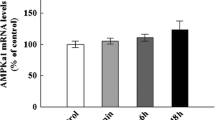
Abstract
In the present work, we studied the effects of toxic ammonia levels on the cytoskeleton of neural cells, with emphasis in the homeostasis of the phosphorylating system associated with the intermediate filaments (IFs). We used in vivo and in vitro models of acute hyperammonemia in 10- and 21-day-old rats. In the in vivo model, animals were intraperitoneally injected with ammonium acetate (7 mmol/Kg), and the phosphorylation level of the cytoskeletal proteins was analyzed in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus 30 and 60 min after injection. The injected ammonia altered the IF phosphorylation of astrocytes (GFAP and vimentin) and neurons (neurofilament subunits of low, middle, and high molecular weight, respectively: NFL, NFM, and NFH) from cerebral cortex of 21-day-old rats. This was a transitory effect observed 30 min after injection, recovering 30 min afterward. Phosphorylation was not altered in the cerebral cortex of 10-day-old pups. The homeostasis of hippocampal IFs was preserved at the studied ages and times. In the in vitro model, cortical slices of 10- and 21-day-old rats were incubated with 0.5, 1, or 5 mM NH4Cl, and the phosphorylation level of the IF proteins was analyzed after 30 min. The IF phosphorylation was not altered in cortical slices of 10-day-old rats; however, in cortical slices of 21-day-old pups, 5 mM NH4Cl induced hypophosphorylation of GFAP and vimentin, preserving neurofilament phosphorylation levels. Hypophosphorylation was mediated by the protein phosphatases 1 (PP1) and 2B (PP2B), and this event was associated with Ca2+ influx via N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors. The aim of this study is to show that acute ammonia toxicity targets the phosphorylating system of IFs in the cerebral cortex of rats in a developmentally regulated manner, and NMDA-mediated Ca2+ signaling plays a central role in this mechanism. We propose that the disruption of cytoskeletal homeostasis could be an endpoint of the acute hyperammonemia in the developing brain. We believe that these results contribute for better understanding the molecular basis of the ammonia toxicity in brain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azorin I, Minana MD, Felipo V, Grisolia S (1989) A simple animal model of hyperammonemia. Hepatology 10:311–314
Back A, Tupper KY, Bai T, Chiranand P, Goldenberg FD, Frank JI, Brorson JR (2011) Ammonia-induced brain swelling and neurotoxicity in an organotypic slice model. Neurol Res 33:1100–1108
Barry DM, Stevenson W, Bober BG, Wiese PJ, Dale JM, Barry GS, Byers NS, Strope JD, Chang R, Schulz DJ, Shah S, Calcutt NA, Gebremichael Y, Garcia ML (2012) Expansion of neurofilament medium C terminus increases axonal diameter independent of increases in conduction velocity or myelin thickness. J Neurosci 32:6209–6219
Bender AS, Norenberg MD (1996) Effects of ammonia on l-glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem Res 21:567–573
Bezanilla M, Gladfelter AS, Kovar DR, Lee W-L (2015) Cytoskeletal dynamics: a view from the membrane. J Cell Biol 209:329–337
Bjerring PN, Dale N, Larsen FS (2015) Acute hyperammonemia and systemic inflammation is associated with increased extracellular brain adenosine in rats: a biosensor study. Neurochem Res 40:258–264
Bodega G, Suárez I, Paniagua C, Vacas E, Fernández B (2007) Effect of ammonia, glutamine, and serum on calcineurin, p38MAPK-diP, GADD153/CHOP10, and CNTF in primary rat astrocyte cultures. Brain Res 1175:126–133
Braissant O, Henry H, Villard AM, Zurich MG, Loup M, Eilers B, Parlascino G, Matter E, Boulat O, Honegger P, Bachmann C (2002) Ammonium-induced impairment of axonal growth is prevented through glial creatine. J Neurosci 22:9810–9820
Braissant O, McLin VA, Cudalbu C (2013) Ammonia toxicity to the brain. J Inherit Metab Dis 36:595–612
Brownlees J, Yates A, Bajaj NP, Davis D, Anderton BH, Leigh PN, Shaw CE, Miller CC (2000) Phosphorylation of neurofilament heavy chain side-arms by stress activated protein kinase-1b/Jun N-terminal kinase-3. J Cell Sci 113:401–407
Cagnon L, Braissant O (2007) Hyperammonemia-induced toxicity for the developing central nervous system. Brain Res Rev 56:183–197
