:195–202
Nestler EJ (2005) Is there a common molecular pathway for addiction? Nat Neurosci 8:1445–1449
NIDA(1969). Methamphetamine. Vol., ed.^eds. NIDA(1969)
Paxinos G, Franklin KB (2004) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Gulf Professional Publishing, Vol.
Robertson SD, Matthies HJ, Galli A (2009) A closer look at amphetamine-induced reverse transport and trafficking of the dopamine and norepinephrine transporters. Mol Neurobiol 39:73–80
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (2003) Addiction. Annu Rev Psychol 54:25–53
Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (2011) Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:623–637
Rodriguez-Munoz M, de la Torre-Madrid E, Sanchez-Blazquez P, Wang JB, Garzon J (2008) NMDAR-nNOS generated zinc recruits PKCgamma to the HINT1-RGS17 complex bound to the C terminus of mu-opioid receptors. Cell Signal 20:1855–1864
Rodriguez-Munoz M, Sanchez-Blazquez P, Vicente-Sanchez A, Bailon C, Martin-Aznar B, Garzon J (2011) The histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 supports mu-opioid receptor-glutamate NMDA receptor cross-regulation. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:2933–2949
Rodriguez-Munoz, M, Sanchez-Blazquez, P, Merlos, M, Garzon-Nino, J (2016) Endocannabinoid control of glutamate NMDA receptors: the therapeutic potential and consequences of dysfunction. Oncotarget
Romanova EV, Lee JE, Kelleher NL, Sweedler JV, Gulley JM (2010) Mass spectrometry screening reveals peptides modulated differentially in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats with disparate initial sensitivity to cocaine. AAPS J 12:443–454
Sabeti J, Gerhardt GA, Zahniser NR (2003) Individual differences in cocaine-induced locomotor sensitization in low and high cocaine locomotor-responding rats are associated with differential inhibition of dopamine clearance in nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:180–190
Straub RE, MacLean CJ, O'Neill FA, Walsh D, Kendler KS (1997) Support for a possible schizophrenia vulnerability locus in region 5q22-31 in Irish families. Mol Psychiatry 2:148–155
Su T, Suzui M, Wang L, Lin CS, Xing WQ, Weinstein IB (2003) Deletion of histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1/PKC-interacting protein in mice enhances cell growth and carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:7824–7829
Su HL, Zhu J, Chen YJ, Zhao N, Han W, Dang YH, Xu M, Chen T (2013) Roles of levo-tetrahydropalmatine in modulating methamphetamine reward behavior. Physiol Behav 118:195–200
Tzschentke TM (2007) Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm: update of the last decade. Addict Biol 12:227–462
Vicente-Sanchez A, Sanchez-Blazquez P, Rodriguez-Munoz M, Garzon J (2013) HINT1 protein cooperates with cannabinoid 1 receptor to negatively regulate glutamate NMDA receptor activity. Mol Brain 6:42
Volkow ND, Morales M (2015) The brain on drugs: from reward to addiction. Cell 162:712–725
Volz TJ, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE (2007) The role of the plasmalemmal dopamine and vesicular monoamine transporters in methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic deficits. J Neurochem 101:883–888
Wolf ME (1998) The role of excitatory amino acids in behavioral sensitization to psychomotor stimulants. Prog Neurobiol 54:679–720
Zhao N, Chen Y, Zhu J, Wang L, Cao G, Dang Y, Yan C, Wang J, Chen T (2014) Levo-tetrahydropalmatine attenuates the development and expression of methamphetamine-induced locomotor sensitization and the accompanying activation of ERK in the nucleus accumbens and caudate putamen in mice. Neuroscience 258:101–110
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC81171262, 81771435, 81371473 to Yong-hui Dang), and the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2016JM8078 to Yong-hui Dang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee of Xi’an Jiaotong University.
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Jp., Liu, P., Lei, G. et al. The Role of HINT1 in Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference. Neurotox Res 33, 353–361 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9797-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9797-7