Abstract
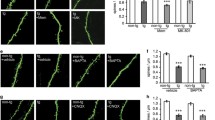
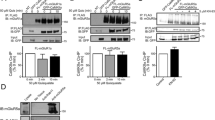
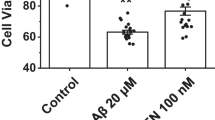
It is unknown whether amyloid beta-protein 31–35 (Aβ[31–35]) has effects similar to Aβ[1–40] and Aβ[25–35] on the intracellular calcium ([Ca2+]i) to induce a disruption of calcium homeostasis. In this study, we investigated the effects of Aβ[31–35] on [Ca2+]i in primary cultured cortical neurons using real time fluorescence imaging technique and the Ca2+-sensitive dye Furo-2/AM. It was found that Aβ[31–35] (25 μM) could induce a significant elevation in [Ca2+]i and a decrease in the average latency in the cortical neurons in a dose-dependent manner. To examine whether the activation of group III mGluRs could block the changes in [Ca2+]i and protect neurons from apoptosis induced by Aβ[31–35], we then investigated the effects of l-serine-O-phosphate (l-SOP) and (R,S)-4-phosphonophenylglycine ((R,S)-PPG), the selective agonists of group III metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), on [Ca2+]i and apoptosis in neurons treated by Aβ[31–35]. We demonstrated that l-SOP or (R,S)-PPG (100 μM) treatment suppresses significantly the elevation of [Ca2+]i induced by Aβ[31–35] and also induces an almost complete recovery of both the fluorescence intensity and apoptotic cells (%) to the control level in the neurons. These results suggest that Aβ[31–35] may be the shortest sequence responsible for the neuronal toxicity of Aβ protein and that the neuroprotective role of the activation of group III mGluRs from the apoptosis induced by Aβ[31–35] might be partly due to its ability to inhibit the increased calcium influx, which results from Aβ[31–35].






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]i:
-
Intracellular calcium concentration
- DMEM:
-
Dubecco’s modified Eagle medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- fura-2AM:
-
Fura-2-pentacetoxymethylester
- MAP2:
-
Microtubule-associated protein 2
- l-SOP:
-
l-Serine-O-phosphate
- l-AP4:
-
l-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutanoate
- mGluR:
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- Aβ[31–35]:
-
Amyloid beta-protein 31–35
- (R,S)-PPG:
-
(R,S)-4-phosphonophenylglycine
References
Arispe N, Rojas E, Pollard HB (1993a) Alzheimer disease amyloid beta protein forms calcium channels in bilayer membranes: blockade by tromethamine and aluminum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(2):567–571
Arispe N, Rojas E, Pollard HB (1993b) Giant multilevel cation channels formed by Alzheimer disease amyloid β protein [AβP-(1-40)] in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10573–10577
Barger SW, Smith-Swintosky VL, Rydel RE, Mattson MP (1993) beta-Amyloid precursor protein mismetabolism and loss of calcium homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 95:158–164
Brorson JR, Bindokas VP, Iwama T, Marcuccilli CJ, Chisholm JC, Miller RJ (1995) The Ca2+ influx induced by beta-amyloid peptide 25-35 in cultured hippocampal neurons results from network excitation. J Neurobiol 26(3):325–338
Bruno V, Battaglia G, Ksiazek I, van der Putten H, Catania MV, Giuffrida R, Lukic S, Leonhardt T, Inderbitzin W, Gasparini F, Kuhn R, Hampson DR, Nicoletti F, Flor PJ (2000) Selective activation of mGlu4 metabotropic glutamate receptors is protective against excitotoxic neuronal death. J Neurosci 20(17):6413–6420
Clementi ME, Marini S, Coletta M, Orsini F, Giardina B, Misiti F (2005) Abeta(31-35) and Abeta(25-35) fragments of amyloid beta-protein induce cellular death through apoptotic signals: role of the redox state of methionine-35. FEBS Lett 579(13):2913–2918
Conn PJ, Pin JP (1997) Pharmacology and functions of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:205–237
Copani A, Bruno VM, Barresi V, Battaglia G, Condorelli DF, Nicoletti F (1995) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors prevents neuronal apoptosis in culture. J Neurochem 64(1):101–108
