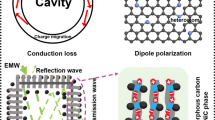
Abstract
At present, metal—organic framework (MOF)-derived nano—micro architectures are actively explored for electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption owing to their flexible composition and structural manipulation that enhance dielectric and magnetic attenuations. However, the basic design principles in MOF-derived microwave absorption materials have not been summarized. This review is devoted to analyzing design principles in MOF-derived microwave absorption materials from the following perspectives: diverse monomers (ligands and ions of MOFs), topologies, chemical states, and physical properties. The derived essential information regarding the EM wave absorption mechanism and the structural—functional dependency is also comprehensively summarized. Finally, a clear insight into the challenges and perspectives of the industrial revolution upgrading in this promising field is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Iqbal, F. Shahzad, K. Hantanasirisakul, et al., Anomalous absorption of electromagnetic waves by 2D transition metal carbonitride Ti3CNTx (MXene), Science, 369(2020), No. 6502, p. 446.
H.H. Zhao, X.Z. Xu, Y.H. Wang, et al., Heterogeneous interface induced the formation of hierarchically hollow carbon microcubes against electromagnetic pollution, Small, 16(2020), No. 43, art. No. 2003407.
J.C. Shu, W.Q. Cao, and M.S. Cao, Diverse metal—organic framework architectures for electromagnetic absorbers and shielding, Adv. Funct. Mater., 31(2021), No. 23, art. No. 2100470.
M.Q. Huang, L. Wang, W.B. You, and R.C. Che, Single zinc atoms anchored on MOF-derived N-doped carbon shell cooperated with magnetic core as an ultrawideband microwave absorber, Small, 17(2021), No. 30, art. No. e2101416.
H.H. Zhao, F.Y. Wang, L.R. Cui, X.Z. Xu, X.J. Han, and Y.C. Du, Composition optimization and microstructure design in MOFs-derived magnetic carbon-based microwave absorbers: A review, Nano-Micro Lett., 13(2021), No. 1, art. No. 208.
J.C. Shu, X.Y. Yang, X.R. Zhang, et al., Tailoring MOF-based materials to tune electromagnetic property for great microwave absorbers and devices, Carbon, 162(2020), p. 157.
K. Zhou, C. Zhang, Z. Xiong, et al., Template-directed growth of hierarchical MOF hybrid arrays for tactile sensor, Adv. Funct. Mater., 30(2020), No. 38, art. No. 2001296.
X. Zhang, J. Qiao, Y.Y. Jiang, et al., Carbon-based MOF derivatives: Emerging efficient electromagnetic wave absorption agents, Nano-Micro Lett., 13(2021), No. 1, art. No. 135.
C. Zhang, M.J. Xu, Z.X. Yang, M.H. Zhu, J. Gao, and Y.F. Han, Uncovering the electronic effects of zinc on the structure of Fe5C2-ZnO catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to linear α-olefins, Appl. Catal. B Environ., 295(2021), art. No. 120287.
L.L. Liang, W.H. Gu, Y. Wu, et al., Heterointerface engineering in electromagnetic absorbers: New insights and opportunities, Adv. Mater., 34(2022), No. 4, art. No. e2106195.
Q. Li, Z. Zhang, L.P. Qi, et al., Toward the application of high frequency electromagnetic wave absorption by carbon nanostructures, Adv. Sci., 6(2019), No. 8, art. No. 1801057.
L.X. Huang, Y.P. Duan, X.H. Dai, et al., Bioinspired metamaterials: Multibands electromagnetic wave adaptability and hydrophobic characteristics, Small, 15(2019), No. 40, art. No. e1902730.
H.L. Lv, Z.H. Yang, P.L. Wang, et al., A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device, Adv. Mater., 30(2018), No. 15, art. No. e1706343.
Y. Cheng, H.Q. Zhao, H.L. Lv, T.F. Shi, G.B. Ji, and Y.L. Hou, Lightweight and flexible cotton aerogel composites for electromagnetic absorption and shielding applications, Adv. Electron. Mater., 6(2020), No. 1, art. No. 1900796.
