Abstract
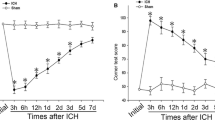
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) has been described to exert beneficial and detrimental effects in various neurologic disorders. These conflicting roles of PGE2 could be attributed to its diverse receptor subtypes, EP1–EP4. At present, the precise role of EP1 in intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is unknown. Therefore, to elucidate its possible role in ICH, intrastriatal injection of collagenase was given in randomized groups of adult male wildtype (WT) and EP1 receptor knockout (EP1−/−) C57BL/6 mice. Functional outcomes including neurologic deficits, rotarod performance, open field activity, and adhesive removal performance were evaluated at 24, 48, and 72 h post-ICH. Lesion volume, cell survival and death, were assessed using Cresyl Violet, and Fluoro-Jade staining, respectively. Microglial activation and phagocytosis were estimated using Iba1 immunoreactivity and fluorescently-labeled microspheres. Following 72 h post-ICH, EP1−/− mice showed deteriorated outcomes compared to the WT control mice. These outcomes were demonstrated by elevated neurological deficits, exacerbated lesion volume, and significantly worsened sensorimotor functions. Fluoro-Jade staining showed significantly increased numbers of degenerating neurons and reduced neuronal survival in EP1−/− compared to WT mice. To assess in vivo phagocytosis, the number of microspheres phagocytosed by Iba1-positive cells was 145.4 ± 15.4 % greater in WT compared to EP1−/− mice. These data demonstrate that EP1 deletion exacerbates neuro-behavioral impairments following ICH, potentially by slowing down/impairing microglial phagocytosis. A better understanding of this EP1 mechanism could lead to improved intervention strategies for hemorrhagic stroke.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Kunz A, Shimamura M, Zhou P, Anrather J, Iadecola C (2009) The neuroprotective effect of prostaglandin E2 EP1 receptor inhibition has a wide therapeutic window, is sustained in time and is not sexually dimorphic. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29(1):66–72. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2008.88
Abe S, Watabe H, Takaseki S, Aihara M, Yoshitomi T (2013) The effects of prostaglandin analogues on intracellular Ca2 + in ciliary arteries of wild-type and prostanoid receptor-deficient mice. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 29(1):55–60. doi:10.1089/jop.2011.0197
Ahmad AS, Saleem S, Ahmad M, Doré S (2006) Prostaglandin EP1 receptor contributes to excitotoxicity and focal ischemic brain damage. Toxicol Sci 89(1):265–270. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfj022
Ahmad AS, Yun YT, Ahmad M, Maruyama T, Doré S (2008) Selective blockade of PGE2 EP1 receptor protects brain against experimental ischemia and excitotoxicity, and hippocampal slice cultures against oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neurotox Res 14(4):343–351
Ahmad AS, Maruyama T, Narumiya S, Doré S (2013) PGE2 EP1 receptor deletion attenuates 6-OHDA-induced parkinsonism in mice: old switch. New Target Neurotox Res 23(3):260–266. doi:10.1007/s12640-013-9381-8
Aronowski J, Hall CE (2005) New horizons for primary intracerebral hemorrhage treatment: experience from preclinical studies. Neurol Res 27(3):268–279. doi:10.1179/016164105X25225
Aronowski J, Zhao X (2011) Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral hemorrhage: secondary brain injury. Stroke 42(6):1781–1786. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.596718
Broderick JP, Adams HP Jr, Barsan W, Feinberg W, Feldmann E, Grotta J, Kase C, Krieger D, Mayberg M, Tilley B, Zabramski JM, Zuccarello M (1999) Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the stroke council. Am Heart Assoc Stroke 30(4):905–915
Carlson NG, Rojas MA, Black JD, Redd JW, Hille J, Hill KE, Rose JW (2009) Microglial inhibition of neuroprotection by antagonists of the EP1 prostaglandin E2 receptor. J Neuroinflammation 6:5. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-6-5
