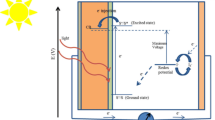
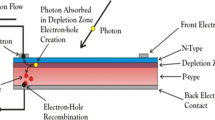
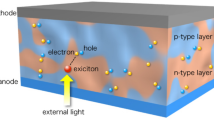
Abstract
As a high potential renewable power source, solar energy is becoming one of the most important energies of the future. Recently, there has been an enormous increase in the understanding of the operational principle of photovoltaic devices, which has led to a rapid increase in the power conversion efficiencies of such devices. Solar cells vary under temperature changes; the change in temperature will affect the power output from the cells. This paper discusses the effect of light intensity and temperature on the performance parameters of monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon solar devices. In this paper, the performance and overview use of solar cells is expressed. The role of temperature on the electric parameters of solar cells has been studied. The experimental results show that all electrical parameters of the solar cells, such as maximum output power, open circuit voltage, short circuit current, and fill factor, have changed with temperature variation. Solar cell performance decreases with increasing temperature, fundamentally owing to increased internal carrier recombination rates caused by increased carrier concentrations. The operating temperature plays a key role in the photovoltaic conversion process. Both the electrical efficiency and the power output of a photovoltaic (PV) module depend linearly upon the operating temperature. Solar cells vary under temperature changes; the change in temperature will affect the power output from the cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffith JS, Rathod NS, Paslaski J (1981) Some tests of flat plate photovoltaic module cell temperatures in simulated field conditions. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE photovoltaic specialists conference, Kissimmee, FL, pp 822–30
Tripanagnostopoulos Y, Nousia Th, Souliotis M, Yianoulis P (2002) Hybrid photovoltaic/thermal solar systems. Sol Energy 72(3):217–34
Ji J, Chow TT, He W (2003) Dynamic performance of hybrid photovoltaic/thermal collector wall in Hong Kong. Build Environ 38:1327–34
Affolter P, Haller A, Ruoss D, Toggweiler P (2000) A new generation of hybrid solar collectors absorption and high temperature behaviour evaluation of amorphous modules. In: Proceedings of the 16th european photovoltaic solar energy conference, Glasgow, UK
New generation of hybrid solar PV/t collectors. Report DIS 56360/16868, 2000
Platz R, Fischer D, Zufferey MA, Anna Selvan JA, Haller A, Shah A (1997) Hybrid collectors using thin-film technology. In: Proceedings of the 26th photovoltaic specialists conference, Anaheim, CA
Zondag HA, De Vries DW, Van Helden WGJ, Van Zolingen RJC, Van Steenhoven AA (2003) The yield of different combined PVthermal collector designs. Sol Energy 253(69):74
Chow TT (2003) Performance analysis of PVT collector by explicit dynamic model. Sol Energy 75:143–52
Naveed AT, Kang EC, Lee EJ (2006) Effect of unglazed transpired collector on the performance of a polycrystalline silicon photovoltaic module. J Sol Energy Eng 128:349–53
Krauter SCW, Ochs F (2003) An integrated solar home system history. In: Proceedings of the third WCPEC, Osaka
Krauter SCW (2004) Development of an integrated solar home system. SEMS 82:119–30
Krauter SCW (2004) Enhanced integrated solar home system. In: Proceedings of the 19th European photovoltaic solar energy conference, Paris
Nishioka K, Sakitani N, Uraoka Y, Fuyuki T (2007) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 91:1222
Mazhari B (2006) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:1021
Wolf M, Rauschenbach H (1963) Adv Energy Convers 3:455
Handy RJ (1967) Solid State Electron 10:765
Pysch D, Mette A, Glunz SW (2007) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 91:1698
Hussein R, Borchert D, Grabosch G, Fahrner WR (2016) 2001 Sol. Energy. Mater. Sol. 3rd euro-mediterranean conference on materials and renewable energies (EMCMRE-3)IOP publishing journal of physics: conference series 758
Radziemska E (2005) Energy. Convers Manage 46:1485
Rajkanan K, Shewchun J (1979) Solid-State Electron 22:193
Servaites JD, Yeganeh S, Marks TJ, Ratner MA (2010) Adv Funct Mater 20:97
Mialhe P, Khoury A, Charles JP (1984) Phys Status Solidi (a) 83:403
Singh P (2008) Temperature dependence of I–V characteristics and performance parameters of silicon solar cell. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 92(12):1611–1616
Singh P, Ravindra NM (2012) Temperature dependence of solar cell performance—an analysis. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 101:36–45
Sze SM (1981) Physics of semiconductor devices. Wiley, New York, p 264 (Chapter14)
Landis G, Rafaelle R, Merritt D (2004) High temperature solar cell development. In: 19th European photovoltaic science and engineering conference, Paris, France
Wysocki JJ, Rappaport P (1960) Effect of temperature on photovoltaic solar energy conversion. J Appl Phys 31:571– 578
Fan JCC (1986) Theoretical temperature dependence of solar cell parameters. Solar Cells 17:309–315
Singh P, Singh SN, Lal M, Husain M (2008) Temperature dependence of I–V characteristics and performance parameters of silicon solar cell. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 92:1611– 1616
Friedman DJ (1996) Modeling of tandem cell temperature coefficients. In: 25th IEEE photovoltaic specialists conference, Washington DC. IEEE, New York, pp 89–92
Contreras MA, Nakada T, Pudov AO, Sites R (2003) ZnO/ZnS(O, OH)/Cu(In, Ga)Se2/ Mo solar cell with 18.6% efficiency. In: Proceedings of the third world conference of photovoltaic energy conversion, pp 570–573
Jeng MJ, Lee YL, Chang LB (2009) Temperature dependences of lnxga1_xn multiple quantum well solar cells. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:105101, 6
Vandewal K, Tvingstedt K, Gadisa A, Inganas O, Manca JV (2010) Relating the open-circuit voltage to interface molecular properties of donor: acceptor bulk heterojunction solar cells. Phys Rev B 81:125204
Koster LJA, Mihailetchi VD, Blom PWM (2006) Ultimate efficiency of polymer/ fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 88:093511
Dennler G, Scharber MC, Brabec CJ (2009) Polymer–fullerene bulk-heterojunction solar cells. Adv Mater 21:1323–1338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, A.A.E., Al-Maghrabi, M.A. The Analysis of Temperature Effect for mc-Si Photovoltaic Cells Performance. Silicon 10, 1551–1555 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9639-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9639-5