X.Q. Xu, F.T. Ran, Z.M. Fan, et al., Bimetallic metal—organic framework-derived pomegranate-like nanoclusters coupled with CoNi-doped graphene for strong wideband microwave absorption, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 12(2020), No. 15, p. 17870.
P. Miao, Z. Yu, W.X. Chen, et al., Synergetic dielectric and magnetic losses of a core—shell Co/MnO/C nano complex toward highly efficient microwave absorption, Inorg. Chem., 61(2022), No. 3, p. 1787.
W. Wang, H. Zhang, Y.Z. Zhao, et al., A novel MOF-drived self-decomposition strategy for CoO@N/C-Co/Ni-NiCo2O4 multi-heterostructure composite as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing materials, Chem. Eng. J., 426(2021), art. No. 131667.
Y.H. Cui, Z.H. Liu, X.X. Li, et al., MOF-derived yolk-shell Co@ZnO/Ni@NC nanocage: Structure control and electromagnetic wave absorption performance, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 600(2021), p. 99.
L. Wang, M.Q. Huang, X. Qian, et al., Confined magnetic-dielectric balance boosted electromagnetic wave absorption, Small, 17(2021), No. 30, art. No. e2100970.
H. Furukawa, U. Müller, O.M. Yaghi, “Heterogeneity within order” in metal-organic frameworks, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 54(2015), pp. 3417–3430.
Z.G. Gao, J.Q. Zhang, S.J. Zhang, J. Wang, and Y.H. Song, Cationic etching of ZIF-67 derived LaCoO3/Co3O4 as high-efficiency electromagnetic absorbents, Chem. Eng. J., 421(2021), art. No. 127829.
P. Miao, R. Zhou, K.J. Chen, J. Liang, Q.F. Ban, and J. Kong, Tunable electromagnetic wave absorption of supramolecular isomer-derived nanocomposites with different morphology, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 7(2020), No. 4, art. No. 1901820.
W.B. Li, J. Chen, and P. Gao, MOFs-derived hollow copper-based sulfides for optimized electromagnetic behaviors, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 606(2022), p. 719.
X. Zhang, J. Qiao, C. Liu, et al., A MOF-derived ZrO2/C nanocomposite for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption, Inorg. Chem. Front., 7(2020), No. 2, p. 385.
J. Qiao, X. Zhang, C. Liu, et al., Non-magnetic bimetallic MOF-derived porous carbon-wrapped TiO2/ZrTiO4 composites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption, Neno-Micro Lett., 13(2021), No. 1, art. No. 75.
X.B. Liu, T.T. Liang, R.T. Zhang, et al., Iron-based metal-organic frameworks in drug delivery and biomedicine, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 13(2021), No. 8, p. 9643.
Y. Lü, Y.T. Wang, H.L. Li, et al., MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 7(2015), No. 24, p. 13604.
H.F. Qiu, X.Y. Zhu, P. Chen, Y.Z. Chen, G.Z. Chen, and W.X. Min, Construction of core—shell structured ZnO/C@PPy composite as high-performance dielectric electromagnetic wave absorber, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 543(2022), art. No. 168604.
H.H. Zhao, X.Z. Xu, D.G. Fan, et al., Anchoring porous carbon nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes as a high-performance composite with a unique core-sheath structure for electromagnetic pollution precaution, J. Mater. Chem. A, 9(2021), No. 39, p. 22489.
H.F. Qiu, X.Y. Zhu, P. Chen, N. Li, and X.L. Zhu, Synthesis of ternary core—shell structured ZnOC@CoC@PAN for high-performance electromagnetic absorption, J. Alloys Compd., 868(2021), art. No. 159260.
T. Gao, Z.Y. Zhu, Y.X. Li, et al., Highly efficient electromagnetic absorption on ZnN4-based MOFs-derived carbon composites, Carbon, 177(2021), p. 44.
J.X. Wang, J.F. Yang, J. Yang, and H. Zhang, Design of novel CNT/RGO/ZIF-8 ternary hybrid structure for lightweight and highly effective microwave absorption, Nanotechnology, 31(2020), No. 41, art. No. 414001.
