Abstract
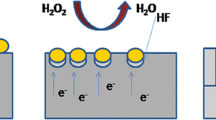
Herein, we prepare vertical and single crystalline silicon nanowires (SiNWs) via a one-step metal-assisted chemical etching method in aqueous NH4HF2/AgNO3 solution. The effects of silicon substrate resistivity and concentrations of NH4HF2 and AgNO3 on the etching process were examined. Two properties were studied, the morphology and the wettability of etched layers. The morphology of the silicon nanowire (SiNW) layers was investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) while the wettability was studied by contact angle measurement system. It was established that the morphology is strongly influenced by etching parameters and their wettability changes from superhydrophilic to hydrophobic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang Y, Duan XF, Cui Y, Lauhon LJ, Kim KH, Lieber CM (2001) Logic gates and computation from assembled nanowire building blocks. Science. 294:1313–1317
Ahn Y, Dunning J, Park J (2005) Scanning photocurrent imaging and electronic band studies in silicon nanowire field effect transistors. Nano Lett 5:1367–1370
Li QL, Koo SM, Edelstein MD, Suehle JS, Richter CA (2007) Silicon nanowire electromechanical switches for logic device application. Nanotechnology. 18:315202–315206
Koo SM, Li QL, Edelstein MD, Richter CA, Vogel EM (2005) Enhanced channel modulation in dual-gated silicon nanowire transistors. Nano Lett 5:2519–2523
Li Z, Chen Y, Li X, Kamins TI, Nauka K, Williams RS (2004) Sequence-specific label-free DNA sensors based on silicon nanowires. Nano Lett 4:245–247
Yang K, Wang H, Zou K, Zhang XH (2006) Gold nanoparticle modified silicon nanowires as biosensors. Nanotechnology. 17:S276–S279
Zheng GF, Patolsky F, Cui Y, Wang WU, Lieber CM (2005) Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat Biotechnol 23:1294–1301
Cui Y, Wei QQ, Park HK, Lieber CM (2001) Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science. 293:1289–1292
Peng KQ, Wang X, Lee ST (2009) Gas sensing properties of single crystalline porous silicon nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 95:243112–243114
Chan CK, Peng HL, Liu G, Mcllwrath K, Zhang XF, Huggins RA, Cui Y (2008) High-performance lithium battery anodes using silicon nanowires. Nat Nanotechnol 3:31–35
Peng KQ, Jie JS, Zhang WJ, Lee ST (2008) Silicon nanowires for rechargeable lithium-ion battery anodes. Appl Phys Lett 93:033105
Tian BZ, Zheng XL, Kempa TJ, Fang Y, Yu NF, Yu GH, Huang JL, Lieber CM (2007) Coaxial silicon nanowires as solar cells and nanoelectronic power sources. Nature. 449:885–889
Garnett EC, Yang PD, Am J (2008) Silicon nanowire radial p−n junction solar cells. Chem Soc 130:9224–9225
Peng KQ, Wang X, Lee ST (2008) Silicon nanowire array photoelectrochemical solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 92:163103
Huq SE, Chen L, Prewett PD (1995) Sub10nm silicon field emitters produced by electron beam lithography and isotropic plasma etching. Microelectron Eng 27:95–98
Kayes BM, Filler MA, Putnam MC, Kelzenberg MD, Lewis NS, Atwater HA (2007) Growth of vertically aligned Si wire arrays over large areas (>1cm2) with Au and Cu catalysts. Appl Phys Lett 91:103110–103113
Xu L, Li W, Xu J, Zhou J, Wu L, Zhang XG, Ma Z, Chen K (2009) Morphology control and electron field emission properties of high-ordered Si nanoarrays fabricated by modified nanosphere lithography. App Surf Sci 255:5414–5417
Hsu CM, Connor ST, Tang MX, Cui Y (2008) Wafer-scale silicon nanopillars and nanocones by Langmuir–Blodgett assembly and etching. Appl Phys Lett 93:133109–133111
Li X, Bohn PW (2000) Metal-assisted chemical etching in HF/H2O2 produces porous silicon. Appl Phys Lett 77:2572–2574
Peng KQ, Fang H, Hu JJ, Wu Y, Zhu J, Yan YJ, Lee S (2006) Metal-Particle-induced, highly localized site-specific etching of Si and formation of single-crystalline Si nanowires in aqueous fluoride solution. Chem-Eur J 12:7942–7947
Peng KQ, Fang H, Zhang XY, Xu Y, Zhu J (2005) Uniform, axial-orientation alignment of one-dimensional single-crystal silicon nanostructure arrays. Angew Chem Int Edn 44:2737–2742