Chen L, Zhang X, Chen-Roetling J, Regan RF (2011) Increased striatal injury and behavioral deficits after intracerebral hemorrhage in hemopexin knockout mice. J Neurosurg 114(4):1159–1167. doi:10.3171/2010.10.JNS10861
Choi JS, Kim HY, Chun MH, Chung JW, Lee MY (2006) Expression of prostaglandin E2 receptor subtypes, EP2 and EP4, in the rat hippocampus after cerebral ischemia and ischemic tolerance. Cell Tissue Res 324(2):203–211. doi:10.1007/s00441-005-0121-0
Chu K, Jeong SW, Jung KH, Han SY, Lee ST, Kim M, Roh JK (2004) Celecoxib induces functional recovery after intracerebral hemorrhage with reduction of brain edema and perihematomal cell death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24(8):926–933. doi:10.1097/01.WCB.0000130866.25040.7D
Cimino PJ, Keene CD, Breyer RM, Montine KS, Montine TJ (2008) Therapeutic targets in prostaglandin E2 signaling for neurologic disease. Curr Med Chem 15(19):1863–1869
Clark W, Gunion-Rinker L, Lessov N, Hazel K (1998) Citicoline treatment for experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Stroke 29(10):2136–2140
Davis SM, Donnan GA (2006) The stroke-prone state: rapid assessment of transient ischemic attacks. Stroke 37(4):1140. doi:01.STR.0000209245.05915.df
Doré S, Otsuka T, Mito T, Sugo N, Hand T, Wu L, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Andreasson K (2003) Neuronal overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 increases cerebral infarction. Ann Neurol 54(2):155–162. doi:10.1002/ana.10612
Dunham NW, Miya TS (1957) A note on a simple apparatus for detecting neurological deficit in rats and mice. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc (Baltim) 46(3):208–209
Funk CD, Furci L, FitzGerald GA, Grygorczyk R, Rochette C, Bayne MA, Abramovitz M, Adam M, Metters KM (1993) Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the human prostaglandin E receptor EP1 subtype. J Biol Chem 268(35):26767–26772
Giulian D, Chen J, Ingeman JE, George JK, Noponen M (1989) The role of mononuclear phagocytes in wound healing after traumatic injury to adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci 9(12):4416–4429
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Magid D, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Schreiner PJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB (2013) Heart disease and stroke statistics–2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 127(1):e6–e245. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e31828124ad
Gu Y, Hua Y, Keep RF, Morgenstern LB, Xi G (2009) Deferoxamine reduces intracerebral hematoma-induced iron accumulation and neuronal death in piglets. Stroke 40(6):2241–2243. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.539536
Hebert RL, Jacobson HR, Breyer MD (1990) PGE2 inhibits AVP-induced water flow in cortical collecting ducts by protein kinase C activation. Am J Physiol 259(2 Pt 2):F318–F325
Hoffmann PR, Kench JA, Vondracek A, Kruk E, Daleke DL, Jordan M, Marrack P, Henson PM, Fadok VA (2005) Interaction between phosphatidylserine and the phosphatidylserine receptor inhibits immune responses in vivo. J Immunol 174(3):1393–1404. doi:174/3/1393
Huynh ML, Fadok VA, Henson PM (2002) Phosphatidylserine-dependent ingestion of apoptotic cells promotes TGF-beta1 secretion and the resolution of inflammation. J Clin Invest 109(1):41–50. doi:10.1172/JCI11638
Ito D, Tanaka K, Suzuki S, Dembo T, Fukuuchi Y (2001) Enhanced expression of Iba1, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1, after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Stroke 32(5):1208–1215
James ML, Wang H, Venkatraman T, Song P, Lascola CD, Laskowitz DT (2010) Brain natriuretic peptide improves long-term functional recovery after acute CNS injury in mice. J Neurotrauma 27(1):217–228. doi:10.1089/neu.2009.1022
Jones BJ, Roberts DJ (1968) The quantitative measurement of motor inco-ordination in naive mice using an accelerating rotarod. J Pharm Pharmacol 20(4):302–304
