Abstract
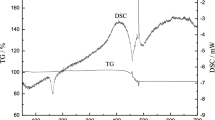
The present work investigates about the feasibility of polyethylene wax (PW) powder as a successful additive in the investment casting (IC) ceramic shell system for mainly, enhancing its porosity and permeability. This was achieved by modifying the usual secondary ceramic slurry with 4 wt% of PW powder to have secondary coats containing it. The experimental results affirmed that the PW powder modified shell displayed superior green flexural strength, porosity and permeability in contrast to the traditional shell system without any additives. But, a small decrease in fired flexural strength was observed, which is acceptable as ultimately ceramic shells are broken at the end to remove the casting from it. The tensile and impact strengths of the cast parts acquired from PW powder substituted shell were more by 9 and 30 % from that of the traditional shell system. Thus, it is ascertained that the cheaply and easily available PW powder can be a good substitute for improving the investment cast part’s mechanical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Pattnaik SR, Karunakar DB, Jha PK (2012) Developments in investment casting process- A review. J Mater Process Technol 212:2332–2348
Li Z, Liu X, Lv K (2019) Study on the strength of short carbon fiber-reinforced silicon sol shells for the investment casting process. Int J Metal cast. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00362-9
Clegg AJ (1991) Precision casting processes. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Pattnaik SR (2017) An investigation on enhancing ceramic shell properties using naturally available additives. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91:3061–3078
Beeley PR, Smart RF (1995) Investment Casting. Institute of Materials, London
Watts CH (1987) Investment casting method and stucco therefor. U.S. Patent No. 4,689,081
Pattnaik SR (2017) Influence of saw dust on the properties of the ceramic shell used in investment casting process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(1–4):691–707
Pattnaik S, Sutar MK (2021) Influence of ultra-sonic drilling on colloidal silica based ceramic moulds for investment casting. silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01166-5
Xu M, Qing J (2019) Effect of firing temperature and duration on fused silica investment shell strength at room temperature. Int J Metal cast 13:923–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00312-5
Li Y, Liu X, Lu K (2019) Preparation of fiber-reinforced shell by airflow placement fiber technology for investment casting. Int J Metal cast. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00323-2
Wang F, Li F, He B, Sun B (2014) Microstructure and strength of needle coke modified ceramic casting molds. Ceramics Int 40(1):479–486
Pattnaik SR, Karunakar DB, Jha PK (2014) Parametric optimization of the investment casting process using utility concept and Taguchi method. Proc Inst Mech Eng L 228(4):288–300
Pattnaik SR, Karunakar DB, Jha PK (2012) Influence of injection process parameters on dimensional stability of wax patterns made by the lost wax process using Taguchi approach. Proc Inst Mech Eng L 227(1):52–60
Sidhu BS, Kumar P, Mishra BK (2008) Effect of slurry composition on plate weight in ceramic shell investment casting. J Mater Eng Perform 17:489–498
Berger MB. The importance and testing of density / porosity / permeability / pore size for refractories, The Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy Refractories 2010 Conference, 101–116
Amira S, Dube D, Tremblay R (2011) Method to determine hot permeability and strength of ceramic shell moulds. J Mater Process Technol 211:1336–1340
Wang F, Zhu G, Li F (2018) Effect of needle coke on gas permeability of ceramic casting molds. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Sci) 23:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-018-2032-8
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Deptt. of Mechanical Engineering, VSSUT Burla, for providing support to write this journal article.
Funding
Authors are thankful to Bee Chems India Pvt. Ltd, Kanpur for supplying the slurry materials for constructing the ceramic shells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author has conducted the experimentation and the second author has done all editing of text and figures, and critically revised the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The present research work complies with ethical standard.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest for the present work.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
The authors give their consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pattnaik, S., Sutar, M.K. Investigation on the Influence of Polyethylene Wax Powder on the Characteristics of Ceramic Shells Used for Investment Casting. Silicon 14, 6089–6096 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01386-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01386-9