X.K. Wang, P.P. Zhou, G.H. Qiu, et al., Excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous core—shell CoO/Co@C nanocomposites derived from a needle-shaped Co(OH)2@ZIF-67 template, J. Alloys Compd., 842(2020), art. No. 155807.
Y. Fei, M. Liang, Y. Chen, and H.W. Zou, Sandwich-like magnetic graphene papers prepared with MOF-derived Fe3O4-C for absorption-dominated electromagnetic interference shielding, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 59(2020), No. 1, p. 154.
W.T. Wu, R. Xu, Y.M. Zhou, et al., Biomimetic 3D coral reeflike GO@TiO2 composite framework inlaid with TiO2-C for low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption, Carbon, 178(2021), p. 144.
N. Liu, J.X. Wu, F.H. Fei, et al., Ibuprofen degradation by a synergism of facet-controlled MIL-88B(Fe) and persulfate under simulated visible light, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 612(2022), p. 1.
X.Y. Li, Y.H. Pi, Q.B. Xia, Z. Li, and J. Xiao, TiO2 encapsulated in Salicylaldehyde-NH2-MIL-101(Cr) for enhanced visible light-driven photodegradation of MB, Appl. Catal. B, 191(2016), p. 192.
F.G. Cirujano and A. Dhakshinamoorthy, Engineering of active sites in metal—organic frameworks for biodiesel production, Adv. Sustainable Syst., 5(2021), No. 8, art. No. 2100101.
R.D. Guo, D. Su, F. Chen, et al., Hollow beaded Fe3C/N-doped carbon fibers toward broadband microwave absorption, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 14(2022), No. 2, p. 3084.
V.N. le, T.K. Vo, J.H. Lee, et al., A novel approach to prepare Cu(I)Zn@MIL-100(Fe) adsorbent with high CO adsorption capacity, CO/CO2 selectivity and stability via controlled host-guest redox reaction, Chem. Eng. J., 404(2021), art. No. 126492.
S.S. Peng, S.Y. Wang, G.Z. Hao, et al., Preparation of magnetic flower-like carbon-matrix composites with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties by carbonization of MIL-101(Fe), J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 487(2019), art. No. 165306.
J. Zhou, D. Liu, Y. Xiong, and Y. Akinay, A novel approach to prepare polyaniline/Polypyrrole@Cu-BTC/NH2-MIL-101(Fe) MOFs for electromagnetic wave absorption, Ceram. Int., 46(2020), No. 12, p. 19758.
T.G. Zhu, Y. Sun, Y.J. Wang, et al., A MOF-driven porous iron with high dielectric loss and excellent microwave absorption properties, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 31(2020), No. 9, p. 6843.
J.N. Ma, W. Liu, X.H. Liang, et al., Nanoporous TiO2/C composites synthesized from directly pyrolysis of a Ti-based MOFs MIL-125(Ti) for efficient microwave absorption, J. Alloys Compd., 728(2017), p. 138.
P. Ge, S. Li, H. Shuai, et al., Ultrafast sodium full batteries derived from X—Fe (X = Co, Ni, Mn) Prussian blue analogs, Adv. Mater., 31(2019), No. 3, art. No. e1806092.
W. Liu, P.T. Duan, H.W. Xiong, et al., Multicomponent Fe-based composites derived from the oxidation and reduction of Prussian blue towards efficient electromagnetic wave absorption, J. Mater. Chem. C, 9(2021), No. 16, p. 5505.
K. Peng, R.Q. Wang, H. Chen, et al., Prussian blue derived Fe/C anchoring on multiwalled carbon nanotubes forming chain-like efficient electromagnetic wave absorbent, J. Electron. Mater., 49(2020), No. 11, p. 6631.
P.S. Yi, X.F. Zhang, L.Q. Jin, et al., Regulating pyrolysis strategy to construct CNTs-linked porous cubic Prussian blue analogue derivatives for lightweight and broadband microwave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 430(2022), art. No. 132879.