Kawano T, Anrather J, Zhou P, Park L, Wang G, Frys KA, Kunz A, Cho S, Orio M, Iadecola C (2006) Prostaglandin E2 EP1 receptors: downstream effectors of COX-2 neurotoxicity. Nat Med 12(2):225–229. doi:nm1362
Keep RF, Xi G, Hua Y, Hoff JT (2005) The deleterious or beneficial effects of different agents in intracerebral hemorrhage: think big, think small, or is hematoma size important? Stroke 36(7):1594–1596. doi:01.STR.0000170701.41507.e1
Keep RF, Hua Y, Xi G (2012) Intracerebral haemorrhage: mechanisms of injury and therapeutic targets. Lancet Neurol 11(8):720–731. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70104-7
Koizumi S, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Nasu-Tada K, Shinozaki Y, Ohsawa K, Tsuda M, Joshi BV, Jacobson KA, Kohsaka S, Inoue K (2007) UDP acting at P2Y6 receptors is a mediator of microglial phagocytosis. Nature 446(7139):1091–1095. doi:nature05704
Komotar RJ, Kim GH, Sughrue ME, Otten ML, Rynkowski MA, Kellner CP, Hahn DK, Merkow MB, Garrett MC, Starke RM, Connolly ES (2007) Neurologic assessment of somatosensory dysfunction following an experimental rodent model of cerebral ischemia. Nat Protoc 2(10):2345–2347. doi:nprot.2007.359
MacLellan CL, Silasi G, Poon CC, Edmundson CL, Buist R, Peeling J, Colbourne F (2008) Intracerebral hemorrhage models in rat: comparing collagenase to blood infusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28(3):516–525. doi:9600548
Matsushita K, Meng W, Wang X, Asahi M, Asahi K, Moskowitz MA, Lo EH (2000) Evidence for apoptosis after intercerebral hemorrhage in rat striatum. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20(2):396–404. doi:10.1097/00004647-200002000-00022
Nguyen VT, Benveniste EN (2002) Critical role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and NF-kappa B in interferon-gamma -induced CD40 expression in microglia/macrophages. J Biol Chem 277(16):13796–13803. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111906200
Phillis JW, Horrocks LA, Farooqui AA (2006) Cyclooxygenases, lipoxygenases, and epoxygenases in CNS: their role and involvement in neurological disorders. Brain Res Rev 52(2):201–243. doi:S0165-0173(06)00011-7
Qureshi AI, Tuhrim S, Broderick JP, Batjer HH, Hondo H, Hanley DF (2001) Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 344(19):1450–1460. doi:10.1056/NEJM200105103441907
Regan RF, Panter SS (1993) Neurotoxicity of hemoglobin in cortical cell culture. Neurosci Lett 153(2):219–222
Ribo M, Grotta JC (2006) Latest advances in intracerebral hemorrhage. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 6(1):17–22
Saleem S, Li RC, Wei G, Doré S (2007) Effects of EP1 receptor on cerebral blood flow in the middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in mice. J Neurosci Res 85(11):2433–2440. doi:10.1002/jnr.21399
Schallert T, Fleming SM, Leasure JL, Tillerson JL, Bland ST (2000) CNS plasticity and assessment of forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke, cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology 39(5):777–787. doi:S0028390800000058
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874(2):123–130. doi:S0006-8993(00)02513-0
Shah ZA, Nada SE, Dore S (2011) Heme oxygenase 1, beneficial role in permanent ischemic stroke and in Gingko biloba (EGb 761) neuroprotection. Neuroscience 180:248–255. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.02.031
Simmer JP, Hu Y, Lertlam R, Yamakoshi Y, Hu JC (2009) Hypomaturation enamel defects in Klk4 knockout/LacZ knockin mice. J Biol Chem 284(28):19110–19121. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.013623
Smirkin A, Matsumoto H, Takahashi H, Inoue A, Tagawa M, Ohue S, Watanabe H, Yano H, Kumon Y, Ohnishi T, Tanaka J (2010) Iba1(+)/NG2(+) macrophage-like cells expressing a variety of neuroprotective factors ameliorate ischemic damage of the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(3):603–615. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.233
Takahashi K, Rochford CD, Neumann H (2005) Clearance of apoptotic neurons without inflammation by microglial triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2. J Exp Med 201(4):647–657. doi:jem.20041611
