Abstract
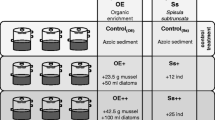
The influence of an addition of either sand and/or spring-bloom algae on the efflux of nutrients from intact sediment cores from the Baltic Sea was studied in a flow-through experiment. The addition of sand significantly increased the efflux of silicon (Si) from sediment, but the algal addition did not. The effects on phosphorus (P) were not as clear, and fluxes of nitrogen (NH4 and NO2 + 3) remained relatively unaffected by the additions. The small effect of the algal addition was caused by the short time-period covered by the experiment and possibly by adsorption of released Si by the sediment. A follow-up bottle experiment showed that despite the apparently lower content of easily available Si and biogenic silica, BSi, in the sand, the sand-induced Si efflux was caused by release of Si from the sand itself, rather than by indirectly increasing the dissolution of BSi present in the sediment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hecky R, Mopper K, Kilham P, Degens E (1973) The amino acid and sugar composition of diatom cell walls. Mar Biol 19:323–331
Hurd D (1983) Physical and chemical properties of siliceous skeletons. In: Aston S (ed) Silicon geochemistry and biogeochemistry. Academic Press, London, pp 187–244
Lewin J (1961) The dissolution of silica from diatom walls. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 21:182–198
Tréguer P, Pondaven P (2000) Silica control of carbon dioxide. Nature 406:358–359
Smetacek V (1980) Annual cycling of sedimentation in relation to plankton ecology in western Kiel Bight. Ophelia Suppl 1:65–76
Ragueneau O, Chavaud L, Leynaert A, Thozeau G, Paulet Y-M, Bonnet S, Lorrain A, Grall J, Corvaisier R, Le Hir M, Jean F, Clavier J (2002) Direct evidence of a biologically active coastal silicate pump: ecological implications. Limnol Oceanogr 47:1849–54
Lerman A (1988) Weathering rates and major transport processes: an introduction. In: Lerman A, Meybeck M (eds) Physical and chemical weathering in geochemical cycles. Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp 1–10
Hingston FJ, Atkinson RJ, Posner AM, Quirk JP (1967) Specific adsorption of anions. Nature 215:1459–1461
Golterman HL (1975) Physiological limnology. An approach to the physiology of lake ecosystems. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, pp 124–133
Sommer M, Kaczorek D, Kuzyakov Y, Breuer J (2006) Silicon pools and fluxes in soils and landscapes: a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169:294–314
Gehlen M, Van Raaphorst W (1993) Early diagenesis of silica in sandy North Sea sediments: quantification of the solid phase. Mar Chem 42:71–83
Gehlen M, Van Raaphorst W (2002) The role of adsorption-desorption reactions in controlling interstitial Si(OH)4 concentrations and enhancing Si(OH)4 turn-over in shallow shelf areas. Cont Shelf Res 22:1529–47
Emery KO (1968) Relict sediments on continental shelves of the world. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 52:445–464
Ehrenhauss S, Huettel M (2004) Advective transport and decomposition of chain-forming planktonic diatoms in permeable sediments. J Sea Res 52:179–197
Ehrenhauss S, Witte U, Buhring SI, Huettel M (2004) Effect of advective pore water transport on distribution and degradation of diatoms in permeable North Sea sediments. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 271:99–111
Koroleff F (1983) In: Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (eds) Methods of seawater analysis. Verlag Chimie, Weinheim
Nielsen LP (1992) Denitrification in sediment determined from nitrogen isotope pairing. FEMS Microbiol Lett 86: 357–362
DeMaster D (1981) The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:1715–1732
Mullin J, Riley J (1955) The colorimetric determination of silicate with special reference to sea and natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 12:162–176
Lignell R, Heiskanen AS, Kuosa H, Gundersen K, Kuuppo-Leinikki P, Pajuniemi R, Uitto A (1993) Fate of a phytoplankton spring bloom—sedimentation and carbon flow in the planktonic food web in the northern Baltic. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 94:239–252
Conley D J, Johnstone RW (1995) Biogeochemistry of N, P and Si in Baltic Sea sediments—response to a simulated deposition of a spring diatom bloom. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 122: 265–276
Heiskanen AS, Tallberg P (1999) Sedimentation and particulate nutrient dynamics along a coastal gradient from a Fjord-like bay to the open sea. Hydrobiologia 393:127–140
Conley DJ, Kilham SS, Theriot E (1989) Differences in silica content between marine and fresh-water diatoms. Limnol Oceanogr 34:205–213
Tallberg P, Lehtoranta J (2005) Changes in phosphorus and silicon fluxes and pools at the sediment surface following an experimental spring bloom deposition. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 29:528–530
Azam F, Chisholm S (1976) Silicic acid uptake and incorporation by natural marine phytoplankton populations. Limnol Oceanogr 21:427–435
Brzezinski M, Nelson D (1989) Seasonal-changes in the silicon cycle within a gulf-stream warm-core ring. Deep-Sea Res Part A, Oceanogr Res Pap 36:1009–1030
Kelderman P, Lindeboom H, Klein J (1988) Light dependent sediment-water exchange of dissolved reactive phosphorus and silicon in a producing microflora mat. Hydrobiologia 159:137–147
Srithongouthai S, Sonoyama Y-I, Tada K, Montani S (2003) The influence of environmental variability on silicate exchange rates between sediment and water in a shallow-water coastal ecosystem, the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Mar Pollut Bull 47:10–17
Tallberg P, Lukkari K, Räike A, Lehtoranta J, Leivuori M (2009) Applicability of a sequential P fractionation procedure to Si in sediment. J Soil Sed 9:594–603
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tallberg, P., Lehtoranta, J. & Hietanen, S. Silicate Release from Sand-Manipulated Sediment Cores: Biogenic or Adsorbed Si?. Silicon 5, 67–74 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9127-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9127-x