Abstract
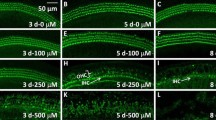
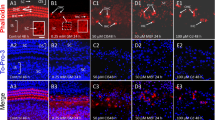
Trimethyltin (TMT), which has a variety of applications in industry and agricultural, is a neurotoxin that is known to affect the auditory system as well as central nervous system of humans and experimental animals. However, the mechanisms underlying TMT-induced auditory dysfunction are poorly understood. To gain insights into the neurotoxic effect of TMT on the peripheral auditory system, we treated cochlear organotypic cultures with concentrations of TMT ranging from 5 to 100 μM for 24 h. Interestingly, TMT preferentially damaged auditory nerve fibers and spiral ganglion neurons in a dose-dependent manner, but had no noticeable effects on the sensory hair cells at the doses employed. TMT-induced damage to auditory neurons was associated with significant soma shrinkage, nuclear condensation, and activation of caspase-3, biomarkers indicative of apoptotic cell death. Our findings show that TMT is exclusively neurotoxicity in rat cochlear organotypic culture and that TMT-induced auditory neuron death occurs through a caspase-mediated apoptotic pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge WN, Street BW, Skilleter DN (1977) Oxidative phosphorylation. Halide-dependent and halide-independent effects of triorganotin and trioganolead compounds on mitochondrial functions. Biochem J 168:353–364
Ali SF, LeBel CP, Bondy SC (1992) Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methylmercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 13:637–648
Balaban CD, O’Callaghan JP, Billingsley ML (1988) Trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in the rat brain: comparative studies using silver degeneration stains, immunocytochemistry and immunoassay for neuronotypic and gliotypic proteins. Neuroscience 26:337–361
Barclay M, Ryan AF, Housley GD (2011) Type I vs type II spiral ganglion neurons exhibit differential survival and neuritogenesis during cochlear development. Neural Dev 6:33
Bas E, Van De Water TR, Lumbreras V, Rajguru S, Goss G, Hare JM et al (2014) Adult human nasal mesenchymal-like stem cells restore cochlear spiral ganglion neurons after experimental lesion. Stem Cells Dev 23:502–514
Berkingali N, Warnecke A, Gomes P, Paasche G, Tack J, Lenarz T et al (2008) Neurite outgrowth on cultured spiral ganglion neurons induced by erythropoietin. Hear Res 243:121–126
Billingsley ML, Yun J, Reese BE, Davidson CE, Buck-Koehntop BA, Veglia G (2006) Functional and structural properties of stannin: roles in cellular growth, selective toxicity, and mitochondrial responses to injury. J Cell Biochem 98:243–250
Braman RS, Tompkins MA (1979) Separation and determination of nanogram amounts of inorganic tin and methyltin compounds in the environment. Anal Chem 51:12–19
Brown MC, Ledwith JVIII (1990) Projections of thin (type-II) and thick (type-I) auditory-nerve fibers into the cochlear nucleus of the mouse. Hear Res 49:105–118
Brown AW, Aldridge WN, Street BW, Verschoyle RD (1979) The behavioral and neuropathologic sequelae of intoxication by trimethyltin compounds in the rat. Am J Pathol 97:59–82
Bruce LL, Christensen MA, Warr WB (2000) Postnatal development of efferent synapses in the rat cochlea. J Comp Neurol 423:532–548
Buck-Koehntop BA, Mascioni A, Buffy JJ, Veglia G (2005) Structure, dynamics, and membrane topology of stannin: a mediator of neuronal cell apoptosis induced by trimethyltin chloride. J Mol Biol 354:652–665
Chang LW, Dyer RS (1983a) A time-course study of trimethyltin induced neuropathology in rats. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 5:443–459
Chang LW, Dyer RS (1983b) Trimethyltin induced pathology in sensory neurons. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 5:673–696
Cima F (2011) Tin: environmental pollution and health effects. In: Jerome ON (ed) Encyclopedia of environmental health. Elsevier, Burlington, pp 351–359
