Abstract
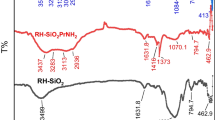
The silica-ortho-phenylenediamine(RHAOPDA) derived from Rice Husk Ash and o- phenylenediamine (OPDA) were synthesized. The prepared material was characterized by different techniques; N2- adsorption-desorption measurements of the synthesized material showed that the surface area for RHAOPDA is 25.10 m2 g−1 with a mean pore diameter of 15.10 nm. CHNS and FT-IR analyses proved that the o-phenylenediamine was successfully incorporated on modified silica RHACI. X-ray diffraction technique been showed the amorphous nature of RHAOPDA with maximum intensity at 22° (2θ), while the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) technique showed that the shapes of the particles resemble the fruit of the cauliflower with average particle size to be 22.62 nm. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA-DTA) of RHAOPDA indicated that the physically adsorbed water was lost between (30–150) °C which means it is weakly bonded in the silica- ortho-phenylenediamine, while the residual parts of material decomposed up to 820 °C. The RHAOPDA showed a high possibility for uptake and removal of Ni(II) ion from aqueous solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patil R, Dongre R, Meshram J (2014) Preparation of silica powder from rice husk. J Appl Chem 27:26–29
Hello KM, Mihsen HH, Mosa MJ (2014) Modification of silica with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazan-omethylphenol for monosaccharide productions. Iranian Journal of Catalysis 4:195–203
Seyfferth AL, Morris AH, Gill R, Kearns KA, Mann JN, Paukett M, Corey L (2016) Soil incorporation of silica-rich Rice husk decreases inorganic arsenic in Rice grain. J Agric Food Chem 64:3760–3766
De Souza MF, Magalhães WLE, Persegil MC (2002) Silica derived from burned rice hulls. Mater Res 5:467–474
Kamath SR, Proctor A (1998) Silica gel from rice hull ash: preparation and characterization. Cereal Chem 75:484–487
Della VP, Kühn I, Hotza D (2002) Rice husk ash as an alternate source for active silica production. Mater Lett 57:818–821
Sharma NK, Williams WS, Zangvil A (1984) Formation and structure of silicon carbide whiskers from rice hulls. J Am Ceram Soc 67:715–720
França AA, Schultz J, Borges R, Wypych F, Mangrich AS (2017) Rice husk ash as raw material for the synthesis of silicon and potassium slow-release fertilizer. J Braz Chem Soc 28:2211–2217
Adam F, Chew TS, Andas J (2011) A simple template-free sol–gel synthesis of spherical nanosilica from agricultural biomass. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 59:580–583
Al-Hasani TJ, Mihsen HH, Hello KM, Adam F (2017) Catalytic esterification via silica immobilized p-phenylenediamine and dithiooxamide solid catalysts. Arab J Chem 10:S1492–S1500
Hello KM, Mihsen HH, Mosa MJ, Magtoof MS (2015) Hydrolysis of cellulose over silica-salicylaldehyde phenylhydrazone catalyst. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 46:74–81
Franco DSP, Cunha JM, Dortzbacher GF, Dotto GL (2017) Adsorption of co (II) from aqueous solutions onto rice husk modified by ultrasound assisted and supercritical technologies. Process Saf Environ Prot 109:55–62
El-Ashgar NM, El-Nahhal IM, Chehimi MM, Babonneau F, Livage J (2009) Preparation of ethylenediaminetriacetic acid silica-gel immobilised ligand system and its application for trace metal analysis in aqueous samples. Int J Environ Anal Chem 89:1057–1069
Halim A, Alif Z, Yajid M, Azizi M, Hamdan H (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Rice husk ash derived - silica aerogel beads prepared by ambient pressure drying. Key Eng Mater 694:106–110
Lee JH, Kwon JH, Lee JW, Lee HS, Chang JH, Sang BI (2017) Preparation of high purity silica originated from rice husks by chemically removing metallic impurities. J Ind Eng Chem 50:79–85
Mihsen HH (2012) Synthesis and characterization of heterogeneous catalysts via silica obtained from Iraqi Rice husks. Ph.D. thesis, College of Science , Baghdad University
Adam F, Kandasamy K, Balakrishnan S (2006) Iron incorporated heterogeneous catalyst from rice husk ash. 304:137–143
El-Nahhal IM, El-Ashgar NM (2007) A review on polysiloxane-immobilized ligand systems: synthesis, characterization and applications. J Organomet Chem 692:2861–2886
Fang GZ, Tan J, Yan XP (2005) An ion-imprinted functionalized silica gel sorbent prepared by a surface imprinting technique combined with a sol-gel process for selective solid-phase extraction of cadmium(II). Anal Chem 77:1734–1739
El-Nahhal IM, El-Shetary BA, Salib KA, El-AshgarNM E-HA (2001) Uptake of divalent metal ions (Cu2+, Ni2+, and Co2+) by polysiloxane immobilized triamine-thiol and thiol-acetate ligand system. Anal Lett 34:2189–2202
Zaggout FR, El-Nahhal IM, El-Ashgar NM (2001) Uptake of divalent metal ions (Cu2+, Zn2+, and Cd2+) by polysiloxane immobilized diamine ligand system. Anal Lett 34:247–266
Dupont D, Brullot W, Bloemen M, Verbiest T, Binnemans K (2014) Selective uptake of rare earths from aqueous solutions by EDTA-functionalized magnetic and nonmagnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:4980–4988
Adam F, Chua J-H (2004) The adsorption of palmytic acid on rice husk ash chemically modified with Al (III) ion using the sol–gel technique. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:55–61
Ahmed AE, Adam F (2007) Indium incorporated silica from rice husk and its catalytic activity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 103(103):284–295
Vaisman I (2018) Rice hulls as a renewable complex material resource, pp 1–11
Adam F, Osman H, Hello KM (2009) The immobilization of 3- ( chloropropyl ) triethoxysilane onto silica by a simple one-pot synthesis. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:143–147
Mihsen HH, Sobh HS (2018) Preparation and characterization of Thiourea-silica hybrid as Heterogenous catalyst. Asian J Chem 30:937–943
Mureseanu M, Reiss A, Stefanescu I, David E, Parvulescu V, Renard G, Hulea V (2008) Chemosphere modified SBA-15 mesoporous silica for heavy metal ions remediation. Chemosphere 73:1499–1504
Adam F, Hello KM, Osman H (2010) The heterogenation of melamine and its catalytic activity. Appl Catal A Gen 382:115–121
Silverstein RM, Bassler GC (1962) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. J Chem Educ 39:546
Kuila U, Prasad M (2013) Specific surface area and pore-size distribution in clays and shales. Geophys Prospect 61:341–362
El-Nahhal IM, Zaggout FR, Nizam M (2000) Uptake of divalent metal ions ( cu , Zn and cd ) by Polysiloxane immobilized monoamine ligand system. Anal Lett 33(10):2031–2053
Mahmoud ME (2012) Comparison of metal uptake properties of silica gel-bound ion exchangers and some amine derivatives. Anal Lett 29:1791–1804
Acknowledgments
The authors of the research paper would like to thank Kerbala University, College of Science, Department of Chemistry for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, S.K., Hassan, Z.M., Mihsen, H.H. et al. Uptake of Nickel(II) Ion by Silica-o-Phenylenediamine Derived from Rice Husk Ash. Silicon 12, 1103–1110 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00207-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00207-4