Abstract
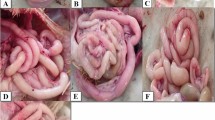
This work assesses the cell-mediated immune reaction IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ of experimentally challenged broiler chicken with Eimeria tenella (E. tenella). Therefore, ninety, 2-weeks-old healthy broiler chicks were allocated as eighty chicks infected orally with 2.5 × 104 E. tenella sporulated oocysts, and the other ten birds were kept as control negative birds. Post-challenge, mortality rate, symptoms, oocysts shedding, and lesion score were evaluated. Tissue samples (cecum and spleen) were collected at 0, 4, 8, and 12 days post-infection (dpi). Ten chickens were ethically slaughtered at 0, 4, 8, and 12 days post-infection, as well as two birds from the negative control group; parts from cecal and spleen samples were kept in cryopreservation containers, and other parts were preserved in formaline 10% for further investigation. The evaluated genes (IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ) were normal at 0 days and upregulated at 4 and 8 days, which reached maximum upregulation at eight dpi. The histopathological examination of the ceca and spleen were evaluated before and after challenge. It could be concluded that E. tenella revealed direct severe macroscopic and microscopic changes in cecal tissues and indirectly induced alteration in splenic tissues, resulting in upregulation of different cell mediated immune response in cecum and spleen in relation to the experimental period.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Al-Shaibani IRM, Al-Khadher AMA, AlHibah AZH (2020) Anticoccidial activity of Allium sativum and Punica granatum against experimentally induced Eimeria tenella infection in broiler chickens. Asian J Res Anim Vet Sci 5(4):20–29
Attia MM, Salem HM (2022) Morphological and molecular characterization of Pseudolynchia canariensis (Diptera: Hippoboscidae) infesting domestic pigeons. Int J Trop Insect Sci 42:733–740
Attia MM, El-Gameel SM, Ismael E (2020) Evaluation of Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α); gamma interferon (IFN-γ) genes and oxidative stress in sheep: immunological responses induced by Oestrus ovis (Diptera: Oestridae) infestation. J Parasit Dis 44(2):332–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-020-01220-w
Attia MM, Ibrahim MM, Mahmoud MA (2023) Heavy Infection of the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) with Huffmanela japonica: morphological, ultrastructural identification, tissue reactions and immunological analysis. Aquac Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01124-5
Attia MM, Khalifa MM (2023) Virulence of Babesia bigemina in infected cattle (Bos taurus): olecular and immunological studies. Res Vet Sci 156:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2023.01.017
Attia MM, Yehia N, Soliman MM, Shukry M, El-Saadony MT, Salem HM (2022) Evaluation of the antiparasitic activity of the chitosan-silver nanocomposites in the treatment of experimentally infested pigeons with Pseudolynchia canariensis. Saudi J Biol Sci 29:1644–1652
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (eds) (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Botwright NA, Mohamed AR, Slinger J, Lima PC, Wynne JW (2021) Host-parasite interaction of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and the ectoparasite Neoparamoeba perurans in amoebic gill disease. Front Immunol 12:1900
Breed DG, Dorrestein J, Schetters TP, Waart LV, Rijke E, Vermeulen AN (1997) Peripheral blood lymphocytes from Eimeria tenella infected chickens produce gamma interferon after stimulation in vitro. Parasite Immunol 19(3):127–135
Cornelissen JBWJ, Swinkels WJC, Boersma WA, Rebel JMJ (2009) Host response to simultaneous Infections with Eimeria acervulina, maxima and tenella: a cumulation of single responses. Vet Parasitol 162(1–2):58–66
Cribillero G, Molina D, Reyna P, Salgado V, Gonzalez R, Icochea VME (2014) Comparison of two infection dosage of Eimeria tenella in broiler chickens for anticoccidials efficacy trials. In: Conference: annual meeting American Association of Avian Pathologist at Denver-Colorado, USA
del Cacho E, Gallego M, Lee SH, Lillehoj HS, Quilez J, Lillehoj EP, Sánchez-Acedo C (2012) Induction of protective immunity against Eimeria tenella, Eimeria maxima, and Eimeria acervulina infections using dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Infect Immun 80(5):1909–1916
Ding X, Lillehoj HS, Quiroz MA, Bevensee E, Lillehoj EP (2004) Protective immunity against Eimeria acervulina following in ovo immunization with a recombinant subunit vaccine and cytokine genes. Infect Immun 72(12):6939–6944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2021.101542