Cuajungco MP, Faget KY, Huang X, Tanzi RE, Bush AI (2000) Metal chelation as a potential therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920:292–304
Dante S, Hauss T, Dencher NA (2002) Beta-amyloid 25 to 35 is intercalated in anionic and zwitterionic lipid membranes to different extents. Biophys J 83(5):2610–2616
Flor PJ, Van Der Putten H, Rüegg D, Lukic S, Leonhardt T, Bence M, Sansig G, Knopfel T, Kuhn R (1997) A novel splice variant of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, human mGluR7b. Neuropharmacology 36:153–159
Furukawa K, Abe Y, Akaike N (1994) Amyloid β protein-induced irreversible current in rat cortical neurones. Neuroreport 27:2016–2018
Gasparini F, Bruno V, Battaglia G, Lukic S, Leonhardt T, Inderbitzin W, Laurie D, Sommer B, Varney MA, Hess SD, Johnson EC, Kuhn R, Urwyler S, Sauer D, Portet C, Schmutz M, Nicoletti F, Flor PJ (1999) (R,S)-4-phosphonophenylglycine, a potent and selective group III metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist, is anticonvulsive and neuroprotective in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:1678–1687
Haass C, Selkoe DJ (1993) Cellular processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein and the genesis of amyloid beta-peptide. Cell 75(6):1039–1042
Hardy JA, Higgins GA (1992) Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 256(5054):184–185
Heredia L, Helguera P, de Olmos S, Kedikian G, Sola Vigo F, LaFerla F, Staufenbiel M, de Olmos J, Busciglio J, Caceres A, Lorenzo A (2006) Phosphorylation of actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilin by LIM-kinase mediates amyloid beta-induced degeneration: a potential mechanism of neuronal dystrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 26(24):6533–6642
Hiruma H, Katakura T, Takahashi S, Ichikawa T, Kawakami T (2003) Glutamate and amyloid beta-protein rapidly inhibit fast axonal transport in cultured rat hippocampal neurons by different mechanisms. J Neurosci 23(26):8967–8977
Ho KP, Li L, Zhao L, Qian ZM (2003) Genistein protects primary cortical neurons from iron-induced lipid peroxidation. Mol Cell Biochem 247(1–2):219–222
Johansen PA, Chase LA, Sinor AD, Koerner JF, Johnson RL, Robinson MB (1995) Type 4a metabotropic glutamate receptor: identification of new potent agonists and differentiation from the L-(+)-2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid-sensitive receptor in the lateral perforant pathway in rats. Mol Pharmacol 48:140–149
Kawahara M, Kuroda Y (2000) Molecular mechanism of neurodegeneration induced by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid protein: channel formation and disruption of calcium homeostasis. Brain Res Bull 53(4):389–397
Kawahara M, Kuroda Y (2001) Intracellular calcium changes in neuronal cells induced by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid protein are blocked by estradiol and cholesterol. Cell Mol Neurobiol 21(1):1–13
Luyt K, Varadi A, Molnar E (2003) Functional metabotropic glutamate receptors are expressed in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. J Neurochem 84(6):1452–1464
Luyt K, Varadi A, Durant CF, Molnar E (2006) Oligodendroglial metabotropic glutamate receptors are developmentally regulated and involved in the prevention of apoptosis. J Neurochem 99(2):641–656
Lynch T, Cherny RA, Bush AI (2000) Oxidative processes in Alzheimer’s disease: the role of abeta-metal interactions. Exp Gerontol 35(4):445–451
Misiti F, Sampaolese B, Pezzotti M, Marini S, Coletta M, Ceccarelli L, Giardina B, Clementi ME (2005) Abeta(31–35) peptide induce apoptosis in PC 12 cells: contrast with Abeta(25-35) peptide and examination of underlying mechanisms. Neurochem Int 46(7):575–583
Mogensen HS, Beatty DM, Morris SJ, Jorgensen OS (1998) Amyloid beta-peptide(25-35) changes [Ca2+] in hippocampal neurons. Neuroreport 9(7):1553–1558
