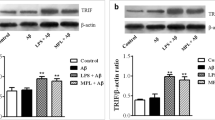
Abstract
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the accumulation of β amyloid (Aβ) aggregates. Aβ induces the inflammatory activation of glia, inducing secretion of Interleukin 1β (IL1β), nitric oxide (NO) and superoxide radicals. The specific receptor responsible for the induction of inflammatory activation by Aβ, is still an open question. We propose that scavenger receptors (SR) participate in the activation of glia by Aβ. We assessed production of NO, synthesis of IL1β and activation of ERK, JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways by Western blot, in primary rat glial cultures exposed to SR ligands (fucoidan and Poly I), LPS + IFNγ (LI), and Aβ. Poly I but not fucoidan nor fibrillar Aβ increased threefold NO production by astrocytes in a time-dependent manner. Fucoidan and Poly I increased 5.5- and 3.5-fold NO production by microglia, and co-stimulation with Aβ increased an additional 60% NO induced by SR ligands. Potentiation by Aβ was observed later for astrocytes than for microglia. In astrocytes, co-stimulation with Aβ potentiated ERK and JNK activation in response to Fucoidan and Poly I, whereas it reduced induction of JNK activation by LI and left unaffected NF-κB activation induced by LI. Levels of pro-IL1β in astrocytes increased with Aβ, SR ligands and LI, and were potentiated by co-stimulation with Aβ. Our results suggest that SRs play a role on inflammatory activation, inducing production of NO and IL1β, and show potentiation by Aβ. Potentiation of the inflammatory response of Aβ could be meaningful for the activation of glia observed in AD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, Barger S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O’Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss Coray T (2000) Inflammation and alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:383–421
Alarcón R, Fuenzalida C, Santibáñez M, von Bernhardi R (2005) Expression of scavenger receptors in glial cells: comparing the adhesion of astrocytes and microglia from neonatal rats to surface-bound beta amyloid. J Biol Chem 280:30406–30415
Bamberger M, Landreht G (2001) Microglial interaction with beta-amyloid: implication for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Microsc Res Tech 54:59–70
Borsello T, Forloni G (2007) JNK signaling: a possible target to prevent neurodegeneration. Curr Pharm Des 13:1875–1886
Brambilla R, Bracchi-Ricard V, Hu WH, Frydel B, Bramwell A, Karmally S, Green EJ, Bethea JR (2005) Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor kappaB reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Exp Med 202:145–156
Campa VM, Iglesias JM, Caicedo MT, Rodríguez R, Riera J, Ramos S, Lazo PS (2005) Polyinosinic acid induced TNF and NO production as well as NF-kappaB and AP-1 transcriptional activation in the monocyte-macrophage cell line RAW264.7. Inflamm Res 54:328–337
Chen B, Keshive M, Deen WM (1998) Diffusion and reaction of nitric oxide in suspension cell cultures. Biophys J 75:745–754
Cogswell JP, Godlevski MM, Wisely GB, Clay WC, Leesnitzer LM, Ways JP, Gray JG (1994) NF-kappa B regulates IL-1 beta transcription through a consensus NF-kappa B binding site and a non consensus CRE-like site. J Immunol 153:712–723
Contestabile A, Monti B, Contestabile A, Ciani E (2003) Brain nitric oxide and its dual role in neurodegeneration/neuroprotection: understanding molecular mechanisms to devise drug approaches. Curr Med Chem 10:2147–2174
Coraci IS, Husemann J, Berman JW, Hulette C, Dufour JH, Campanella GK, Luster AD, Silverstein SC, El-Khoury JB (2002) CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is expressed on microglia in Alzheimer’s disease brains and can mediate production of reactive oxygen species in response to beta-amyloid fibrils. Am J Pathol 160:101–112
Dell’Albani P, Santangelo R, Torrisi L, Nicoletti VG, de Vellis J, Giuffrida Stella AM (2001) JAK/STAT signaling pathway mediates cytokine-induced iNOS expression in primary astroglial cell cultures. J Neurosci Res 65:417–424
Farina C, Aloise F, Meinl E (2007) Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol 28:138–145
Fassbender K, Walter S, Khul S, Landmann R, Ishii K, Bertsch T, Stalder AK, Muehlhauser F, Liu Y, Ulmer AJ, Rivest S, Lentschat A, Gulbins E, Jucker M, Staufenbiel M, Brechtel K, Walter J, Multhaup G, Penke B, Adachi Y, Hartmann T, Beyreuther K (2004) The LPS receptor CD14 links innate immunity with Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 18:203–205