Cagnon L, Braissant O (2009) CNTF protects oligodendrocytes from ammonia toxicity: intracellular signaling pathways involved. Neurobiol Dis 33:133–142
Cai J, Tuong CM, Zhang Y, Shields CB, Guo G, Fu H, Gozal D (2012) Mouse intermittent hypoxia mimicking apnea of prematurity: effects on myelinogenesis and axonal maturation. J Pathol 226:495–508
Cauli O, González-Usano A, Cabrera-Pastor A, Gimenez-Garzó C, López-Larrubia P, Ruiz-Sauri A, Hernández-Rabaza V, Duszczyk M, Malek M, Lazarewicz JW, Carratalá A, Urios A, Miguel A, Torregrosa I, Carda C, Montoliu C, Felipo V (2014) Blocking NMDA receptors delays death in rats with acute liver failure by dual protective mechanisms in kidney and brain. Neuromol Med 16:360–375
Cooper AJL (2013) Possible treatment of end-stage hyperammonemic encephalopathy by inhibition of glutamine synthetase. Metab Brain Dis 28:119–125
Cudalbu C (2013) In vivo studies of brain metabolism in animal models of hepatic encephalopathy using 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Metab Brain Dis 28:167–174
de Almeida LM, Funchal C, Pelaez PL, Pessutto FD, Loureiro SO, Vivian L, Wajner M, Pessoa-Pureur R (2003) Effect of propionic and methylmalonic acids on the in vitro phosphorylation of intermediate filaments from cerebral cortex of rats during development. Metab Brain Dis 18:207–219
Felipo V (2009) Hyperammonemia. In: Lajtha A et al (eds) Handbook of neurochemistry and molecular neurobiology. Springer, US, pp 43–69
Felipo V, Butterworth RF (2002) Neurobiology of ammonia. Prog Neurobiol 67:259–279
Felipo V, Grau E, Miñana MD, Grisolía S (1993) Hyperammonemia decreases protein-kinase-C-dependent phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein 2 and increases its binding to tubulin. Eur J Biochem 214:243–249
Fernandes CG, Pierozan P, Soares GM, Ferreira F, Zanatta Â, Amaral AU, Borges CG, Wajner M, Pessoa-Pureur R (2015) NMDA receptors and oxidative stress induced by the major metabolites accumulating in HMG lyase deficiency mediate hypophosphorylation of cytoskeletal proteins in brain from adolescent rats: potential mechanisms contributing to the neuropathology of this disease. Neurotox Res 28:239–252
Funchal C, de Lima Pelaez P, Loureiro SO, Vivian L, Pessutto FDB, de Almeida LM, Wofchuk ST, Wajner M, Pureur RP (2002) Alpha-Ketoisocaproic acid regulates phosphorylation of intermediate filaments in postnatal rat cortical slices through ionotropic glutamatergic receptors. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 139:267–276
Funchal C, de Almeida LM, Oliveira Loureiro S, Vivian L, de Lima Pelaez P, Pessutto FDB, Rosa AM, Wajner M, Pureur RP (2003) In vitro phosphorylation of cytoskeletal proteins from cerebral cortex of rats. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 11:111–118
González-Usano A, Cauli O, Agustí A, Felipo V (2013) Hyperammonemia alters the modulation by different neurosteroids of the glutamate-nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway through NMDA- GABAA—or sigma receptors in cerebellum in vivo. J Neurochem 125:133–143
Grant P, Sharma P, Pant HC (2001) Cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (Cdk5) and the regulation of neurofilament metabolism. Eur J Biochem 268:1534–1546
Guidato S, Bajaj NPS, Miller CCJ (1996) Cellular phosphorylation of neurofilament heavy-chain by cyclin-dependent kinase-5 masks the epitope for monoclonal antibody N52. Neurosci Lett 217:157–160
Heimfarth L, Loureiro SO, Reis KP, de Lima BO, Zamboni F, Lacerda S, Soska AK, Wild L, da Rocha JBT, Pureur RP (2012) Diphenylditelluride induces hypophosphorylation of intermediate filaments through modulation of DARPP-32-dependent pathways in cerebral cortex of young rats. Arch Toxicol 86:217–230
Helfand BT, Chang L, Goldman RD (2004) Intermediate filaments are dynamic and motile elements of cellular architecture. J Cell Sci 17:133–141
Hemmings HC Jr, Greengard P, Tung HY, Cohen P (1984) DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature 310:503–505
Hoffman PN, Griffin JW, Gold BG, Price DL (1985) Slowing of neurofilament transport and the radial growth of developing nerve fibers. J Neurosci 5:2920–2929
Holopainen IE (2008) Seizures in the developing brain: cellular and molecular mechanisms of neuronal damage, neurogenesis and cellular reorganization. Neurochem Int 52:935–947
