Abstract
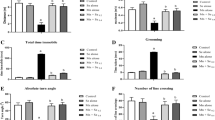
Excessive manganese (Mn) exposure can lead to oxidative injury. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) exerts an antioxidant response toward various environmental toxicants in the brain. However, the role of Nrf2 against Mn-induced oxidative injury remains largely unexplored. This study investigated the role of melatonin (MLT), an agent that was recently shown to induce the activation of the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)–Nrf2–antioxidant response elements (ARE) pathway against manganism. Mice were randomly divided into six groups, including control, 12.5, 25, 50 mg/kg MnCl2, MLT control, and MLT + 50 mg/kg MnCl2. The following were determined: behavioral activity; pathological changes; immunofluorescence staining of Neuronal Nuclei and glial fibrillary acidic protein; cell apoptosis; the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA), and glutathione (GSH); the immunohistochemical expression; and the protein levels of Nrf2, Keap1, and downstream enzymes. Mn-induced motor disorders, pathological damage, neuron degeneration, astrocytes activation, apoptosis, ROS and MDA generation, and GSH depletion. Nrf2, keap1, heme oxygenase-1 and NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, and quinone 1 showed a biphasic expression trend, which was most evidenced in the 12.5 mg/kg MnCl2 group. Changes in γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase, glutathione peroxidase 1, glutathionine S-transferase, glutathione reductase, and superoxide dismutase decreased in a concentration-dependent manner as a result of Mn exposure. MLT antagonized oxidative injury through the activation of the Keap1–Nrf2–ARE signaling pathway. In conclusion, disturbance of the Keap1–Nrf2–ARE signaling pathway partly caused oxidative injury. MLT can activate Nrf2 and its downstream enzymes and reverse Mn-induced oxidative injury.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- MnO2 :
-
Manganese dioxide
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- MMT:
-
Methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant response elements
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- NQO1:
-
NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- γ-GCS:
-
γ-Glutamylcysteine synthetase
- GPx-1:
-
Glutathione peroxidase 1
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GST:
-
Glutathionine S-transferase
- MLT:
-
N-Acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine
- –HO· :
-
Hydroxyl radical
- NO· :
-
Nitric oxide
- O −·2 :
-
Superoxide anion
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MnCl2·4H2O:
-
Manganese chloride
- DCFH-DA:
-
2,7-Dichlorofluorescin-diacetate
- SABC:
-
Strept avidin–biotin complex
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- HE:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DCF:
-
Dichlorofluorescein
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- TEP:
-
Tetraethoxypropane
- DTNB:
-
1,2-Dithio-bis-nitrobenzoic acid
- IOD:
-
Integral optical density
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- bZIP:
-
Basic region leucine zipper
References
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2012) Toxicological profile for manganese. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp151.pdf. Accessed Sept 2012
Ateşşahin A, Karahan I, Yilmaz S et al (2003) The effect of manganese chloride on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol Res 48(6):637–642
Barhoumi R, Faske J, Liu X, et al. (2004) Manganese potentiates lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of NOS2 in C6 glioma cells through mitochondrial-dependent activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 122(2):167–179
Bowman AB, Kwakye GF, Hernández H et al (2011) Role of manganese in neurodegenerative diseases. J Trace Elem Med Biol 25(4):191–203
Cordova FM, Aguiar AS Jr, Peres TV et al (2013) Manganese-exposed developing rats display motor deficits and striatal oxidative stress that are reversed by Trolox. Arch Toxicol 87(7):1231–1244
Deng Y, Xu Z, Xu B et al (2009) The protective effect of riluzole on manganese caused disruption of glutamate-glutamine cycle in rats. Brain Res 1289:106–117
Farina M, Avila DS, da Rocha JB et al (2013) Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: a focus on iron, manganese and mercury. Neurochem Int 62(5):575–594
Finkelstein MM, Jerrett M (2007) A study of the relationships between Parkinson’s disease and markers of traffic-derived and environmental manganese air pollution in two Canadian cities. Environ Res 104(3):420–432
Food and Drug Administration (2005) Guidance for industry: estimating the maximum safe starting dose in initial clinical trials for therapeutics in adult healthy volunteers. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Rockville
Fu J, Woods CG, Yehuda-Shnaidman E et al (2010) Low-level arsenic impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells: involvement of cellular adaptive response to oxidative stress. Environ Health Perspect 118(6):864–870
Gorell JM, Johnson CC, Rybicki BA et al (1998) Occupational exposure to manganese, copper, lead, iron, mercury and zinc and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 20(2–3):239–247