Fernández-Vizarra P, Fernández AP, Castro-Blanco S, Encinas JM, Serrano J, Bentura ML, Muñoz P, Martínez-Murillo R, Rodrigo J (2004) Expression of nitric oxide system in clinically evaluated cases of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 15:287–305
Giulian D, Baker TJ (1986) Characterization of ameboid microglia isolated from developing mammalian brain. J Neurosci 8:2163–2178
Giulian D, Corpuz M (1993) Microglial secretion products and their impact on the nervous system. Adv Neurol 59:315–320
Giulian D, Vaca K, Corpuz M (1993) Brain glial release factors with opposing actions upon neuronal survival. J Neurosci 13:29–37
Giulian D, Li J, Li X, George J, Rutecki P (1994) The impact of microglia-derived cytokine upon gliosis in the CNS. Dev Neurosci 16:128–136
Hsu HY, Chiu SL, Wen MH, Chen KY, Hua KF (2001) Ligands of macrophage scavenger receptor induce cytokine expression via differential modulation of protein kinase signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 276:28719–28730
Husemann J, Loike JD, Anakov R, Febbraio M, Silverstein SC (2002) Scavenger receptors in neurobiology and neuropathology: their role on microglia and other cells of the nervous system. Glia 40:195–205
Jana M, Anderson JA, Saha RN, Liu X, Pahan K (2005) Regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in proinflammatory cytokine-stimulated human primary astrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 38:655–664
Jarret JT, Berger EP, Lansbury PT Jr (1993) The carboxy terminus of the beta amyloid protein is critical for the seeding of amyloid formation: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 32:4693–4697
Johnstone M, Gearing AJ, Miller KM (1999) A central role for astrocytes in the inflammatory response to beta-amyloid; chemokines, cytokines and reactive oxygen species are produced. J Neuroimmunol 93:182–193
Kim SH, Smith CJ, Van Eldik LJ (2004) Importance of MAPK pathways for microglial pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1 beta production. Neurobiol Aging 25:431–439
Koppenol WH, Moreno JJ, Pryor WA, Ischiropoulos H, Beckman JS (1992) Peroxynitrite, a cloaked oxidant formed by nitric oxide and superoxide. Chem Res Toxicol 5:834–842
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1(6):a001651. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a001651
Liu J, Lin A (2005) Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res 15:36–42
Marcus J, Karackattu S, Fleegal M, Sumners C (2003) Cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in astroglia. Role of Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB. Glia 41:152–160
Marzolo MP, von Bernhardi R, Bu G, Inestrosa NC (2000) Expression of alpha(2)-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) in rat microglial cells. J Neurosci Res 60:401–411
McGeer P, McGeer E (1995) The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev 21:195–218
Mrak RE, Griffin WS (2000) Interleukin-1, neuroinflammation, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:903–908
Nadjar A, Combe C, Busquet P, Dantzer R, Parnet P (2005) Signaling pathways of Interleukin-1 actions in the brain: anatomical distribution of phosphor-ERK1/2 in the brain of rat treated systemically with Interleukin-1beta. Neuroscience 134:921–932
Nakamura T, Suzuki H, Wada Y, Kodama T, Doi T (2006) Fucoidan induces nitric oxide production via p-38 mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-kappaB-dependent signaling pathways through macrophage scavenger receptors. Biochem Biphys Res Commun 343:286–294
Neyen C, Pluddemann A, Gordon S (2011) Identification of scavenger receptor ligands. Methods Mol Biol 748:35–50
Nims RW, Cook JC, Krishna M, Christodoulou D, Poore CM, Miles AM, Grisham MB, Wink DA (1996) Colorimetric assays for nitric oxide and nitrogen oxide species formed from nitric oxide stock solutions and donor compounds. Methods Enzymol 268:93–105
Palkama T (1991) Induction of interleukin-1 production by ligands binding to the scavenger receptor in human monocytes and the THP-1 cell line. J Immunol 74:432–438
Paresce DM, Ghosh RN, Maxfield FR (1996) Microglial cells internalize aggregates of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta-protein via a scavenger receptor. Neuron 17:553–565
