Abstract
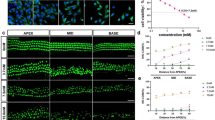
The spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) located in the Rosenthal’s canal of cochlea are essential target for cochlear implant. Previous studies found that the canaliculi perforantes, small pores on the surface of the osseous spiral lamina (OSL) of the scala tympanic (ST) of cochlea, may provide communication between the cochlear perilymph and SGNs. In this study, we found that chronic treatment of aminoglycosides antibiotics, which is well known to cause sensory cell damage in the cochlea, induced significant damage of bone lining cells on the OSLs and increased the permeability of the Rosenthal’s canal. The pores among the bone lining cells became significantly wider after chronic treatment of amikacin (100 mg/kg/day for 3–7 days). Injection of Evans Blue in the ST resulted in significant increase in its migration in the modulus in the amikacin-treated cochlea compared to the control ears, suggesting increased permeability of these passages. Treatment of amikacin with oxytetracycline, an inhibitor of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs), significantly reduced the amount of dye migrated from the ST to the modiolus. These results suggest that amikacin enhanced the permeability between the ST and SGNs by increasing MMPs. Aggregating the permeability of the bone lining cells on the OSLs may benefit gene and stem cell delivery to the SGNs in the cochlea.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- OSLs:
-
Osseous spiral laminaes
- SGNs:
-
Spiral ganglion neurons
- SNHL:
-
Sensorineural hearing loss
- ST:
-
Scala tympani
- SV:
-
Scala vestibule
- Ami-7D:
-
Amikacin - 7 days
- Ami-3D:
-
Amikacin - 3 days
- Ami + Oxy-7D:
-
Amikacin + Oxytetracycline - 7 days
- Ami + Oxy-3D:
-
Amikacin + Oxytetracycline - 3 days
- BM:
-
Basement membrane
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- BCA:
-
Bicinchonininc acid
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecylsulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- OCT:
-
Optimal cutting temperature (compound)
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Angelborg C (1974) Distribution of macromolecular tracer particles (Thorotrast-r) in the cochlea. An electron microscopic study in guinea pig. Part I the organ of Corti, the basilar membrane and the tympanic covering layer. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 319:19–41
Atkinson PJ, Wise AK, Flynn BO, Nayagam BA, Hume CR, O’Leary SJ, Shepherd RK, Richardson RT (2012) Neurotrophin gene therapy for sustained neural preservation after deafness PLoS One 7:e52338 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052338
Dai M, Yang Y, Omelchenko I, Nuttall AL, Kachelmeier A, Xiu R, Shi X (2010) Bone marrow cell recruitment mediated by inducible nitric oxide synthase/stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha signaling repairs the acoustically damaged cochlear blood-labyrinth barrier. Am J Pathol 177:3089–3099. doi:10.2353/ajpath. 2010. 100340
Deem TL, Cook-Mills JM (2004) Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) activation of endothelial cell matrix metalloproteinases: role of reactive oxygen species. Blood 104:2385–2393. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-02-0665
Dehne N, Rauen U, de Groot H (2002) Lautermann J. Involvement of the mitochondrial permeability transition in gentamicin ototoxicity Hear Res 169:47–55
Duckert LG, Duvall AJ 3rd (1978) Cochlear communication routes in the guinea pig—spiral ganglia and osseous spiral laminae: an electron microscope study using microsphere tracers. Otolaryngology 86:ORL434–ORL446
El-Hakim H, Abdolell M, Mount RJ, Papsin BC, Harrison RV (2002) Influence of age at implantation and of residual hearing on speech outcome measures after cochlear implantation: binary partitioning analysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 189:102–108
Ernfors P, Duan ML, ElShamy WM, Canlon B (1996) Protection of auditory neurons from aminoglycoside toxicity by neurotrophin-3. Nat Med 2:463–467