Huang FL, Glinsmann WH (1976) Separation and characterization of two phosphorylase phosphatase inhibitors from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem 70:419–426
Izumi Y, Svrakic N, O’Dell K, Zorumski CF (2013) Ammonia inhibits long-term potentiation via neurosteroid synthesis in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuroscience 233:166–173
Kawaguchi T, Brusilow SW, Traystman RJ, Koehler RC (2005) Glutamine-dependent inhibition of pial arteriolar dilation to acetylcholine with and without hyperammonemia in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 88:R1612–R1619
Kosenko E, Kaminsky Y, Miñana MD, Grisolia S, Felipo V (1994) High ammonia levels decrease brain acetylcholinesterase activity both in vivo and in vitro. Mol Chem Neuropathol 22:177–184
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Laser-Azogui A, Kornreich M, Malka-Gibor E, Beck R (2015) Neurofilament assembly and function during neuronal development. Curr Opin Cell Biol 32:92–101
Liberto CM, Albrecht PJ, Herx LM, Yong VW, Levison SW (2004) Pro-regenerative properties of cytokine-activated astrocytes. J Neurochem 89:1092–1100
Liu Y, Peterson DA, Kimura H, Schubert D (1997) Mechanism of cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction. J Neurochem 69:581–593
Llansola M, Montoliu C, Cauli O, Hernández-Rabaza V, Agustí A, Cabrera-Pastor A, Giménez-Garzó C, González-Usano A, Felipo V (2013) Chronic hyperammonemia, glutamatergic neurotransmission and neurological alterations. Metab Brain Dis 8:151–154
Loureiro SO, Heimfarth L, Lacerda BA, Vidal LF, Soska A, dos Santos NG, de Souza Wyse AT, Pessoa-Pureur R (2010a) Homocysteine induces hypophosphorylation of intermediate filaments and reorganization of actin cytoskeleton in C6 glioma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30:557–568
Loureiro SO, Romão L, Alves T, Fonseca A, Heimfarth L, MouraNeto V, Wyse AT, Pessoa-Pureur R (2010b) Homocysteine induces cytoskeletal remodeling and production of reactive oxygen species in cultured cortical astrocytes. Brain Res 1355:151–164
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mans AM, De Joseph MR, Hawkins RA (1994) Metabolic abnormalities and grade of encephalopathy in acute hepatic failure. J Neurochem 63:1829–1838
Mehrotra A, Trigun SK (2013) Moderate grade hyperammonemia activates lactate dehydrogenase-4 and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase to support increased lactate turnover in the brain slices. Mol Cell Biochem 81:157–161
Middeldorp J, Hol EM (2011) GFAP in health and disease. Prog Neurobiol 93:421–443
Monfort P, Munõz MD, ElAyadi A, Kosenko E, Felipo V (2002) Effects of hyperammonemia and liver disease on glutamatergic neurotransmission. Metab Brain Dis 17:237–250
Nixon RA, Sihag RK (1991) Neurofilament phosphorylation: a new look at regulation and function. Trends Neurosci 14:501–506
Norenberg MD (1987) The role of astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Pathol 6:13–33
Norenberg MD, Rama Rao KV, Jayakumar AR (2003) The mitochondrial permeability transition in ammonia neurotoxicity. In: Jones EA, Meijer AF, Chamuleau RA (eds) Hepatic encephalopathy and nitrogen metabolism. Kluwer, Dordtrecht, pp 267–285
Obara-Michlewska M, Tuszyńska P, Albrecht J (2013) Ammonia upregulates kynurenine aminotransferase II mRNA expression in rat brain: a role for astrocytic NMDA receptors? Metab Brain Dis 28:161–165
Omary MB, Ku NO, Tao GZ, Toivola DM, Liao J (2006) Heads and tails of intermediate filament phosphorylation: multiple sites and functional insights. Trends Biochem Sci 31:383–394
Paz Soldán MM, Pirko I (2012) Biogenesis and significance of central nervous system myelin. Semin Neurol 32:9–14
Pierozan P, Zamoner A, Soska AK, Silvestrin RB, Oliveira Loureiro S, Heimfarth L, Mello e Souza T, Wajner M, Pessoa-Pureur R (2010) Acute intrastriatal administration of quinolinic acid provokes hyperphosphorylation of cytoskeletal intermediate filament proteins in astrocytes and neurons of rats. Exp Neurol 224:188–196
Pierozan P, Zamoner A, Soska ÂK, de Lima BO, Reis KP, Zamboni F, Wajner M, Pessoa-Pureur R (2012) Signaling mechanisms downstream of quinolinic acid targeting the cytoskeleton of rat striatal neurons and astrocytes. Exp Neurol 233:391–399