Clerici WJ, Ross B Jr, Fechter LD (1991) Acute ototoxicity of trialkyltins in the guinea pig. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 109:547–556
Cookson MR, Slamon ND, Pentreath VW (1998) Glutathione modifies the toxicity of triethyltin and trimethyltin in C6 glioma cells. Arch Toxicol 72:197–202
Crofton KM, Dean KF, Menache MG, Janssen R (1990) Trimethyltin effects on auditory function and cochlear morphology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 105:123–132
Davidson CE, Reese BE, Billingsley ML, Yun JK (2004) Stannin, a protein that localizes to the mitochondria and sensitizes NIH-3T3 cells to trimethyltin and dimethyltin toxicity. Mol Pharmacol 66:855–863
Dechesne CJ, Winsky L, Kim HN, Goping G, Vu TD, Wenthold RJ et al (1991) Identification and ultrastructural localization of a calretinin-like calcium-binding protein (protein 10) in the guinea pig and rat inner ear. Brain Res 560:139–148
Diensthuber M, Zecha V, Wagenblast J, Arnhold S, Edge AS, Stover T (2014) Spiral ganglion stem cells can be propagated and differentiated into neurons and glia. Biores Open Access 3:88–97
Ding D, Roth J, Salvi R (2011) Manganese is toxic to spiral ganglion neurons and hair cells in vitro. Neurotoxicology 32:233–241
Ding D, Salvi R, Roth JA (2014) Cellular localization and developmental changes of Zip8, Zip14 and transferrin receptor 1 in the inner ear of rats. Biometals 27:731–744
Dong Y, Ding D, Jiang H, Shi JR, Salvi R, Roth JA (2014) Ototoxicity of paclitaxel in rat cochlear organotypic cultures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:526–533
Dorman DC (2000) An integrative approach to neurotoxicology. Toxicol Pathol 28:37–42
Durrant JD, Wang J, Ding DL, Salvi RJ (1998) Are inner or outer hair cells the source of summating potentials recorded from the round window? J Acoust Soc Am 104:370–377
Dyer RS, Walsh TJ, Wonderlin WF, Bercegeay M (1982) The trimethyltin syndrome in rats. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 4:127–133
Eastman CL, Young JS, Fechter LD (1987) Trimethyltin ototoxicity in albino rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 9:329–332
Fechter LD, Liu Y (1994) Trimethyltin disrupts N1 sensitivity, but has limited effects on the summating potential and cochlear microphonic. Hear Res 78:189–196
Fechter LD, Liu Y (1995) Elevation of intracellular calcium levels in spiral ganglion cells by trimethyltin. Hear Res 91:101–109
Fiedorowicz A, Figiel I, Kaminska B, Zaremba M, Wilk S, Oderfeld-Nowak B (2001) Dentate granule neuron apoptosis and glia activation in murine hippocampus induced by trimethyltin exposure. Brain Res 912:116–127
Geloso MC, Vinesi P, Michetti F (1996) Parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons are not affected by trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampus. Exp Neurol 139:269–277
Geloso MC, Vinesi P, Michetti F (1997) Calretinin-containing neurons in trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampus: an immunocytochemical study. Exp Neurol 146:67–73
Geloso MC, Vinesi P, Michetti F (1998) Neuronal subpopulations of developing rat hippocampus containing different calcium-binding proteins behave distinctively in trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol 154:645–653
Geloso MC, Vercelli A, Corvino V, Repici M, Boca M, Haglid K et al (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 and caspase 3 expression in trimethyltin-induced apoptosis in the mouse hippocampus. Exp Neurol 175:152–160
Geloso MC, Corvino V, Michetti F (2011) Trimethyltin-induced hippocampal degeneration as a tool to investigate neurodegenerative processes. Neurochem Int 58:729–738
Gunasekar PG, Mickova V, Kotyzova D, Li L, Borowitz JL, Eybl V et al (2001) Role of astrocytes in trimethyltin neurotoxicity. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 15:256–262
Hoch M (2001) Organotin compounds in the environment: an overview. Appl Geochem 16:719–743
Hoeffding V, Fechter LD (1991) Trimethyltin disrupts auditory function and cochlear morphology in pigmented rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 13:135–145
