Abstract
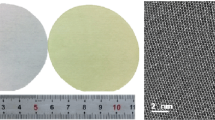
An experimental study on the surface texturization of diamond wire sawn multi-crystalline silicon (DWS mc-Si) wafers by acid vapor etching followed by acid solution post-treatment was carried out. The vapor composition, vapor etching time and the acid solution post-treatment time were optimized based on the surface morphology and reflectance measurement of DWS mc-Si wafers. It is found that acid vapor etching could effectively remove the sawn marks generated by surface cutting and produce micro-pits on the surface, which were the “start etching points” of subsequent acid solution texturization. The uniformity of the surface structure of silicon wafer was greatly improved by adjusting the proportion of acid vapor source, vapor etching time and subsequent solution processing time. An optimized average reflectance of 18.6 % between 400 nm and 1100 nm was achieved, which was expected to be used in the industrial production of high-efficiency solar cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Xiao ZG, Wei XQ, Yue ZH et al (2016) Morphology of etch-pits on HF-HNO3-H2O vapor etched diamond wire sawn multi-crystalline silicon wafers[J]. Semicond Sci Technol 31:115018
Liu XM, Li M, Chen WH et al (2014) The surface characteristics of diamond wire sawn Multicrystalline silicon wafers and their acidic texturization[J]. Acta Photon Sin 43(8):0816001
Wang SD, Chen TW (2018)Texturization of diamond-wire-sawnmulticrystalline silicon wafer using Cu, Ag, or Ag/Cuas a metal catalyst[J]. Appl Surf Sci 444:530–541
Fan Z, Cui D, Zhang Z et al (2021) Recent progress of black silicon: from fabrications to applications. Nanomaterials 11(1):41–45
Omar HD, Hashim R, Pakhuruddin MZ (2021)Surface morphological and optical properties of flexible black silicon fabricated by metal-assistedchemical etching. Opt Laser Technol 136:106765
Steglich M, Kaesebier T, Zilk M et al (2014)The structural and optical properties of black silicon by inductively coupled plasma reactive ion etching[J]. J Appl Phys 116(17):173503
Liu XM, Chen WH, Li M et al (2014)Vapor etching method for diamond wire sawn Multicrystalline silicon wafers[J]. Acta Photon Sin 43(11):26–29
Sun PY, Tsai PC, Liang PY et al (2020)Green scalable vapor texture etching for multicrystalline silicon wafers. Prog Photovolt 28(10):933–1000
Zheng CF, Shen HL, Pu T et al (2017)High-efficientsolar cells by the Ag/Cu-assistedchemical etching process on diamond-wire-sawnMulticrystalline silicon[J]. IEEE J Photovolt 7(1):153–156
Niu YC, Liu HT, Liu XJ et al (2016)Study on nano-poresenlargement during Ag-assistedelectroless etching of diamond wire sawn polycrystalline silicon wafers[J]. Mater Sci Semicond Process 56:119–126
Liu SY, Niu XW, Shan W et al (2014)Improvement of conversion efficiency of multicrystalline silicon solar cells by incorporating reactive ion etching texturing[J]. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 127(4):21–26
Ju M, Balaji N, Lee YJ et al (2012)Novel vapor texturing method for EFG silicon solar cell applications[J]. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 107(107):366–372
Kern W (1990)ChemInform abstract: the evolution of silicon wafer cleaning technology[J]. ChemInform 21(34):1887–1892
Acker J, Koschwitz T, Meinel B et al (2013)HF/HNO3etching of the saw damage[J]. Energy Procedia 38(38):223–233
Chen WH, Liu XM, Li M et al (2014)On the nature and removal of saw marks on diamond wire sawn multicrystalline silicon wafers[J]. Mater Sci Semicond Process 27(1):220–227
Xiao Z, Geng G, Wei X et al (2016)On the mechanism of the vapor etching of diamond wire sawn multi-crystallinesilicon wafers for texturing[J]. Mater Sci Semicond Process 53:8–12
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the special fund of Jiangsu province for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements, the open project of Key Laboratory of Materials Preparation and Protection for Harsh Environment, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and The Special Scientific Innovation Found of Sihong County for their financial support.
Funding
This work has been financially supported the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61774084), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NG2019003), the special fund of Jiangsu province for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements (BA2019047), the open project of Key Laboratory of Materials Preparation and Protection for Harsh Environment, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (XCA20013-3) and The Special Scientific Innovation Found of Sihong County (H201901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weitao Fan: Conceptualization, experimental investigation, writing;
Honglie Shen: resources, project administration;
Chunming Chen: experimental investigation;
Yanqi Li: software, formal analysis;
Shun Wang: data curation;
Xin Zhang: writing-review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for Publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Research involving human participants and/ or animals
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, W., Shen, H., Chen, C. et al. Texturization of Diamond Wire Sawn Mc-silicon by Acid Vapor Etching Followed by Acid Solution Post-treatment. Silicon 14, 4831–4838 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01272-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01272-4