Abstract
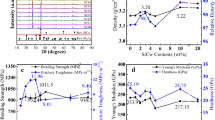
SiC nanowires are excellent high-temperature electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorbing materials. However, their polymer matrix composites are difficult to work at temperatures above 300°C, while their ceramic matrix composites must be prepared above 1000°C in an inert atmosphere. Thus, for addressing the abovementioned problems, SiC/low-melting-point glass composites were well designed and prepared at 580°C in an air atmosphere. Based on the X-ray diffraction results, SiC nanowires were not oxidized during air atmosphere sintering because of the low sintering temperature. Additionally, SiC nanowires were uniformly distributed in the glass matrix material. The composites exhibited good mechanical and EMW absorption properties. As the filling ratio of SiC nanowires increased from 5wt% to 20wt%, the Vickers hardness and flexural strength of the composite reached HV 564 and 213 MPa, which were improved by 27.7% and 72.8%, respectively, compared with the low-melting-point glass. Meanwhile, the dielectric loss and EMW absorption ability of SiC nanowires at 8.2–12.4 GHz were also gradually improved. The dielectric loss ability of low-melting-point glass was close to 0. However, when the filling ratio of SiC nanowires was 20wt%, the composite showed a minimum reflection loss (RL) of −20.2 dB and an effective absorption (RL ≤ −10 dB) bandwidth of 2.3 GHz at an absorber layer thickness of 2.3 mm. The synergistic effect of polarization loss and conductivity loss in SiC nanowires was responsible for this improvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.G. Gao, K. Yang, Z.H. Zhao, et al., Design principles in MOF-derived electromagnetic wave absorption materials: Review and perspective, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 30(2023), No. 3, p. 405.
S.J. Zhang, J.Y. Li, X.T. Jin, and G.L. Wu, Current advances of transition metal dichalcogenides in electromagnetic wave absorption: A brief review, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 30(2023), No. 3, p. 428.
Z.Z. Shen, J.H. Chen, B. Li, G.Q. Li, Z.J. Zhang, and X.M. Hou, Recent progress in SiC nanowires as electromagnetic microwaves absorbing materials, J. Alloys Compd., 815(2020), art. No. 152388.
P. Feng, H.J. Wei, P. Shang, et al., Enhanced electromagnetic microwave absorption of SiC nanowire-reinforced PDC-SiC ceramics catalysed by rare earth, Ceram. Int., 48(2022), No. 17, p. 24915.
Y.T. Fan, D. Yang, H. Mei, et al., Tuning SiC nanowires interphase to improve the mechanical and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of SiCf/SiCnw/Si3N4 composites, J. Alloys Compd., 896(2022), art. No. 163017.
P. Zhou, J.H. Chen, M. Liu, P. Jiang, B. Li, and X.M. Hou, Microwave absorption properties of SiC@SiO2@Fe3O4 hybrids in the 2–18 GHz range, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 24(2017), No. 7, p. 804.
C.C. Dang, Q. Mu, X.B. Xie, et al., Recent progress in cathode catalyst for nonaqueous lithium oxygen batteries: A review, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 5(2022), No. 2, p. 606.
R. Zhang, C.P. Mu, B.C. Wang, et al., Composites of In/C hexagonal nanorods and graphene nanosheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 30(2023), No. 3, p. 485.
S.P. Wang, Z.Y. Liu, Q.C. Liu, et al., Promoting the microwave absorption performance of hierarchical CF@NiO/Ni composites via phase and morphology evolution, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 30(2023), No. 3, p. 494.
H. Gao, F. Luo, Q.L. Wen, Y.C. Qing, and W.C. Zhou, Effect of preparation conditions on mechanical, dielectric and microwave absorption properties of SiC fiber/mullite matrix composite, Ceram. Int., 45(2019), No. 9, p. 11625.
Q. Zhou, X.W. Yin, F. Ye, Z.M. Tang, R. Mo, and L.F. Cheng, High temperature electromagnetic wave absorption properties of SiCf/Si3N4 composite induced by different SiC fibers, Ceram. Int., 45(2019), No. 5, p. 6514.
Z.W. Ren, W.C. Zhou, Y.C. Qing, et al., Effect of different kinds of SiC fibers on microwave absorption and mechanical properties of SiCf/SiC composites, J. Mater. Sci., 32(2021), No. 21, p. 25668.
X.Y. Lv, F. Ye, L.F. Cheng, and L.T. Zhang, 3D printing “wire-on-sphere” hierarchical SiC nanowires/SiC whiskers foam for efficient high-temperature electromagnetic wave absorption, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 109(2022), p. 94.
K. Su, Y. Wang, K.X. Hu, et al., Ultralight and high-strength SiCnw@SiC foam with highly efficient microwave absorption and heat insulation properties, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 13(2021), No. 18, p. 22017.
T. Han, R.Y. Luo, G.Y. Cui, and L.Y. Wang, Effect of SiC nanowires on the high-temperature microwave absorption properties of SiCf/SiC composites, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 39(2019), No. 5, p. 1743.