Takahashi K, Prinz M, Stagi M, Chechneva O, Neumann H (2007) TREM2-transduced myeloid precursors mediate nervous tissue debris clearance and facilitate recovery in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. PLoS Med 4(4):e124. doi:06-PLME-RA-0690R2
Tang ZP, Xie XW, Shi YH, Liu N, Zhu SQ, Li ZW, Chen Y (2010) Combined transplantation of neural stem cells and olfactory ensheathing cells improves the motor function of rats with intracerebral hemorrhage. Biomed Environ Sci 23(1):62–67
Tikka TM, Koistinaho JE (2001) Minocycline provides neuroprotection against N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglia. J Immunol 166(12):7527–7533
Wang J, Doré S (2007a) Heme oxygenase-1 exacerbates early brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Brain 130(Pt 6):1643–1652. doi:130/6/1643
Wang J, Doré S (2007b) Inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(5):894–908. doi:9600403
Wang J, Zhuang H, Doré S (2006) Heme oxygenase 2 is neuroprotective against intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurobiol Dis 22(3):473–476. doi:S0969-9961(05)00343-8
Wang J, Fields J, Zhao C, Langer J, Thimmulappa RK, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S, Doré S (2007) Role of Nrf2 in protection against intracerebral hemorrhage injury in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 43(3):408–414. doi:S0891-5849(07)00287-0
Wasserman JK, Schlichter LC (2007) Neuron death and inflammation in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage: effects of delayed minocycline treatment. Brain Res 1136(1):208–218. doi:S0006-8993(06)03576-1
Watabe A, Sugimoto Y, Honda A, Irie A, Namba T, Negishi M, Ito S, Narumiya S, Ichikawa A (1993) Cloning and expression of cDNA for a mouse EP1 subtype of prostaglandin E receptor. J Biol Chem 268(27):20175–20178
Wu G, Xi G, Huang F (2006) Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in humans: hematoma enlargement, clot lysis, and brain edema. Acta Neurochir Suppl 96:78–80
Xue M, Del Bigio MR (2000) Intracerebral injection of autologous whole blood in rats: time course of inflammation and cell death. Neurosci Lett 283(3):230–232. doi:S030439400000971X
Yang SX, Wang YR, Qian C, He C (2008) Neuron regeneration in aged rats after intracerebral hemorrhage. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 37(4):386–392
Yrjanheikki J, Tikka T, Keinanen R, Goldsteins G, Chan PH, Koistinaho J (1999) A tetracycline derivative, minocycline, reduces inflammation and protects against focal cerebral ischemia with a wide therapeutic window. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(23):13496–13500
Zhao X, Sun G, Zhang J, Strong R, Song W, Gonzales N, Grotta JC, Aronowski J (2007) Hematoma resolution as a target for intracerebral hemorrhage treatment: role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in microglia/macrophages. Ann Neurol 61(4):352–362. doi:10.1002/ana.21097
Zhao X, Grotta J, Gonzales N, Aronowski J (2009) Hematoma resolution as a therapeutic target: the role of microglia/macrophages. Stroke 40(3 Suppl):S92–S94. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.533158
Zhou P, Qian L, Chou T, Iadecola C (2008) Neuroprotection by PGE2 receptor EP1 inhibition involves the PTEN/AKT pathway. Neurobiol Dis 29(3):543–551. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.11.010
Acknowledgements and Financial support
We thank all Doré lab team members for their active participation. National Institutes of Health (NS046400, AG022971) to SD, and the American Heart Association (09POST2080364) to BM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nilendra Singh and Bo Ma contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N., Ma, B., Leonardo, C.C. et al. Role of PGE2 EP1 Receptor in Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Brain Injury. Neurotox Res 24, 549–559 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9410-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9410-7