Abstract
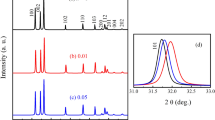
ZnO nanoparticles with hexagonal wurtzite structure were synthesized by using microwave irradiation. The effects of annealing temperatures on the structural, surface morphology and dielectric properties of annealed ZnO nanoparticles were investigated by XRD, FTIR spectra, and dielectric measurements. The XRD reveals the presence of hexagonal wurtzite structure of ZnO average grain size 25.7–36.4 nm. The spectra obtained from FTIR containing two intense absorption bands are attributed to bending and stretching vibrations absorption of Zn–O bond for all annealed ZnO nanoparticles. Dielectric properties of annealed ZnO nanoparticles at different temperatures were studied with respect to frequency. The dielectric measurements reveal that the dielectric response of ZnO nanoparticles is significantly enhanced, especially in the low-frequency range. In conclusion, both the rotation direction polarization and space charge polarization due to a large amount of oxygen vacancies and nano-size effects are responsible for the enhancement of the dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu S, Wang ZL (2011) One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res 4(11):1013–1098
Govender K, Boyle DS, O’Brien P, Binks D, West D, Coleman D (2002) Roomtemperature lasing observed from ZnO nanocolumns grown by aqueous solution deposition. Adv Mater 14:1221–1224
Park WI, Yi GC (2004) Electroluminescence in n-ZnO nanorod arrays vertically grown on p-GaN. Adv Mater 16:87–90
Mao DS, Wang X, Li W, Liu XH, Li Q, Xu JF (2002) Electron field emission from hydrogen-free amorphous carbon-coated ZnO tip array. J Vac Sci Technol B 20:278–281
Wang WZ, Zeng BQ, Yang J, Poudel B, Huang JY, Naughton MJ, Ren ZF (2006) Aligned ultralong ZnO nanobelts and their enhanced field emission. Adv Mater 18:3275–3278
Wei TY, Yeh PH, Lu SY, Wang ZL (2009) Gigantic enhancement in sensitivity using Schottky contacted nanowire nanosensor. J Am Chem Soc 131:17690–17695
Al-Assiri MS, Mostafa MM, Ali MA, El Desoky MM (2016) Structural and gas sensing properties of annealed ZnO thin film. Silicon 8:361–367
Law M, Greene LE, Johnson JC, Saykally R, Yang PD (2005) Nanowire dyesensitized solar cells. Nature Mater 4:455–459
Wei YG, Xu C, Xu S, Li C, Wu WZ, Wang ZL (2010) Planar waveguide-nanowire integrated three-dimensional dyesensitized solar cells. Nano Lett 10:2092–2096
Rabenau A (1985) The role of hydrothermal synthesis in preparative chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 24:1026–1040
Huang J, Matsunaga N, Shimanoe K, Yamazoe N, Kunitake T (2005) Nanotubular SnO2 templated by cellulose fibers: synthesis and gas sensing. Chem Mater 17:3513–3518
Yadav A, Prasad V, Kathe A, Raj S, Yadav D, Sundaramoorthy C, Vigneshwaran N (2006) Functional finishing in cotton fabrics using ZnO nanoparticles. Bull Mater Sci 29:641–645
Izu N, Murayama N, Shin W, Itoh T, Matsubara I (2008) Preparation of SnO2 nanoparticles less than 10 nm in size by precipitation using hydrophilic carbon black powder. Mater Lett 62-2:313–316
Liu Y, Zheng C, Wang W, Yin C, Wang G (2001) Production of SnO2 nanorods by redox reaction. Adv Mater 13:1883–1887
Liu YK, Zheng CL, Wang WZ, Zhan YJ, Wang GG (2001) Production of SnO2 nanorods by redox reaction. J Cryst Growth 233:8–12
Xu CK, Xu GD, Liu YK, Zhao XL, Wang GH (2002) Preparation and characterization of SnO2 nanorods by thermal decomposition of SnC2O4 precursor. Scripta Mater 46:789–792
El-Desoky MM, Ali MA, Afifi G, Imam H (2014) Annealing effects on the structural and optical properties of growth ZnO thin films fabricated by pulsed laser deposition (PLD). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25:5071–5077
Wang H, Xu JZ, Zhu JJ., Chen HY (2002) Preparation of CuO nanoparticles by microwave irradiation. J Cryst Growth 244:88–94
Kapustianyk V, Eliyashevskyy Y, Turkoa B, Czapla Z, Dacko S, Barwinski B (2012) Influence of technological factors on conductivity and dielectric dispersion in ZnO nanocrystalline thin films. J Alloy Compounds 531:64–69
Al-Assiri MS, Mostafa MM, Ali MA, El Desoky MM (2015) Optical properties of annealed ZnO thin films fabricated by pulsed laser deposition. Silicon 7:393–400
Al-Assiri MS, Mostafa MM, Ali MA, El Desoky MM (2014) Synthesis, structural and electrical properties of annealed ZnO thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition (PLD). Superlattice Microst 75:127–135
Ghosh D, Saha Sardar P, Biswas M, Mondal A, Mukherjee N (2010) Dielectric characteristics of poly(N-vinylcarbazole) and its nanocomposites with ZnO and acetylene black. Mater Chem Phys 123:9–12
Wei XQ, Zhang Z, Yu YX, Man BY (2009) Comparative study on structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by PLD using ZnO powder target and ceramic target. Optics, Laser Technology 41:530–534
Faal Hamedani N, Farzaneh F (2006) Synthesis of ZnO nanocrystals with hexagonal (Wurtzite) structure in water using microwave irradiation. Journal of Sciences, Islamic Republic of Iran 17:231–234
EwaMarkiewicz AK-R, Jesionowski T (2012) Structural characterisation of ZnO particles obtained by the emulsion precipitation method. J Nanomater 2012:9
Ramo S, Winnery J, Van Duzer T (1965) Fields and waves in communication electronics, first ed. Wiley, New York
Lanje AS., Sharma SJ, Ningthoujam RS, Ahn J-S, Pode RB (2013) Low temperature dielectric studies of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles prepared by precipitation method. Adv Powder Technol 24:331–335
Kapustianyka V, Eliyashevskyya Y, Turkoa B, Czaplab ZC, Dackob S, Barwinski B (2012) Influence of technological factors on conductivity and dielectric dispersion in ZnO nanocrystalline thin films. J Alloys Compd 531:64–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Desoky, M.M., Ali, M.A., Afifi, G. et al. Effects of Annealing Temperatures on the Structural and Dielectric Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. Silicon 10, 301–307 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9445-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9445-5