Evans AJ, Thompson BC, Wallace GG, Millard R, O’Leary SJ, Clark GM, Shepherd RK, Richardson RT (2009) Promoting neurite outgrowth from spiral ganglion neuron explants using polypyrrole/BDNF-coated electrodes. J Biomed Mater Res A 91:241–250. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32228
Gao WQ (1998) Therapeutic potential of neurotrophins for treatment of hearing loss. Mol Neurobiol 17:17–31
Geers A, Brenner C, Nicholas J, Uchanski R, Tye-Murray N, Tobey E (2002) Rehabilitation factors contributing to implant benefit in children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 189:127–130
Gunewardene N, Dottori M, Nayagam BA (2012) The convergence of cochlear implantation with induced pluripotent stem cell therapy. Stem Cell Rev 8:741–754. doi:10.1007/s12015-011-9320-0
Heinrich UR, Helling K, Sifferath M, Brieger J, Li H, Schmidtmann I, Mann WJ (2008) Gentamicin increases nitric oxide production and induces hearing loss in guinea pigs. Laryngoscope 118:1438–1442. doi:10.1097/MLG.0b013e3181739bd9
Hu T, Luan R, Zhang H, Lau WB, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Wang HC, Tao L (2009) Hydrogen peroxide enhances osteopontin expression and matrix metalloproteinase activity in aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 36:626–630. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05124.x
Hu Z, Wei D, Johansson CB, Holmstrom N, Duan M, Frisen J, Ulfendahl M (2005) Survival and neural differentiation of adult neural stem cells transplanted into the mature inner ear. Exp Cell Res 302:40–47. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.023
Keithley EM, Croskrey KL (1990) Spiral ganglion cell endings in the cochlear nucleus of young and old rats. Hear Res 49:169–177
Kesser BW, Lalwani AK (2009) Gene therapy and stem cell transplantation: strategies for hearing restoration. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 66:64–86. doi:10.1159/000218208
Kilpatrick LA, Zhu J, Lee FS, Lang H (2011) Role of stromal cell-derived factor-1 expression in the injured mouse auditory nerve. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145:1007–1015. doi:10.1177/0194599811416778
Kim KH, Cho YS, Park JM, Yoon SO, Kim KW, Chung AS (2007) Pro-MMP-2 activation by the PPARgamma agonist, ciglitazone, induces cell invasion through the generation of ROS and the activation of ERK. FEBS Lett 581:3303–3310. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.06.012
Konomi U, Suzuki M, Otsuka K, Shimizu A, Inagaki T, Hasegawa G, Shimizu S, Motohashi R (2010) Morphological change of the cupula due to an ototoxic agent: a comparison with semicircular canal pathology. Acta Otolaryngol 130:652–658. doi:10.3109/00016480903370779
Landry TG, Wise AK, Fallon JB, Shepherd RK (2011) Spiral ganglion neuron survival and function in the deafened cochlea following chronic neurotrophic treatment. Hear Res 282:303–313. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2011.06.007
Lapidot T (2001) Mechanism of human stem cell migration and repopulation of NOD/SCID and B2mnull NOD/SCID mice. The role of SDF-1/CXCR4 interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 938:83–95
Lim D, Kim HN (1983) The canaliculae perforantes of Schuknecht. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 31:85–117
Liu HY, Chi FL, Gao WY (2008) Taurine attenuates aminoglycoside ototoxicity by inhibiting inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the cochlea. Neuroreport 19:117–120. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e3282f3b0ec
Lopez-Gonzalez MA, Delgado F, Lucas M (1999) Aminoglycosides activate oxygen metabolites production in the cochlea of mature and developing rats. Hear Res 136:165–168
Marquez-Curtis LA, Janowska-Wieczorek A (2013) Enhancing the migration ability of mesenchymal stromal cells by targeting the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis Biomed Res Int 2013:561098 doi:10.1155/2013/561098