Ito M, Spicer SS, Schulte BA (1995) Cytological changes related to maturation of the organ of Corti and opening of Corti’s tunnel. Hear Res 88:107–123
Jenkins SM, Barone S (2004) The neurotoxicant trimethyltin induces apoptosis via caspase activation, p38 protein kinase, and oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Toxicol Lett 147:63–72
Jenkins SM, Ehman K, Barone S Jr (2004) Structure-activity comparison of organotin species: dibutyltin is a developmental neurotoxicant in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 151:1–12
Koczyk D (1996) How does trimethyltin affect the brain: facts and hypotheses. Acta Neurobiol Exp 56:587–596
Komulainen H, Bondy SC (1987) Transient elevation of intrasynaptosomal free calcium by putrescine. Brain Res 401:50–54
Kuramoto N, Seko K, Sugiyama C, Shuto M, Ogita K (2011) Trimethyltin initially activates the caspase 8/caspase 3 pathway for damaging the primary cultured cortical neurons derived from embryonic mice. J Neurosci Res 89:552–561
LeBel CP, Ali SF, McKee M, Bondy SC (1990) Organometal-induced increases in oxygen reactive species: the potential of 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate as an index of neurotoxic damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 104:17–24
Lim DJ (1976) Ultrastructural cochlear changes following acoustic hyperstimulation and ototoxicity. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 85:740–751
Lobarinas E, Salvi R, Ding D (2013) Insensitivity of the audiogram to carboplatin induced inner hair cell loss in chinchillas. Hear Res 302:113–120
Misiti F, Orsini F, Clementi ME, Lattanzi W, Giardina B, Michetti F (2008) Mitochondrial oxygen consumption inhibition importance for TMT-dependent cell death in undifferentiated PC12 cells. Neurochem Int 52:1092–1099
Morita M, Imai H, Liu Y, Xu X, Sadamatsu M, Nakagami R et al (2008) FK506-protective effects against trimethyltin neurotoxicity in rats: hippocampal expression analyses reveal the involvement of periarterial osteopontin. Neuroscience 153:1135–1145
Moriya K, Sekitani T, Yamashita H (1993) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-like immunoreactivity in the vestibular endorgan of the rat. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 503:119–120
Mundy WR, Freudenrich TM (2006) Apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells induced by organotin compounds found in drinking water: involvement of MAP kinases. Neurotoxicology 27:71–81
Mushak P, Krigman MR, Mailman RB (1982) Comparative organotin toxicity in the developing rat: somatic and morphological changes and relationship to accumulation of total tin. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 4:209–215
O’Callaghan JP, Niedzwiecki DM, Means JC (1989) Variations in the neurotoxic potency of trimethyltin. Brain Res Bull 22:637–642
Perkins RE, Morest DK (1975) A study of cochlear innervation patterns in cats and rats with the Golgi method and Nomarkski Optics. J Comp Neurol 163:129–158
Philbert MA, Billingsley ML, Reuhl KR (2000) Mechanisms of injury in the central nervous system. Toxicol Pathol 28:43–53
Piacentini R, Gangitano C, Ceccariglia S, Del Fa A, Azzena GB, Michetti F et al (2008) Dysregulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis is responsible for neuronal death in an experimental model of selective hippocampal degeneration induced by trimethyltin. J Neurochem 105:2109–2121
Qu M, Zhou Z, Chen C, Li M, Pei L, Chu F et al (2011) Lycopene protects against trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Neurochem Int 59:1095–1103
Reese BE, Davidson C, Billingsley ML, Yun J (2005) Protein kinase C epsilon regulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced stannin gene expression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314:61–69
Reuhl KR, Smallridge EA, Chang LW, Mackenzie BA (1983) Developmental effects of trimethyltin intoxication in the neonatal mouse. I. Light microscopic studies. Neurotoxicology 4:19–28