Parker LC, Luheshi GN, Rothwell NJ, Pinteaux E (2002) IL-1 beta signaling in glial cells in wild type and IL-1RI deficient mice. Br J Pharmacol 136:312–320
Pfeiffer S, Gorren AC, Schmidt K, Werner ER, Hansert B, Bohle DS, Mayer B (1997) Metabolic fate of peroxynitrite in aqueous solution. Reaction with nitric oxide and pH-dependent decomposition to nitrite and oxygen in a 2:1 stoichiometry. J Biol Chem 272:3465–3470
Platt N, Gordon S (1998) Scavenger receptors: diverse activities and promiscuous binding of polyanionic ligands. Chem Biol 5:R193–R203
Pyo H, Jou I, Jung S, Hong S, Joe EH (1998) Mitogen-activated protein kinases activated by lipopolysaccharide and beta-amyloid in cultured rat microglia. Neuroreport 9:871–874
Ramírez G, Toro R, Döbeli H, von Bernhardi R (2005) Protection of rat primary hippocampal cultures from A beta cytoxicity by pro-inflammatory molecules is mediated by astrocytes. Neurobiol Dis 19:243–254
Rossi F, Bianchini E (2006) Synergistic induction of nitric oxide by beta-amyloid and cytokines in astrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 225:474–478
Rotshenker S (2009) The role of Galectin-3/MAC-2 in the activation of the innate-immune function of phagocytosis in microglia in injury and disease. J Mol Neurosci 39:99–103
Saha RN, Pahan K (2006) Regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene in glial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:929–947
Schubert P, Morino T, Miyazaki H, Ogata T, Nakamura Y, Marchini C, Ferroni S (2000) Cascading glia reactions: a common pathomechanism and its differentiated control by cyclic nucleotide signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 903:24–33
Sheng JG, Bora SH, Xu G, Borchelt DR, Price DL, Koliatsos VE (2003) Lipopolysaccharide-induced-neuroinflammation increases intracellular accumulation of amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta peptide in APPswe transgenic mice. Neurobiol Dis 14:133–145
Simi A, Lerouet D, Pinteaux E, Brough D (2007) Mechanisms of regulation for interleukin-1 beta in neurodegenerative disease. Neuropharmacology 52:1563–1569
van Loo G, De Lorenzi R, Schmidt H, Huth M, Mildner A, Schmidt-Supprian M, Lassman H, Prinz MR, Pasparakis M (2006) Inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB in the central nervous system ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Nat Immunol 7:954–961
von Bernhardi R (2007) Glial cell dysregulation: a new perspective on Alzheimer disease. Neurotox Res 12:215–232
von Bernhardi R, Eugenín J (2004) Microglia-astrocyte interaction in Alzheimer’s disease: modulation of cell reactivity to A beta. Brain Res 1025:186–193
von Bernhardi R, Ramírez G (2001) Microglia-astrocyte interaction in Alzheimer’s disease: friends or foes for the nervous system? Biol Res 34:123–128
von Bernhardi R, Ramírez G, Toro R, Eugenín J (2007) Pro-inflammatory conditions promote neuronal damage mediated by Amyloid Precursor Protein and decrease its phagocytosis and degradation by microglial cells in culture. Neurobiol Dis 26:153–164
von Bernhardi R, Tichauer JE, Eugenín J (2010) Aging-dependent changes of microglial cells and their relevance for neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurochem 112:1099–1114
Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ (2004) Deciphering the molecular basis of memory failure in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 44:181–193
Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A, Slattery T, Zhao L, Nagashima M, Morser J, Migheli A, Nawroth P, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1996) RAGE and amyloid-beta peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 382:685–691
Zhang P, Miller BS, Rosenzwig SA, Bhat NR (1996) Activation of C-jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase in primary glial cultures. J Neurosci Res 46:114–121
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grant Fondecyt 1090353 to Dr. R. von Bernhardi.
Conflict of interest
Authors (PM, BG and RvB) declare they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P. Murgas and B. Godoy have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murgas, P., Godoy, B. & von Bernhardi, R. Aβ Potentiates Inflammatory Activation of Glial Cells Induced by Scavenger Receptor Ligands and Inflammatory Mediators in Culture. Neurotox Res 22, 69–78 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9306-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9306-3