F.Y. Wang, N. Wang, X.J. Han, et al., Core-shell FeCo@carbon nanoparticles encapsulated in polydopamine-derived carbon nanocages for efficient microwave absorption, Carbon, 145(2019), p. 701.
J.S. Gao, H.H. Wang, Y. Zhou, Z.M. Liu, and Y. He, Self-template and in situ synthesis strategy to construct MnO2/Mn3O4@Ni-Co/GC nanocubes for efficient microwave absorption properties, J. Alloys Compd., 892(2022), art. No. 162151.
P. Miao, J.X. Chen, Y.S. Tang, K.J. Chen, and J. Kong, Highly efficient and broad electromagnetic wave absorbers tuned via topology-controllable metal-organic frameworks, Sci. China Mater., 63(2020), No. 10, p. 2050.
K.F. Wang, Y.J. Chen, R. Tian, et al., Porous Co-C core—shell nanocomposites derived from Co-MOF-74 with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10(2018), No. 13, p. 11333.
X.K. Wang, Y.K. Guan, R.R. Zhang, et al., Facile synthesis of cobalt nanoparticles embedded in a rod-like porous carbon matrix with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance, Ceram. Int., 47(2021), No. 1, p. 643.
H.L. Yang, Z.J. Shen, H.L. Peng, Z.Q. Xiong, C.B. Liu, and Y. Xie, 1D–3D mixed-dimensional MnO2@nanoporous carbon composites derived from Mn-metal organic framework with full-band ultra-strong microwave absorption response, Chem. Eng. J., 417(2021), art. No. 128087.
L. Wang, X. Wen, J. Li, P. Zeng, Y. Song, and H. Yu, Roles of defects and linker exchange in phosphate adsorption on UiO-66 type metal organic frameworks: Influence of phosphate concentration, Chem. Eng. J., 405(2021), art. No. 126681.
X. Zhang, J. Qiao, J.B. Zhao, et al., High-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption of cobalt-decorated NH2-UIO-66-derived porous ZrO2/C, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11(2019), No. 39, p. 35959.
G. Wu, Z. Guo, Q. Zhang, et al., Refined band structure plus enhanced phonon scattering realizes thermoelectric performance optimization in CuI-Mn codoped SnTe, J. Mater. Chem. A, 9(2021), No. 22, p. 13065.
J.B. Chen, J. Zheng, F. Wang, Q.Q. Huang, and G.B. Ji, Carbon fibers embedded with FeIII-MOF-5-derived composites for enhanced microwave absorption, Carbon, 174(2021), p. 509.
W. Liu, L. Liu, G.B. Ji, et al., Composition design and structural characterization of MOF-derived composites with controllable electromagnetic properties, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 5(2017), No. 9, p. 7961.
W. Hou, M. Chen, C. Chen, Y. Wang, and Y. Xu, Increased production of H2 under visible light by packing CdS in a Ti, Zr-Based metal organic framework, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 604(2021), p. 310.
Y. Wang, W.Z. Zhang, X.M. Wu, C.Y. Luo, T. Liang, and G. Yan, Metal-organic framework nanoparticles decorated with graphene: A high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 416(2016), p. 226.
H.L. Peng, X. Zhang, H.L. Yang, Z.Q. Xiong, C.B. Liu, and Y. Xie, Fabrication of core—shell nanoporous carbon@chiral polyschiff base iron(II) composites for high-performance electromagnetic wave attenuationin the low-frequency, J. Alloys Compd., 850(2021), art. No. 156816.
J. Yan, Y. Huang, Y.H. Yan, L. Ding, and P.B. Liu, High-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers based on two kinds of nickel-based MOF-derived Ni@C microspheres, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11(2019), No. 43, p. 40781.
H.C. Niu, P.X. Liu, F.Z. Qin, X.L. Liu, and Y. Akinay, PE-DOT coated Cu-BTC metal-organic frameworks decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption, Mater. Chem. Phys., 253(2020), art. No. 123458.