McGuinness SL, Shepherd RK (2005) Exogenous BDNF rescues rat spiral ganglion neurons in vivo. Otol Neurotol 26:1064–1072
Miller RJ, Banisadr G, Bhattacharyya BJ (2008) CXCR4 signaling in the regulation of stem cell migration and development. J Neuroimmunol 198:31–38. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.04.008
Naito Y, Nakamura T, Nakagawa T, Iguchi F, Endo T, Fujino K, Kim TS, Hiratsuka Y, Tamura T, Kanemaru S, Shimizu Y, Ito J (2004) Transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells into the cochlea of chinchillas. Neuroreport 15:1–4
Osberger MJ, Zimmerman-Phillips S, Koch DB (2002) Cochlear implant candidacy and performance trends in children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 189:62–65
Parker MA, Corliss DA, Gray B, Anderson JK, Bobbin RP, Snyder EY, Cotanche DA (2007) Neural stem cells injected into the sound-damaged cochlea migrate throughout the cochlea and express markers of hair cells, supporting cells, and spiral ganglion cells. Hear Res 232:29–43. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2007.06.007
Praetorius M, Vicario I, Schimmang T (2008) Efficient transfer of embryonic stem cells into the cochlea via a non-invasive vestibular route. Acta Otolaryngol 128:720–723. doi:10.1080/00016480701714236
Priuska EM, Schacht J (1995) Formation of free radicals by gentamicin and iron and evidence for an iron/gentamicin complex. Biochem Pharmacol 50:1749–1752
Rask-Andersen H, Schrott-Fischer A, Pfaller K, Glueckert R (2006) Perilymph/modiolar communication routes in the human cochlea. Ear Hear 27:457–465. doi:10.1097/01.aud.0000233864.32183.81
Richardson RT, Wise A, O’Leary S, Hardman J, Casley D, Clark G (2004) Tracing neurotrophin-3 diffusion and uptake in the guinea pig cochlea. Hear Res 198:25–35. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2004.02.012
Romand R, Chardin S, Le Calvez S (1996) The spontaneous appearance of hair cell-like cells in the mammalian cochlea following aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Neuroreport 8:133–137
Ruan RS, Leong SK, Mark I, Yeoh KH (1999) Effects of BDNF and NT-3 on hair cell survival in Guinea pig cochlea damaged by kanamycin treatment. Neuroreport 10:2067–2071
Schuknecht HF, Seifi AE (1963) Experimental observations on the fluid physiology of the inner ear. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 72:687–712
Sha SH, Taylor R, Forge A, Schacht J (2001) Differential vulnerability of basal and apical hair cells is based on intrinsic susceptibility to free radicals. Hear Res 155:1–8
Shepherd RK, Colreavy MP (2004) Surface microstructure of the perilymphatic space: implications for cochlear implants and cell- or drug-based therapies. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:518–523. doi:10.1001/archotol.130.5.518
Shi X, Han W, Yamamoto H, Omelchenko I, Nuttall A (2007) Nitric oxide and mitochondrial status in noise-induced hearing loss. Free Radic Res 41:1313–1325. doi:10.1080/10715760701687117
Shin MH, Moon YJ, Seo JE, Lee Y, Kim KH, Chung JH (2008) Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase, xanthine oxidase, and mitochondrial electron transport system mediate heat shock-induced MMP-1 and MMP-9 expression. Free Radic Biol Med 44:635–645. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.10.053
Slepecky N, Angelborg C, Larsen HC (1987) Regional blood flow patterns along the length of the rodent cochlea. Acta Otolaryngol 103:176–181. doi:10.3109/00016488709107781
Slepecky N, Larsen HC, Angelborg C (1984) Computerized reconstruction of the regional blood flow in the rodent cochlea. Hear Res 15:95–101
Suzuka Y, Schuknecht HF (1988) Retrograde cochlear neuronal degeneration in human subjects. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 450:1–20
Suzuki M, Yamasoba T, Ishibashi T, Miller JM, Kaga K (2002) Effect of noise exposure on blood-labyrinth barrier in guinea pigs. Hear Res 164:12–18
Tan J, Wang Y, Yip X, Glynn F, Shepherd RK, Caruso F (2012) Nanoporous peptide particles for encapsulating and releasing neurotrophic factors in an animal model of neurodegeneration. Adv Mater 24:3362–3366. doi:10.1002/adma.201200634
