Abstract
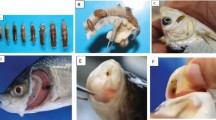
The present study explored the susceptibility of Puntius pulchellus subadults to Lernaea cyprinacea infection subsequent upon their first introduction to an intensive culture system that had a previous history of Lernaea infection and evaluated the efficacy of doramectin against the parasite. All the P. pulchellus introduced to the culture pond got infected demonstrating 100 % susceptibility of this species to Lernaea infection. Pathological changes caused by the parasite as evidenced by the extensive hemorrhage and tissue necrosis of the host at the point of parasite attachment was most severe in P. pulchellus. On the contrary, among the fish species already present in the pond and were previously exposed to the infection before the start of the present study, only Labeo fimbriatus developed mild to moderate infection. Cirrhinus mrigala, Ctenopharyngodon idella and Cyprinus carpio from the same culture pond did not develop Lernaea infection. Doramectin administration at 1 mg/kg b.wt. of fish incorporated in feed and given orally for 10 days or by a single intramuscular injection at 200 μg/kg b.wt. was found to be effective in controlling L. cyprinacea adult parasite infection in P. pulchellus. Doramectin hastened healing of the wounds caused by L. cyprinacea and did not cause any noticeable adverse reactions or toxicity to the fish host during the present study. In conclusion, P. pulchellus was observed to be highly susceptible to L. cyprinacea upon its first exposure to the infective stages of the parasite and a single intramuscular injection of doramectin at 200 μg/kg b.wt. was more effective than oral administration of the drug in controlling L. cyprinacea infection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanc G (1997) L’introduction des agents pathogenes dans les ecosystemes aquatiques: aspects theoriques et realites. In: Proceedings of the seminar les introductions d’ especes dans les milieux aquatiques continentaux en metropole. 13–15 Feb 1996, Paris, pp 471–487
Buchanan DV, Sanders JE, Zinn JL, Fryer JL (1983) Relative susceptibility of four strains of summer steelhead to infection by Ceratomyxa shasta. Trans Am Fish Soc 112:541–543
Chakrabarty NM (1996) Puntus pulchellus (Day)—an endangered native carp of peninsular India: its utility in weed control. Seafood Export J 27:21–22
Daszak P, Cunnignham AA, Hyatt AD (2001) Anthropogenic environmental change and the emergence of infectious diseases in wildlife. Acta Trop 78:103–116
Dubey GP (1992) Endangered, vulnerable and rare fishes of west coast river systems of India. In: Proceedings of national seminar on endangered fishes of India. 25–26 April 1992, Allahabad, pp 77–95
Faisal M, MelS Easa, Shalaby SI, Ibrahim MM (1988) Epizootic of Lernaea cyprinacea (Copepoda: Lernaeidae) in cyprinids imported to Egypt. Egypt J Comp Pathol Clin Pathol 1:127–148
Fernando CH (1991) Impacts of fish introductions in tropical Asia and America. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48(Suppl. 1):24–32
Gokbulut C, Boyacioglu M, Karademir U (2005) Plasma pharmacokinetics and faecal excretion of ivermectin (Eqvalan Reg.paste) and doramectin (Dectomax Reg., 1%) following oral administration in donkeys. Res Vet Sci 79:233–238
Gonzales JC, Muniz RA, Farias A, Goncalves LCB, Rew RS (1993) Therapeutic and persistent efficacy of doramectin against Boophilus microplus in cattle. Vet Parasitol 49:107–119
Hemaparasanth Ravinder Singh, Raghavendra A, Sridhar N, Raghunath MR, Eknath AE (2011) Comparative susceptibility of carp fingerlings to Lernaea cyprinacea infection. Vet Parasitol 178:156–162
Hemaprasanth KP, Raghavendra A, Singh R, Sridhar N, Raghunath MR (2008) Efficacy of doramectin against natural and experimental infections of Lernaea cyprinacea in carps. Vet Parasitol 156:261–269
Hoffman GL (1970) Intercontinental and transcontinental dissemination and transfaunation of fish parasites with emphasis on whirling disease (Myxosoma cerebralis). In: Snieszko SF (ed), A symposium on diseases of fish and shellfish. American Fisheries Society, Washington. Special Publication No. 5, pp 6–81
Iwama GK (1991) Interactions between aquaculture and the environment. Crit Rev Environ Control 21:177–216
Johannson N, Bergstrom E (1977) Transportation in tanks of two year old salmon (Salmo salar L.) as a predisposing factor for infection with Aeromonas hydrophila. Laxforsk Inst 3:1–12
Johnsen BO, Jensen AJ (1991) The gyrodactylus story in Norway. Aquaculture 98:289–302
Johnsen BO, Jensen AJ (1994) The spread of furunculous in salmonids in Norwegian rivers. J Fish Biol 45:47–55
Jones SRM (2009) Controlling salmon lice on farmed salmon and implications for wild salmon. CAB Rev Perspect Agric Vet Sci Nutr Nat Resour 4:1–13