Morishima Y, Gotoh Y, Zieg J, Barrett T, Takano H, Flavell R, Davis RJ, Shirasaki Y, Greenberg ME (2001) Beta-amyloid induces neuronal apoptosis via a mechanism that involves the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and the induction of Fas ligand. J Neurosci 21(19):7551–7760
Pollard HB, Rojas E, Arispe N (1993) Giant multilevel cation channels formed by Alzheimer disease amyloid beta-protein [A beta P-(1-40)] in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(22):10573–10577
Pollard HB, Arispe N, Rojas E (1995) Ion channel hypothesis for Alzheimer amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 15(5):513–526
Qi JS, Qiao JT (2001a) Suppression of large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels by amyloid beta-protein fragment 31–35 in membrane patches excised from hippocampal neurons. Sheng Li Xue Bao 53(3):198–204
Qi JS, Qiao JT (2001b) Amyloid beta-protein fragment 31–35 forms ion channels in membrane patches excised from rat hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 105:845–852
Qi JS, Ye L, Qiao JT (2004) Amyloid beta-protein fragment 31–35 suppresses delayed rectifying potassium channels in membrane patches excised from hippocampal neurons in rats. Synapse 51(3):165–172
Rhee SK, Quist AP, Lal R (1998) Amyloid beta protein-(1-42) forms calcium-permeable, Zn2+-sensitive channel. J Biol Chem 273(22):13379–13382
Selkoe DJ (1991) The molecular pathology of Alzheimer disease. Neuron 6:487–498
Shigemoto R, Kinoshita A, Wada E, Nomura S, Ohishi H, Takada M, Flor PJ, Neki A, Abe T, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N (1997) Differential presynaptic localization of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 17(19):7503–7522
Simmons MA, Schneider CR (1993) Amyloidβpeptide act directly on single neurons. Neurosci Lett 150:133–136
Trombley PQ, Westbrook GL (1992) L-AP4 inhibits calcium currents and synaptic transmission via a G-protein-coupled glutamate receptor. J Neurosci 12(6):2043–2050
Wadghiri YZ, Sigurdsson EM, Sadowski M, Elliott JI, Li Y, Scholtzova H, Tang CY, Aguinaldo G, Pappolla M, Duff K, Wisniewski T, Turnbull DH (2003) Detection of Alzheimer’s amyloid in transgenic mice using magnetic resonance microimaging. Magn Reson Med 50(2):293–302
Wu B, Kitagawa K, Liu B, Zhang NY, Xiong ZM, Inagaki C (2006) Attenuation of amyloid beta (Abeta)-induced inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity by Abeta fragments, Abeta20–29 and Abeta31–35. Neurosci Lett 396(2):148–152
Yan X, Qiao JT, Dou Y, Qiao ZD (1999) Beta-amyloid peptide fragment 31–35 induces apoptosis in cultured cortical neurons. Neuroscience 92(1):177–184
Yan X, Xiao R, Dou Y, Wang S, Qiao Z, Qiao J (2000) Carbachol blocks beta-amyloid fragment 31–35-induced apoptosis in cultured cortical neurons. Brain Res Bull 51(6):465–470
Yankner BA, Duffy LK, Kirschner DA (1990) Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science 250(4978):279–282
Zhao L, Qian ZM, Zhang C, Wing HY, Du F, Ya K (2008) Amyloid beta-peptide 31–35-induced neuronal apoptosis is mediated by caspase-dependent pathways via cAMP-dependent protein kinase A activation. Aging Cell 7(1):47–57
Acknowledgments
The studies in our laboratories were supported by Research Grants from Shanxi Medical University, The Competitive Earmarked Grants of The Hong Kong Research Grants Council (CUHK466907-KY), Direct Grant of The Chinese University of Hong Kong (A/C: 4450226-KY and 4450273-KY), RGC-NSFC Grant (KY), Grants from Hong Kong Polytechnic University (I-BB8L, GU-384 and G-YG11) and National Key Laboratory of CMMP (Shenzhen), and Shenzhen-Hong Kong Innovation Circle Program. We declare that we have no financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Zhao, S.T., Qian, Z.M. et al. Activation of Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Reduces Intracellular Calcium in β-Amyloid Peptide [31–35]-Treated Cortical Neurons. Neurotox Res 16, 174–183 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9068-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9068-3