Tinling SP, Chole RA (1994) Apical cochlear nerve exposed to perilymph in the gerbil and rat. Hear Res 73:203–208
van Loon MC, Ramekers D, Agterberg MJ, de Groot JC, Grolman W, Klis SF, Versnel H (2013) Spiral ganglion cell morphology in guinea pigs after deafening and neurotrophic treatment. Hear Res 298:17–26. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2013.01.013
Yeo SW, Gottschlich S, Harris JP, Keithley EM (1995) Antigen diffusion from the perilymphatic space of the cochlea. Laryngoscope 105:623–628
Ylikoski J, Pirvola U, Virkkala J, Suvanto P, Liang XQ, Magal E, Altschuler R, Miller JM, Saarma M (1998) Guinea pig auditory neurons are protected by glial cell line-derived growth factor from degeneration after noise trauma. Hear Res 124:17–26
Zanin MP, Hellstrom M, Shepherd RK, Harvey AR, Gillespie LN (2014) Development of a cell-based treatment for long-term neurotrophin expression and spiral ganglion neuron survival Neuroscience doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience. 2014.07.044
Zhang HJ, Zhao W, Venkataraman S, Robbins ME, Buettner GR, Kregel KC, Oberley LW (2002) Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 by overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells involves reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem 277:20919–20926. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109801200
Zhang PZ, He Y, Jiang XW, Chen FQ, Chen Y, Xue T, Zhou K, Li X, Wang Y, Wu YX, Mi WJ, Qiu JH (2013) Up-regulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 enhances migration of transplanted neural stem cells to injury region following degeneration of spiral ganglion neurons in the adult rat inner ear. Neurosci Lett 534:101–106. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.11.018
Zhang Y, Zhang W, Johnston AH, Newman TA, Pyykk I, Zou J (2011) Comparison of the distribution pattern of PEG-b-PCL polymersomes delivered into the rat inner ear via different methods. Acta Otolaryngol 131:1249–1256. doi:10.3109/00016489.2011.615066
Zhang Y, Zhang W, Johnston AH, Newman TA, Pyykko I, Zou J (2010) Improving the visualization of fluorescently tagged nanoparticles and fluorophore-labeled molecular probes by treatment with CuSO(4) to quench autofluorescence in the rat inner ear. Hear Res 269:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2010.07.006
Zhao LD, Li L, Wu N, Li DK, Ren LL, Guo WW, Sun JH, Liu HZ, Chen TZ, Xing GQ, Yang SM (2013) Migration and differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells transplanted into mature cochlea of rats with aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 133:136–143. doi:10.3109/00016489.2012.720029
Zheng G, Hu BH (2012) Cell-cell junctions: a target of acoustic overstimulation in the sensory epithelium of the cochlea. BMC Neurosci 13:71. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-13-71
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Ning Yu, Nan Wu, and Ke Liu for the technical support and valuable advice. This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (nos. 2012CB967900 and 2011CBA01000), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC no. 81271082), the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) (2014AA020510). We also want to express our appreciations to Professor Jianhe Sun who passed away several months after this experiment.
Authors’ Contributions
Yang SM, Li DK, and Sun JH designed the experiment; Li DK and Sun JH performed the experiment; Li DK and Sun W wrote the paper; Guo WW and Zhao LD contributed new reagents; and Li DK, Sun W, and Yang SM analyzed data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Sun, J., Zhao, L. et al. Aminoglycoside Increases Permeability of Osseous Spiral Laminae of Cochlea by Interrupting MMP-2 and MMP-9 Balance. Neurotox Res 31, 348–357 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9689-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9689-2