El-Shall NA, El-Hack A, Albaqami ME, Khafaga NM, Taha AF, Swelum AE, El-Saadony AA, Salem MT, El-Tahan HM, AbuQamar AM, El-Tarabily SF, Elbestawy KA (2021) Phytochemical control of poultry coccidiosis: a review. Poult, Sci
Gu Y, Cui L, Chen H, Li W, Li S, Jin G, Liu D (2010) Effect on serum antioxidase of the same age chicken inoculated with different doses E. tenella. Chin J Vet Sci 30(4):462–464
Hong YH, Lillehoj HS, Lee SH, Dalloul RA, Lillehoj EP (2006) Analysis of chicken cytokine and chemokine gene expression following Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria tenella infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 114(3–4):209–223
Jeong J, Kim WH, Yoo J, Lee C, Kim S, Cho JH, Min W (2012) Identification and comparative expression analysis of interleukin 2/15 receptor β chain in chickens infected with E. tenella. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37704
Jiao J, Yang Y, Liu M, Li J, Cui Y, Yin S, Tao J (2018) Artemisinin and Artemisia annua leaves alleviate Eimeria tenella infection by facilitating apoptosis of host cells and suppressing inflammatory response. Vet Parasitol 254:172–177
Kogut MH, Rothwell L, Kaiser P (2003) Differential regulation of cytokine gene expression by avian heterophils during receptor-mediated phagocytosis of opsonized and nonopsonized Salmonella enteritidis. J Interferon Cytokine Res 23(6):319–327
Laurent F, Mancassola R, Lacroix S, Menezes R, Naciri M (2001) Analysis of chicken mucosal immune response to Eimeria tenella and Eimeria maxima infection by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Infect Immun 69(4):2527–2534
Long PL, Rose ME (1976) Growth of Eimeria tenelIa in vitro in macrophages from chicken peritoneal exudates. Z Parasitenk 48:291–294
Ogbe AO, Mgbojikwe LO, Abdu PA, Atawodi SE (2008) Organ and carcass weight variation and histopathological changes in Eimeria tenella infected broiler chickens treated with aqueous extract of a wild mushroom (Ganoderma Lucidum). Electron J Environ Agric Food Chem 7(5):2906–2913
Pham HHS, Matsubayashi M, Tsuji N, Hatabu T (2021) Relationship between Eimeria tenella associated-early clinical signs and molecular changes in the intestinal barrier function. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 240:110321
Razzaq A, Ali T, Saghir A, Arshad S, Cheema A (2011) Training needs assessment of poultry farmers in tehsil Faisalabad. J Anim Plant Sci 21(3):629–631
Salem HM, Khattab MS, Yehia N, Abd El-Hack ME, El-Saadony MT, Alhimaidi AR, Swelum AA, Attia MM (2022b) Morphological and molecular characterization of Ascaridia columbae in the domestic pigeon (Columba livia domestica) and the assessment of its immunological responses. Poult Sci 101(2):101596
Salem HM, Salem MA, Soliman MM, Althobaiti SA, Khafaga AK, El-Tahan AM, El-Saadony MT, Attia MM (2022) Parasitological and histopathological examination of Cocktail love birds infected with Eimeria aratinga (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). Poult Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2022.101781
Wang X, Zou W, Yu H, Lin Y, Dai G, Zhang T, Zhang G, Xie K, Wang J, Shi H (2019) RNA sequencing analysis of chicken cecum tissues following Eimeria tenella Infection in vivo. Genes (Basel) 10:E420
Xu ZY, Zheng MX, Zhang L, Gong X, Xi R, Cui XZ, Bai R (2017) Dynamic expression of death receptor adapter proteins tradd and fadd in Eimeria tenella-induced host cell apoptosis. Poult Sci 96(5):1438–1444
Ye C, You J, Li X, You R, Weng Y, Li J, Wang Y (2010) Design, synthesis and anticoccidial activity of a series of 3-(2-(2-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl) quinazolinone derivatives. Pestic Biochem Physiol 97(3):194–198
Younis NA, Thabit H, El-Samannoudy SI et al (2023) The immune responses of Oreochromis niloticus against Prohemistomum Vivax encysted metacercariae infection with the evaluation of different biomarkers stressors. Sci Rep 13:11885. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-38809-z
Yu Y, Zhao Q, Zhu S, Dong H, Huang B, Liang S, Han H (2020) Molecular characterization of serine/threonine protein phosphatase of Eimeria tenella. J Eukaryot Microbiol 67(5):510–520
Yu H, Zou W, Mi C, Wang Q, Dai G, Zhang T, Shi H (2021) Research note: expression of T cell-related cytokines in chicken cecal and spleen tissues following Eimeria tenella infection in vivo. Poult Sci 100(7):101161
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Attia, M.M., Mohamed, R.I. & Salem, H.M. Impact of Eimeria tenella experimental Infection on intestinal and splenic reaction of broiler chickens. J Parasit Dis 47, 829–836 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-023-01629-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-023-01629-z