Abstract
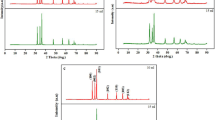
The synthesis of phyto-extract-assisted nanomaterials is very popularity as the process is simple and inexpensive. Euphorbia thymifolia L. belongs to family Euphorbiaceae and it is well-known herb species. The aim of the present research is a green synthesis of silica nanomaterials using the aqueous extract of E. thymifolia. The synthesized silica nanoparticles were characterized by Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometer, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), X-Ray diffraction analysis (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDAX), Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). These results confirmed the successful formation of nanoparticles, which are spherical and amorphous in nature. EDAX analysis determined the purity of the silica nanoparticles, which are composed of Si and O elements with no other impurities. XRD spectroscopy illustrates that characteristic diffraction peaks for silica nanoparticles were observed at 2ϴ range 20° corresponding to 101 planes. The average size of synthesized silica nanoparticles is 17 nm. The surface charge and stability of silica nanomaterials were analysed using dynamic light scattering (DLS), which revealed that the synthesized nanomaterials have a negative charge (-2.00 mV). The results obtained from this investigation confirm that the aqueous extract of E. thymifolia can play a vital role in the capping and stabilization of Tetra Ethyl Ortho Silicate to silica nanoparticles. In addition, the effect of bio-synthesized silica nanoparticles on the germination of Sorghum bicolor was determined, and it was concluded that silica nanoparticles improved the percentage of seed germination and that it would be useful for agricultural application.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable
References
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM (2016) Green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles mediated by Euphorbia thymifolia L. leaf extract: catalytic activity for cyanation of aryl iodides under ligand-free conditions. J Colloid Interface Sci 469:191–195
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Sajjadi M, Issaabadi Z, Atarod M (2019) An Introduction to Green Nanotechnology, Series Interface Science and Technology 28
Jadhav SA, Garud HB, Thoravat SS, Patil VS, Shinde PS, Burungale SH, Patil PS (2021) Synthesis and testing of functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for removal of Cr (VI) ions from water. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 11:8599–8607
Yu JH, Lee CW, Im SS, Lee JS (2003) Structure and magnetic properties of SiO2 coated Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized by chemical vapor condensation process. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02700020
San NO, Kurşungöz C, Tümtaş Y, Yaşa Ö, Ortac B, Tekinay T (2014) Novel one-step synthesis of silica nanoparticles from sugarbeet bagasse by laser ablation and their effects on the growth of freshwater algae culture. Particuology 17:29–35
Azlina HN, Hasnidawani JN, Norita H, Surip SN (2016) Synthesis of SiO2 nanostructures using sol-gel method. Acta Phys Pol A 129(4):842–844
Sharma D, Kanchi S, Bisetty K (2019) Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: a review. Arab J Chem 12(8):3576–3600
Rovani S, Santos JJ, Corio P, Fungaro DA (2018) Highly pure silica nanoparticles with high adsorption capacity obtained from sugarcane waste ash. ACS Omega 3(3):2618–2627
Rajiv P, Vanathi P, Thangamani A (2018) An investigation of phytotoxicity using Eichhornia mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles on Helianthus annuus. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 16:419–424
Vanathi P, Rajiv P, Sivaraj R (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Eichhornia-mediated copper oxide nanoparticles and assessing their antifungal activity against plant pathogens. Bull Mater Sci 39(5):1165–1170
Cuong HN, Pansambal S, Ghotekar S, Oza R, Hai NTT, Viet NM, Nguyen VH (2022) New frontiers in the plant extract mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles and their potential applications: A review. Environ Res 203:111858
Pansambal S, Oza R, Borgave S, Chauhan A, Bardapurkar P, Vyas S, Ghotekar S (2022) Bioengineered cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles and their diverse applications: a review. Applied Nanoscience, 1–26
Rajiv P, Manikandan R, Sangeetha S, Vanathi P, Dhanasekaran S (2022) Fabrication of Biogenic Iron Oxide and their Efficiency to Detect Carbofuran in vegetable samples. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 109649