Gunter TE, Gavin CE, Aschner M et al (2006) Speciation of manganese in cells and mitochondria: a search for the proximal cause of manganese neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 27(5):765–776
Jiang JK, Ma X, Wu QY et al (2014) Upregulation of mitochondrial protease HtrA2/Omi contributes to manganese-induced neuronal apoptosis in rat brain striatum. Neuroscience 268:169–179
Jung KH, Hong SW, Zheng HM et al (2009) Melatonin downregulates nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 and nuclear factor-kappaB during prevention of oxidative liver injury in a dimethylnitrosamine model. J Pineal Res 47(2):173–183
Jung KH, Hong SW, Zheng HM et al (2010) Melatonin ameliorates cerulein-induced pancreatitis by the modulation of nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 and nuclear factor-kappaB in rats. J Pineal Res 48(23):239–250
Kern CH, Smith DR (2011) Preweaning Mn exposure leads to prolonged astrocyte activation and lasting effects on the dopaminergic system in adult male rats. Synapse 65(6):532–544
Kern CH, Smith DR. (2011) Preweaning Mn exposure leads to prolonged astrocyte activation and lasting effects on the dopaminergic system in adult male rats. Synapse 65(6): 532-544.Kilic U, Kilic E, Tuzcu Z et al (2013) Melatonin suppresses cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Nutr Metab (Lond) 10(1):7
Lee ES, Yin Z, Milatovic D et al (2009) Estrogen and tamoxifen protect against Mn-induced toxicity in rat cortical primary cultures of neurons and astrocytes. Toxicol Sci 110(1):156–167
Lin CH, Huang JY, Ching CH, et al (2008) Melatonin reduces the neuronal loss, downregulation of dopamine transporter, and upregulation of D2 receptor in rotenone-induced parkinsonian rats. J Pineal Res 44(2): 205-213
Liu Y, Zhang L, Zhang H et al (2012) Exogenous melatonin modulates apoptosis in the mouse brain induced by high-LET carbon ion irradiation. J Pineal Res 52(1):47–56
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL et al (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Magesh S, Chen Y, Hu L (2012) Small molecule modulators of Keap1–Nrf2–ARE pathway as potential preventive and therapeutic agents. Med Res Rev 32(4):687–726
Milatovic D, Gupta RC, Yu Y (2011) Protective effects of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents against manganese-induced oxidative damage and neuronal injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 256(3):219–226
Negi G, Kumar A, Sharma SS (2011) Melatonin modulates neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy: effects on NF-kappaB and Nrf2 cascades. J Pineal Res 50(2):124–131
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) The Nrf2–antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 284(20):13291–13295
Normandin L, Hazell AS (2002) Manganese neurotoxicity: an update of pathophysiologic mechanisms. Metab Brain Dis 17(4):375–387
Oszlánczi G, Vezér T, Sárközi L et al (2010) Functional neurotoxicity of Mn-containing nanoparticles in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(8):2004–2009
Prabhakaran K, Ghosh D, Chapman GD et al (2008) Molecular mechanism of manganese exposure-induced dopaminergic toxicity. Brain Res Bull 76(4):361–367
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N (2008) Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. Faseb J 22(3):659–661
Reiter RJ (2000) Melatonin: lowering the high price of free radicals. News Physiol Sci 15:246–250
Settivari R, VanDuyn N, LeVora J (2013) The Nrf2/SKN-1-dependent glutathione S-transferase pi homologue GST-1 inhibits dopamine neuron degeneration in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of manganism. Neurotoxicology 38:51–60
Villalba M, Martínez-Serrano A, Börner C et al (1992) NMDA-induced increase in [Ca2+]i and 45Ca2+ uptake in acutely dissociated brain cells derived from adult rats. Brain Res 570(1–2):347–353
Wang Z, Ma C, Meng CJ et al (2012) Melatonin activates the Nrf2–ARE pathway when it protects against early brain injury in a subarachnoid hemorrhage model. J Pineal Res 53(2):129–137
Woods CG, Fu J, Xue P, et al. (2009) Dose-dependent transitions in Nrf2-mediated adaptive response and related stress responses to hypochlorous acid in mouse macrophages. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(1):27-36
Xu B, Wu SW, Lu CW et al (2013) Oxidative stress involvement in manganese-induced alpha-synuclein oligomerization in organotypic brain slice cultures. Toxicology 305:71–78
Zhang F, Xu Z, Gao J et al (2008) In vitro effect of manganese chloride exposure on energy metabolism and oxidative damage of mitochondria isolated from rat brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26(2):232–236
Zhao S, Zhang L, Xu Z et al (2013) Neurotoxic effects of iron overload under high glucose concentration. Neural Regen Res 8(36):3423
Acknowledgments
The Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81302406) and the Specialized Research Fund of New Teachers for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20112104120017) supported this work financially.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Zhu, J., Mi, C. et al. Melatonin Antagonizes Mn-Induced Oxidative Injury Through the Activation of Keap1–Nrf2–ARE Signaling Pathway in the Striatum of Mice. Neurotox Res 27, 156–171 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9489-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9489-5