Ruppert PH, Dean KF, Reiter LW (1984) Trimethyltin disrupts acoustic startle responding in adult rats. Toxicol Lett 22:33–38
Schmiedt RA, Okamura HO, Lang H, Schulte BA (2002) Ouabain application to the round window of the gerbil cochlea: a model of auditory neuropathy and apoptosis. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 3:223–233
Shin EJ, Suh SK, Lim YK, Jhoo WK, Hjelle OP, Ottersen OP et al (2005) Ascorbate attenuates trimethyltin-induced oxidative burden and neuronal degeneration in the rat hippocampus by maintaining glutathione homeostasis. Neuroscience 133:715–727
Snoeij NJ, van Iersel AA, Penninks AH, Seinen W (1985) Toxicity of triorganotin compounds: comparative in vivo studies with a series of trialkyltin compounds and triphenyltin chloride in male rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 81:274–286
Soto-Prior A, Cluzel M, Renard N, Ripoll C, Lavigne-Rebillard M, Eybalin M et al (1995) Molecular cloning and expression of α parvalbumin in the guinea pig cochlea. Mol Brain Res 34:337–342
Spoendlin HH, Gacek RR (1963) Electron microscopic study of the efferent and afferent innervation of the organ of corti in the cat. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 72:660–686
Stine KE, Reiter LW, Lemasters JJ (1988) Alkyltin inhibition of ATPase activities in tissue homogenates and subcellular fractions from adult and neonatal rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 94:394–406
Thompson TA, Lewis JM, Dejneka NS, Severs WB, Polavarapu R, Billingsley ML (1996) Induction of apoptosis by organotin compounds in vitro: neuronal protection with antisense oligonucleotides directed against stannin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:1201–1216
Toggas SM, Krady JK, Billingsley ML (1992) Molecular neurotoxicology of trimethyltin: identification of stannin, a novel protein expressed in trimethyltin-sensitive cells. Mol Pharmacol 42:44–56
Wang X, Cai J, Zhang J, Wang C, Yu A, Chen Y et al (2008) Acute trimethyltin exposure induces oxidative stress response and neuronal apoptosis in Sebastiscus marmoratus. Aquat Toxicol 90:58–64
Wang L, Ding D, Salvi R, Roth JA (2014) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide prevents neuroaxonal degeneration induced by manganese in cochlear organotypic cultures. Neurotoxicology 40:65–74
Weaver SP, Schweitzer L (1994) Development of gerbil outer hair cells after the onset of cochlear function: an ultrastructural study. Hear Res 72:44–52
Wei L, Ding D, Salvi R (2010) Salicylate-induced degeneration of cochlea spiral ganglion neurons-apoptosis signaling. Neuroscience 168:288–299
Young JS, Fechter LD (1986) Trimethyltin exposure produces an unusual form of toxic auditory damage in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 82:87–93
Zhang L, Li L, Prabhakaran K, Borowitz JL, Isom GE (2006) Trimethyltin-induced apoptosis is associated with upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and Bax in a hippocampal cell line. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 216:34–43
Zhang PZ, He Y, Jiang XW, Chen FQ, Chen Y, Shi L et al (2013) Stem cell transplantation via the cochlear lateral wall for replacement of degenerated spiral ganglion neurons. Hear Res 298:1–9
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by grant from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, R01 OH010235, the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81170912), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (No. 2014CB943003), and Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate 71380100016.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This research was approved by the University at Buffalo Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Ding, D., Sun, H. et al. Neurotoxicity of Trimethyltin in Rat Cochlear Organotypic Cultures. Neurotox Res 28, 43–54 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9531-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9531-2