J.Y. Cheng, H.B. Zhang, H.H. Wang, et al., Tailoring self-polarization of bimetallic organic frameworks with multiple polar units toward high-performance consecutive multi-band electromagnetic wave absorption at gigahertz, Adv. Funct. Mater., 32(2022), No. 24, art. No. 2201129.
L. Wang, B. Wen, H.B. Yang, Y. Qiu, and N.R. He, Hierarchical nest-like structure of Co/Fe MOF derived CoFe@C composite as wide-bandwidth microwave absorber, Composites Part A, 135(2020), art. No. 105958.
S.L. Zhao, C.H. Tan, C.T. He, et al., Structural transformation of highly active metal-organic framework electrocatalysts during the oxygen evolution reaction, Nat. Energy, 5(2020), No. 11, p. 881.
Z.H. Zhao, K.C. Kou, L.M. Zhang, and H.J. Wu, Optimal particle distribution induced interfacial polarization in bouquet-like hierarchical composites for electromagnetic wave absorption, Carbon, 186(2022), p. 323.
L. Wang, B. Wen, Y. Qiu, and H.B. Yang, Structurally designed hierarchical carbon nanotubes vertically anchored on elliptical-like carbon nanosheets with enhanced conduction loss as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbent, Synth. Met., 261(2020), art. No. 116301.
J. Su, N. Xu, R. Murase, et al., Persistent radical tetrathiaful-valene-based 2D metal-organic frameworks and their application in efficient photothermal conversion, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl., 60(2021), No. 9, p. 4789.
K. Jayaramulu, D.P. Dubal, A. Schneemann, V. Ranc, C. Perez-Reyes, J. Stráská, Š. Kment, M. Otyepka, R.A. Fischer, and R. Zbořil, Shape-assisted 2D MOF/graphene derived hybrids as exceptional lithium-ion battery electrodes, Adv. Funct. Mater., 29(2019), No. 38, art. No. 1902539.
J.C. Zhang, T.C. Zhang, D.B. Yu, K.S. Xiao, and Y. Hong, Transition from ZIF-L-Co to ZIF-67: A new insight into the structural evolution of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) in aqueous systems, CrystEngComm, 17(2015), No. 43, p. 8212.
X.Q. Xu, F.T. Ran, Z.M. Fan, et al., Cactus-inspired bimetallic metal-organic framework-derived 1D-2D hierarchical Co/N-decorated carbon architecture toward enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing performance, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11(2019), No. 14, p. 13564.
G. Liu, J.Q. Tu, C. Wu, et al., High-yield two-dimensional metal-organic framework derivatives for wideband electromagnetic wave absorption, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 13(2021), No. 17, p. 20459.
Y. Qiu, H.B. Yang, Y. Cheng, and Y. Lin, MOFs derived flower-like nickel and carbon composites with controllable structure toward efficient microwave absorption, Composites Part A, 154(2022), art. No. 106772.
J.W. Fang, Y. Ma, Z.Y. Zhang, et al., Metal—organic framework-derived carbon/carbon nanotubes mediate impedance matching for strong microwave absorption at fairly low temperatures, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 13(2021), No. 28, p. 33496.
Y. Wang, W.Z. Zhang, X.M. Wu, et al., Conducting polymer coated metal-organic framework nanoparticles: Facile synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties, Synth. Met., 228(2017), p. 18.
H.Y. Fan, Z.J. Yao, J.T. Zhou, et al., Enhanced microwave absorption of epoxy composite by constructing 3D Co-C-MW-CNTs derived from metal organic frameworks, J. Mater. Sci., 56(2021), No. 2, p. 1426.
L. Wang, B. Wen, X.Y. Bai, C. Liu, and H.B. Yang, Facile and green approach to the synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework nanosheet-derived 2D Co/C composites for a lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 540(2019), p. 30.
V. Ganesan, S. Lim, and J. Kim, Hierarchical nanoboxes composed of Co9S8-MoS2 nanosheets as efficient electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction, Chem. Asian J., 13(2018), No. 4, p. 413.