Peng KQ, Hu JJ, Yan YJ, Wu Y, Fang H, Xu Y, Lee ST, Zhu J (2006) Fabrication of single-crystalline silicon nanowires by scratching a silicon surface with catalytic metal particles. Adv Funct Matter 16:387–394
Peng KQ, Lu AJ, Zhang RQ, Lee ST (2008) Motility of metal nanoparticles in silicon and induced anisotropic silicon etching. Adv Funct Matter 18:3026–3035
Zhang ML, Peng KQ, Fan X, Jie JS, Zhang RQ, Lee ST, Wang NB, Phys J (2008). Chem C 112:4444–4450
Peng K, Yan Y (2003) Gao. S, J. Zhu. Adv Funct Mater 13:127–132
Rahmani M, Andouni S, Zaibi MA, Meftah A (2020) Effect of etching duration on the morphological and opto-electrical properties of silicon nanowires obtained by Ag-assisted chemical etching. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00416-2
Madhavi K, Ghosh M, Rao GM, Suvarna RP (2020) Surface modification influenced properties of silicon nanowires grown by Ag assisted chemical etching with ECR hydrogen plasma treatment. J Mater Sci-Mater EL 31:1904–1911
Long W, Li H, Yang B, Huang N, Liu L, Gai Z, Jiang X (2020) Superhydrophobic diamond-coated Si nanowires for application of anti-biofouling’. J Mater Sci Technol 48:1–8
Ifires M, Hadjersi T, Chegroune R, Lamrani S, Fatsah M, Mebarki M, Manseri A, Alloys J (2019) One-step electrodeposition of superhydrophobic NiO-Co(OH)2 urchin-like structures on Si nanowires as photocatalyst for RhB degradation under visible light. Compd. 774:908–917
Brahiti N, Bouanik SA, Hadjersi T (2012) Metal-assisted electroless etching of silicon in aqueous NH4HF2 solution. Appl Surf Sci 258:5628–5637
Shibuichi S, Onda T, Satoh N, Tsujii K (1996). J Phys Chem 100:19152–19517
Coninck JD, de Ruijter MJ, Voué M (2001). Science. 6:49–53
Lafuma A, Quéré D (2003) Superhydrophobic states. Nat Mater 2:457–460
Erbil HY, Demirel AL, Avci Y, Mert O (2003) Transformation of a Simple Plastic into a Superhydrophobic Surface. Science. 299:1377–1380
Li XM, Reinhoudt D, Crego-Calama M (2007) What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent progress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem Soc Rev 36:1350–1368
Li Z, Meng F, Liu X (2011) Wettability control by DLC coated nanowire topography. Nanotechnology. 22:135302–135309
Naama S, Hadjersil T, Nezzal G, Guerbous L (2013). J Nano R 21:109–115
Megouda N, Hadjersi T, Piret G, Boukherroub R, Elkechai O (2013) Electroless chemical etching of silicon in aqueous NH4F/AgNO3/HNO3 solution. Appl Surf Sci 284:894–899
Feng L, Li S, Jiang L (2002) Super-hydrophobic surfaces: from natural to artificial. Adv Mater 14:1857–1860
Ren S, Yang S, Zhao Y, Yu T, Xiao X (2003) Preparation and characterization of an ultrahydrophobic surface based on a stearic acid self-assembled monolayer over polyethyleneimine thin films. Surf Sci 546:64–74
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C (1997) Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta. 202:1–8
Schmidt DL, Coburn CE, Benjamin MD (1994) Water-based non-stick hydrophobic coatings. Nature. 368:39–41
Shang H, Wang Y, Limmer LS (2005) Optically transparent superhydrophobic silica-based films. Thin Solid Films 472:37–43
Onda T, Shibuichi S, Satoh N, Tsujii K (1996) Super-water-repellent fractal surfaces. Langmuir. 12:2125–2127
Guo Z, Zhou F, Hao J, Liu W (2005) Stable biomimetic super-hydrophobic engineering materials. J Am Chem Soc 127:15670–15671
Xu Y, Wu D, Sun YH, Huang ZX, Jiang XD, Wei XF, Wei ZH, Dong BZ, Wu ZH (2005) Superhydrophobic antireflective silica films: fractal surfaces and laser-induced damage thresholds. Appl Opt 44:527–533
Li M, Zhai J, Liu H, Song YL, Jiang L, Zhu DB (2003) Electrochemical deposition of conductive superhydrophobic zinc oxide thin films. J Phys Chem B 107:9954–9957
Cassie A, Baxter S (1944) Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans Faraday Soc 40:546–551
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from General Direction of Scientific Research and of Technological Development of Algeria (DGRSDT/MESRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naama, S., Hadjersi, T., Larabi, A. et al. Effect of Silicon Wafer Resistivity on Morphology and Wettability of Silicon Nanowires Arrays. Silicon 13, 893–899 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00511-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00511-4