B. Du, C. He, A.Z. Shui, X.H. Zhang, and C.Q. Hong, Microwave-absorption properties of heterostructural SiC nanowires/SiOC ceramic derived from polysiloxane, Ceram. Int., 45(2019), No. 1, p. 1208.
Y.P. Dong, X.M. Fan, H.J. Wei, et al., Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of a novel SiC nanowires reinforced SiO2/3Al2O3·2SiO2 porous ceramic, Ceram. Int., 46(2020), No. 14, p. 22474.
X.L. Lan, Y.B. Li, and Z.J. Wang, High-temperature electromagnetic wave absorption, mechanical and thermal insulation properties of in situ grown SiC on porous SiC skeleton, Chem. Eng. J., 397(2020), art. No. 125250.
J.J. Qian, A.Z. Shui, C. He, et al., Multifunction properties of SiOC reinforced with carbon fiber and in situ SiC nanowires, Ceram. Int., 47(2021), No. 6, p. 8004.
X. Li, X.K. Lu, M.H. Li, et al., A SiC nanowires/Ba0.75 Sr0.25Al2Si2O8 ceramic heterojunction for stable electromagnetic absorption under variable-temperature, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 125(2022), p. 29.
L. Xia, X.Y. Zhang, Y.N. Yang, et al., Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of laminated SiCNW−Cf/lithium–aluminum–silicate (LAS) composites, J. Alloys Compd., 748(2018), p. 154.
W.B. Li, M.H. Chen, M.Y. Wu, S.L. Zhu, C. Wang, and F.H. Wang, Microstructure and oxidation behavior of a SiC−Al2O3–glass composite coating on Ti−47Al−2Cr−2Nb alloy, Corros. Sci., 87(2014), p. 179.
L. Zhang, S.Q. Yang, M.H. Xiao, et al., Influence of silicon carbide nanowires on the properties of Bi−B−Si−Zn−Al glass based low temperature co-fired ceramics, Ceram. Int., 48(2022), No. 17, p. 25382.
S.H.N. Doo, W.B. Lim, J.S. Lee, C.S. Han, Y.S. Cho, and C.G. Yoo, Silicon carbide whisker-reinforced ceramic tape for high-power components, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 11(2014), No. 2, p. 240.
Y.M. Feng, L. Xia, C.H. Ding, et al., Boosted multi-polarization from silicate-glass@rGO doped with modifier cations for superior microwave absorption, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 593(2021), p. 96.
Y.M. Feng, C.Z. Du, D.X. Meng, et al., Aluminosilicate glass–ceramics/reduced graphene oxide composites doped with lithium ions: The microstructure evolution and tuning for target microwave absorption, Ceram. Int., 48(2022), No. 2, p. 2717.
J.L. Kuang and W.B. Cao, Oxidation behavior of SiC whiskers at 600–1400°C in air, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 97(2014), No. 9, p. 2698.
Q.G. Fu, H. Peng, X.Y. Nan, H.J. Li, and Y.H. Chu, Effect of SiC nanowires on the thermal shock resistance of joint between carbon/carbon composites and Li2O−Al2O3−SiO2 glass ceramics, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 34(2014), No. 10, p. 2535.
Q.G. Fu, B.L. Jia, H.J. Li, K.Z. Li, and Y.H. Chu, SiC nanowires reinforced MAS joint of SiC coated carbon/carbon composites to LAS glass ceramics, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 532(2012), p. 255.
J.L. Kuang and W.B. Cao, Silicon carbide whiskers: Preparation and high dielectric permittivity, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 96(2013), No. 9, p. 2877.
L. Long, J.X. Xu, H. Luo, P. Xiao, W. Zhou, and Y. Li, Dielectric response and electromagnetic wave absorption of novel macroporous short carbon fibers/mullite composites, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 103(2020), p. 6869.
J.L. Kuang and W.B. Cao, Stacking faults induced high dielectric permittivity of SiC wires, Appl. Phys. Lett., 103(2013), No. 11, art. No. 112906.
Z.H. Zhao, L.M. Zhang, and H.J. Wu, Hydro/organo/ionogels: “Controllable” electromagnetic wave absorbers, Adv. Mater., 34(2022), No. 43, art. No. 2205376.
B. Wen, M.S. Cao, Z.L. Hou, et al., Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites, Carbon, 65(2013), p. 124.
M. Zhang, M.S. Cao, J.C. Shu, W.Q. Cao, L. Li, and J. Yuan, Electromagnetic absorber converting radiation for multifunction, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 145(2021), art. No. 100627.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51702011 and 51572018), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (No. FRF-TP-20-006A3), and the Scientific Research Project of Hunan Province Department of Education, China (No. 20B323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Wenbin Cao and Qi Wang are the editorial board member and the youth editorial board member for this journal, respectively, and were not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. All authors have no financial/commercial conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, R., Lin, W., Liu, Z. et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption and mechanical properties of SiC nanowire/low-melting-point glass composites sintered at 580°C in air. Int J Miner Metall Mater 30, 1809–1815 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-023-2653-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-023-2653-2