Gopinath K, Gowri S, Karthika V, Arumugam A (2014) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from fruit extract of Terminalia arjuna, for the enhanced seed germination activity of Gloriosa superba. J Nanostructure Chem 4(3):1–11
Jegadeeswaran P, Rajiv P, Vanathi P, Rajeshwari S, Venckatesh R (2016) A novel green technology: synthesis and characterization of Ag/TiO2 nanocomposites using Padina tetrastromatica (seaweed) extract. Materials Letters 166:137–139
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Honarmand E, Maham M (2015) Preparation of palladium nanoparticles using Euphorbia thymifolia L. leaf extract and evaluation of catalytic activity in the ligand-free Stille and Hiyama cross-coupling reactions in water. N J Chem 39(6):4745–4752
Mali PY, Panchal SS (2013) A review on phyto-pharmacological potentials of Euphorbia thymifolia L. Anc Sci Life 32(3):165
Harborne AJ (1998) Phytochemical methods a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. Springer Science & Business Media
Maroušek J, Maroušková A, Periakaruppan R, Gokul GM, Anbukumaran A, Bohatá A, Kříž P, Bárta J, Černý P, Olšan P (2022) Silica nanoparticles from coir pith synthesized by acidic sol-gel method improve germination economics. Polymers 14(2):266
Singh B, Ahamad A, Pal V (2015) Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity and Phytochemical Screening of Azadirachta indica Leaves Extracts Against Staphylococcus aureus. UK J Pharm Biosci 3(4):43–47
Selvarajan V, Obuobi S, Ee PLR (2020) Silica nanoparticles—a versatile tool for the treatment of bacterial infections. Front Chem 8:602
Prabha S, Durgalakshmi D, Rajendran S, Lichtfouse E (2021) Plant-derived silica nanoparticles and composites for biosensors, bioimaging, drug delivery and supercapacitors: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(2):1667–1691
Karande SD, Jadhav SA, Garud HB, Kalantre VA, Burungale SH, Patil PS (2021) Green and sustainable synthesis of silica nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Environ Eng 6(2):29
Durairaj K, Senthilkumar P, Velmurugan P, Dhamodaran K, Kadirvelu K, Kumaran S (2019) Sol-gel mediated synthesis of silica nanoparticle from Bambusa vulgaris leaves and its environmental applications: kinetics and isotherms studies. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 90:653–664
Li Z, Mu Y, Peng C, Lavin MF, Shao H, Du Z (2021) Understanding the mechanisms of silica nanoparticles for nanomedicine. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology 13(1):e1658
Periakaruppan R, Manju Praveena S, Priya C, Ranjitha P, Gokul Raj S, Danaraj J (2022) Biosynthesis of silica nanoparticles using the leaf extract of punica granatum and assessment of its antibacterial activities against human pathogens. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 1–12
Sankareswaran M, Periakaruppan R, Sasivarnam M, Danaraj J, Dhanasekaran S, Abomughaid MM (2022) Bio-fabrication of bio-inspired silica nanomaterials from Bryophyllum pinnatum leaf for agricultural applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 1–12
Sankareswaran M, Vanitha M, Periakaruppan R, Anbukumaran A (2022) Phyllanthus emblica mediated silica nanomaterials: Biosynthesis, structural and stability analysis. Silicon 1–5
Uda MNA, Gopinath SC, Hashim U, Halim NH, Parmin NA, Afnan Uda MN, Anbu P (2021) Production and characterization of silica nanoparticles from fly ash: Conversion of agro-waste into resources. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 51(1):86–95
Rajendrachari S, Kumara Swamy BE (2020) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves of Acacia melanoxylon and their application as dopamine and hydrogen peroxide sensors. Phys Chem Res 8(1):1–18
Kumar R, Sharma P, Bamal A, Negi S, Chaudhary S (2017) A safe, efficient and environment friendly biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Leucaena leucocephala seed extract and its antioxidant, antimicrobial, antifungal activities and potential in sensing. Green Processes Synth 6(5):449–459
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PR: Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition and Project administration RDN: Investigation and Writing- Original draft preparation SAA: Data Curation PV: Data Curation SKJ: Investigation and Writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable
Consent to Participate
Not applicable
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Periakaruppan, R., N, R.D., Abed, S.A. et al. Production of Biogenic Silica Nanoparticles by Green Chemistry Approach and Assessment of their Physicochemical Properties and Effects on the Germination of Sorghum bicolor. Silicon 15, 4309–4316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02348-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02348-z