Pierozan P, Gonçalves Fernandes C, Ferreira F, Pessoa-Pureur R (2014) Acute intrastriatal injection of quinolinic acid provokes long-lasting misregulation of the cytoskeleton in the striatum, cerebral cortex and hippocampus of young rats. Brain Res 1577:1–10
Pierozan P, Ferreira F, Ortiz de Lima B, Pessoa-Pureur R (2015) Quinolinic acid induces disrupts cytoskeletal homeostasis in striatal neurons. Protective role of astrocyte-neuron interaction. J Neurosci Res 93:268–284
Rao KVR, Norenberg MD (2012) Brain energy metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction in acute and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int 60:697–706
Reis KP, Heimfarth L, Pierozan P, Ferreira F, Loureiro SO, Fernandes CG, Carvalho RV, Pessoa-Pureur R (2015) High postnatal susceptibility of hippocampal cytoskeleton in response to ethanol exposure during pregnancy and lactation. Alcohol. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.06.005
Rodrigo R, Cauli O, Boix J, El Mlili N, Agusti A, Felipo V (2009) Role of NMDA receptors in acute liver failure and ammonia toxicity: therapeutical implications. Neurochem Int 55:113–118
Rose C, Michalak A, Pannunzio P, Therrien G, Quack G, Kircheis G, Butterworth RF (1998) l-ornithine-l-aspartate in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy: therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of action. Metab Brain Dis 13:147–157
Schubert V, Dotti CG (2007) Transmitting on actin: synaptic control of dendritic architecture. J Cell Sci 120:205–212
Shenolikar S (1995) Protein phosphatase regulation by endogenous inhibitors. Seminar Cancer Biol 6:219–227
Sihag RK, Inagaki M, Yamaguchi T, Shea TB, Pant HC (2007) Role of phosphorylation on the structural dynamics and function of types III and IV intermediate filaments. Exp Cell Res 313:2098–2109
Singh S, Koiri RK, Trigun SK (2008) Acute and chronic hyperammonemia modulate antioxidant enzymes differently in cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Neurochem Res 33:103–113
Strack S, Westphal RS, Colbran RJ, Ebner FF, Wadzinski BE (1997) Protein serine/threonine phosphatase 1 and 2A associate with and dephosphorylate neurofilaments. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 49:15–28
Swain M, Butterworth RF, Blei AT (1992) Ammonia and related amino acids in the pathogenesis of brain edema in acute ischemic liver failure in rats. Hepatology 15:449–453
Tuchman M, Lee B, Lichter-Konecki U, Summar ML, Yudkoff M, Cederbaum SD, Kerr DS, Diaz GA, Seashore MR, Lee HS, McCarter RJ, Krischer JP, Batshaw ML (2008) Urea Cycle Disorders Consortium of the Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network. Cross-sectional multicenter study of patients with urea cycle disorders in the United States. Mol Genet Metab 94:397–402
Volterra A, Meldolesi J (2005) Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: the revolution continues. Nat Rev 6:626–640
Wen Z, Guirland C, G-l Ming, Zheng JQ (2004) A CaMKII/calcineurin switch controls the direction of Ca(2+)-dependent growth cone guidance. Neuron 43:835–846
Whitaker AN, McKay DG (1969) Studies of catecholamine shock. I Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Pathol 65:153–176
Willard-Mack CL, Koehler RC, Hirata T, Cork LC, Takahashi H, Traystman RJ, Brusilow SW (1996) Inhibition of glutamine synthetase reduces ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in rat. Neuroscience 71:589–599
Winder DG, Sweatt JD (2001) Roles of serine/threonine phosphatases in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:461–474
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS), and Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa/Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (PROPESQ/UFRGS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, R.V., da Silva Ferreira, F., Heimfarth, L. et al. Acute Hyperammonemia Induces NMDA-Mediated Hypophosphorylation of Intermediate Filaments Through PP1 and PP2B in Cerebral Cortex of Young Rats. Neurotox Res 30, 138–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9607-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9607-7