Abstract
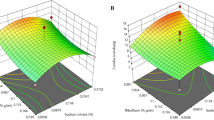
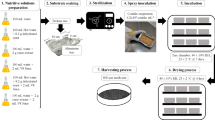
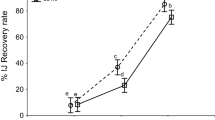
A new Beauveria bassiana isolate, showing high activity against Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae) adults (mortality—100.0 %), larvae (mortality—72.3 %) and pupae (Infection in emerged flies—96.7 %) was used. The isolate was subjected to a combinational approach towards selection of process parameters for its growth optimization. Initial screening of several carbon and nitrogen sources revealed glucose and NaNO3 as the most suitable source for optimal biomass and spore production. Further, optimization through Placket–Burman and a 25 full factorial central composite design revealed highly significant effect of glucose and pH. The optimum composition for maximum biomass yield was (g/l): glucose 28; NaNO3 2.43; KH2PO4 1.32; MgSO4 0.60; and pH 7.00. Glucose concentration showed almost linear relationship with biomass yield, indicating its significant contribution in medium composition for fungal growth. Highly significant interactions were observed between glucose and pH, followed by glucose and NaNO3 concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barson G, Renn N, Bywater AF (1994) Laboratory evaluation of six species of entomopathogenic fungi for the control of house fly (Musca domestica L.), a pest of intensive animal units. J Invertebr Pathol 64:107–113
Bhanu Prakash GVS, Padmaja V, Siva Kiran RR (2008) Statistical optimization of process variables for the large-scale production of Metarhizium anisopliae conidiospores in solid-state fermentation. Bioresour Technol 99:1530–1537
Campbell RK, Barnes GL, Cartwright BO, Eikenbary RD (1983) Growth and sporulation of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae in a basal medium containing various carbohydrate sources. J Invertebr Pathol 41:117–121
Carswell I, Spooner-Hart R, Milner RJ (1998) Laboratory susceptibility of Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae) and Bactrocera tryoni (Frogatt) (Diptera: Tephritidae) to an isolate of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) Sorokin. Aust J Entomol 37:281–284
Deacon JW (2006) A chemically defined liquid culture media for fungus. Fungal biology, 4th edn. Blackwell Publishing limited, Oxford
Fuguet R, The’raud M, Vey A (2004) Production in vitro of toxic macromolecules by strains of Beauveria bassiana, and purification of a chitosanase-like protein secreted by a melanizing isolate. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 138:149–161
Gao Li, Sun MH, Liu XZ, Yong CS (2007) Effects of carbon concentration and carbon to nitrogen ratio on the growth and sporulation of several biocontrol fungi. Mycol Res 111:87–92
Geden CJ, Rutz DA, Steinkraus DC (1995) Virulence of different isolates and formulation of Beauveria bessiana for house flies and the parasitoid Muscidifurax raptor. Biol Control 5:615–621
Gillespie AT (1984) The potential of entomogenous fungi to control glasshouse pests and brown plant hopper of rice. Ph.D. Thesis, Southampton University
Hallsworth JE, Magan N (1996) Culture, age, temperature and pH effect the polyol and trehalose contents of fungal propagules. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2435–2447
Humphreys AM, Matewele P, Trinci APJ, Gillespie AT (1989) Effects of water activity on morphology, growth and blastospore production of Metarhizium anisopliae, Beauveria bassiana and Paecilomyces farinosus in batch and fed-batch culture. Mycol Res 92:257–264
Jackson MA, Schisler DA (1992) The composition and attributes of Colletotrichum truncatum spores are altered by the nutritional environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2260–2265
Kant R, Pandey SD, Sharma SK (1996) Role of biological agents for the control of mosquito breeding in rice fields. Indian J Malariol 33:209–215
Kim S-W, Hwang H-J, Xu C-P, Sung J-M, Choi J-W, Yun J-W (2003) Optimization of submerged culture process for the production of mycelial biomass and exo-polysaccharides by Cordyceps militaris C738. J Appl Microbiol 94:120–126
Lecuona R, Turica M, Tarocco F, Crespo D (2005) Microbial control of Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) with entomopathogenic fungi. J Med Entomol 42:332–336
Lecuona R, Crespo D, Rossa FL (2007) Populational parameters of Spalangia endius walker (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) on Pupae of Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae) treated with two strains of Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuil. (Deuteromycetes). Neotrop Entomol 36(4):537–541
Li DP, Holdom DG (1995) Effects of nutrients on colony formation, growth, and sporulation of Metarhizium anisopliae (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes). J Invertebr Pathol 65:253–260
Mishra S, Kumar P, Malik A, Satya S (2011) Adulticidal and larvicidal activity of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae against housefly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae), in laboratory and simulated field bioassays. Parasitol Res 108:1483–1492
Mochi DA, Monteiro AC, Machado ACR, Yoshida L (2010) Efficiency of entomopathogenic fungi in the control of eggs and larvae of the horn fly Haematobia irritans (Diptera: Muscidae). Vet Parasitol 167:62–66
Mustafa U, Kaur G (2009) Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources and ratio on the germination, growth and sporulation characteristics of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana isolates. Afr J Agric Res 3:922–930
Rangel DEN, Anderson AJ, Roberts DW (2006) Growth of Metarhizium anisopliae on non-preferred carbon sources yields conidia with increased UV-B tolerance. J Invertebr Pathol 93:127–134
Rao YK, Lu S-C, Liu B-L, Tzeng Y-M (2006) Enhanced production of an extracellular protease from Beauveria bassiana by optimization of cultivation processes. Biochem Eng J 28:57–66
Sabu A, Keerthi TR, Kumar SR, Chandrasekaran M (2000) L-Glutaminase production by marine Beauveria sp. under solid state fermentation. Process Biochem 35:705–710
Safavi SA, Farooq AS, Aziz KP, Reza RG, Ali RB, Tariq MB (2007) Effect of nutrition on growth and virulence of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. FEMS Microbiol Lett 270:116–123
Siri A, Scorsetti AC, Dikgolz VE, Lopez Lastra CC (2005) Natural infection caused by the fungus Beauveria bassiana as a pathogen of Musca domestica in the neotropic. Biol Control 50:937–940
St. Leger RJ (1995) The role of cuticle-degrading proteases in fungal pathogens of insects. Can J Bot 73:1119–1125
Vega FE, Jackson MA, Mercadier G, Poprawski TJ (2003) The impact of nutrition on spore yields for various fungal entomopathogens in liquid culture. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:363–368
Watson DW, Geden CJ, Long SJ, Rutz DA (1995) Efficacy of Beaauveria bassiana for the controlling of the House fly and Stable fly (Diptera: Muscadiae). Biol Control 5:405–411
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Indian Council of Medical Research (IRIS_ID No. 2010-07860), India. CSIR fellowship to one of the authors (SM) is gratefully acknowledged. The authors acknowledge Mr. Peeyush Kumar (IIT Delhi, India) for his help in experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S., Malik, A. Nutritional optimization of a native Beauveria bassiana isolate (HQ917687) pathogenic to housefly, Musca domestica L.. J Parasit Dis 37, 199–207 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-012-0165-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-012-0165-5