Kent ML, Fournie W (1993) Importance of marine fish diseases—an overview. In: Couch JA, Fournie JW (eds) Pathobiology of marine estuarine organisms. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, pp 1–24
Koerting W (1990) Neue Fischarten—neue Fischkrankheiten. In: Proceedings of Vortragsveranstaltung des Wissenschaftlichen Beirates des DFV. 12–15 Sep 1990, Coburg, pp 110–123
Krueger CC, May B (1991) Ecological and genetic effects of salmonid introductions in North America. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48:66–77
Macedo DM, Chaaban A, Borja GEM (2005) Desenvolvimento pos-embrionario de Stomoxys calcitrans (Linnaeus, 1758) (Diptera: Muscidae) criadas em fezes de bovinos tratados com diferentes avermectinas. Rev Bras Parasitol 14:45–50
McMicheal GA, Pearson TN (1998) Effects of wild juvenile spring chinook salmon on growth and abundance of wild rainbow trout. Trans Am Fish Soc 127:261–274
Menon AGK (1999) Check list—freshwater fishes of India. Rec Zool Surv India Misc Publ Occas Pap No 175
Meyer FP, Warren JW, Carey TG (1983) A guide to integrated fish health management in the Great Lakes Basin, Great Lakes Fishery Commission. Special Publication No. 83-2, Ann Arbor
Morton A, Routledge RD, Williams R (2005) Temporal patterns of sea louse infestation on wild Pacific salmon in relation to the fallowing of Atlantic salmon farms. N Am J Fish Manage 25:811–821
Moya Borja GE, Muniz RA, Sanavria A, Goncalves LCB, Rew RS (1993) Therapeutic and persistent efficacy of doramectin against Dermatobia hominis in cattle. Vet Parasitol 49:85–93
Oliveira CMB, Muniz RA, Goncalves LCB, Oliveira LO (1993) Eficacia de doramectin contra infestacoes induzidas por Cochliomyia hominivorax (Coquerel, 1858) em bovinos do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 2:7–10
Peeler E, Thrush M, Paisley L, Rodgers C (2006) An assessment of the risk of spreading the fish parasite Gyrodactylus salaris to uninfected territories in the European Union with the movement of live Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) from coastal waters. Aquaculture 258:187–197
Perez JE, Graziani CA, Nirchio M (1997) Hasta cua do los exoticos! Acta Cient Venez 48:127–129
Raghavendra A, Hemaprasanth KP, Singh Ravinder, Sridhar N, Kumar V, Raghunath MR (2012) Ammonium chloride dip bath treatment as a quarantine measure to prevent spread of Lernaea cyprinacea infection during transfer of fish from affected ponds. J Fish Dis 36:243–247
Rema Devi KR, Ali A (2013) Hypselobarbus pulchellus. In: The IUCN red list of threatened species version 2014.3. www.iucnredlist.org. Accessed 03 Feb 2015
Robertson PAW, Austin B (1994) Disease associated with cyprinids imported into the United Kingdom. In: Proceedings of international symposium on aquatic animal health. 4–8 Sep 1994, Seattle, W-17.6
Scott ME, Smith GS (eds) (1994) Parasitic and infectious diseases. Epidemiology and ecology. Academic Press
Sridhar N, Raghunath MR, Hemaprasanth KP, Raghavendra CH, Eknath AE (2015) Induced breeding of threatened Indian medium carp Puntius pulchellus. Indian J Anim Sci 84:1334–1340
Stephen C, Iwama G (1997) Part C. Fish health. Salmon Aquaculture Review Technical advisory Team discussion papers. Volume 3, British Columbia Environmental Assessment Office, Victoria c1-c140
Stephen C, Ribble CS (2001) Death, disease and deformity: using outbreaks of disease in animals as sentinels for emerging environmental health risks. Glob Change Human Health 2:108–117
Stewart JE (1991) Introductions as factors in diseases of fish and aquatic invertebrates. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48:110–117
Vercruysse J (ed) (1993) Doramectin—a novel avermectin. Vet Parasitol 49:1–119
Wood JW (1979) Diseases of Pacific salmon: their prevention and treatment, 2nd edn. State of Washington Department of Fisheries, Hatchery Division, Olympia
Wootten R, Sommerville C, Bron J (1992) Sea lice and wild salmonids: including interaction between wild and farmed fish. In: Proceedings, conference of pathological conditions of wild salmonids. 6–8 May 1992, Aberdeen
Wurtsbaugh WA, Tapia RA (1988) Mass mortality of fishes in Lake Titicaca (Peru-Bolivia) associated with the protozoan parasite Ichthyophthirius multifilis. Trans Am Fish Soc 117:213–217
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Director, Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture, Bhubaneswar, India, for the facilities provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemaprasanth, K.P., Sridhar, N. & Raghuanth, M.R. Lernaea cyprinacea infection in a new host Puntius pulchellus in intensive culture system and its control by doramectin. J Parasit Dis 41, 120–127 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-016-0761-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-016-0761-x