M.Q. Huang, L. Wang, K. Pei, et al., Multidimension-control-lable synthesis of MOF-derived Co@N-doped carbon composite with magnetic-dielectric synergy toward strong microwave absorption, Small, 16(2020), No. 14, art. No. 2000158.
Y.J. Liu, Z.J. Yao, J.T. Zhou, L.Q. Jin, B. Wei, and X.X. He, Facile synthesis of MOF-derived concave cube nanocomposite by self-templated toward lightweight and wideband microwave absorption, Carbon, 186(2022), p. 574.
Z.N. Li, X.J. Han, Y. Ma, et al., MOFs-derived hollow Co/C microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption performance, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 6(2018), No. 7, p. 8904.
Y.T. Zhu, X.M. Guan, Z.H. Yang, and X. Xu, Regulation of component transformation in MOF-derived vanadium oxide@C spindles for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption, J. Alloys Compd., 865(2021), art. No. 158886.
X.Q. Xu, F.T. Ran, H. Lai, et al., In situ confined bimetallic metal-organic framework derived nanostructure within 3D interconnected bamboo-like carbon nanotube networks for boosting electromagnetic wave absorbing performances, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11(2019), No. 39, p. 35999.
Z.J. Shen, H.L. Yang, C.B. Liu, E.W. Guo, S.Y. Huang, and Z.Q. Xiong, Polymetallic MOF-derived corn-like composites for magnetic-dielectric balance to facilitate broadband electromagnetic wave absorption, Carbon, 185(2021), p. 464.
Y. Xiong, L.L. Xu, C.X. Yang, Q.F. Sun, and X.J. Xu, Implanting FeCo/C nanocages with tunable electromagnetic parameters in anisotropic wood carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption, J. Mater. Chem., 8(2020), p. 18863.
J.T. Yuan, Q.C. Liu, S.K. Li, et al., Metal organic framework (MOF)-derived carbonaceous Co3O4/Co microframes anchored on RGO with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances, Synth. Met., 228(2017), p. 32.
P. Miao, J.Y. Yang, Y.K. Liu, H.Z. Xie, K.J. Chen, and J. Kong, Emerging perovskite electromagnetic wave absorbers from Bi-metal—organic frameworks, Cryst. Growth Des., 20(2020), p. 4818.
F.Z. Zeng, L. Li, C.Y. Liu, and Z. Lin, Hollow CoS2 nanobubble prisms derived from ZIF-67 through facile two-step self-engaged method for electromagnetic wave absorption, ChemistrySelect, 6(2021), No. 17, p. 4344.
C.C. Hou, L.L. Zou, Y. Wang, and Q. Xu, MOF-mediated fabrication of a porous 3D superstructure of carbon nanosheets decorated with ultrafine cobalt phosphide nanoparticles for efficient electrocatalysis and zinc—air batteries, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 132(2020), No. 48, p. 21544.
Z.H. Zhao, K.C. Kou, and H.J. Wu, 2-Methylimidazole-mediated hierarchical Co3O4/N-doped carbon/short-carbon-fiber composite as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 574(2020), p. 1.
J. Yan, Y. Huang, X.P. Han, X.G. Gao, and P.B. Liu, Metal organic framework (ZIF-67)-derived hollow CoS2/N-doped carbon nanotube composites for extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption, Composites Part B, 163(2019), p. 67.
Z. Li, X. Hu, Z. Shi, J. Lu, and Z. Wang, MOF-derived iron sulfide nanocomposite with sulfur-doped carbon shell as a promising anode material for high-performance lithium-ion batteries, J. Alloys Compd., 868(2021), p. 159110.
D.M. Xu, Y.F. Yang, K. Le, et al., Bifunctional Cu9S5/C octahedral composites for electromagnetic wave absorption and supercapacitor applications, Chem. Eng. J., 417(2021), art. No. 129350.
S. Bera, A. Chakraborty, S. Karak, et al., Multistimuli-responsive interconvertible low-molecular weight metallohydrogels and the in situ entrapment of CdS quantum dots therein, Chem. Mater., 30(2018), No. 14, p. 4755.
G.L. Song, K.K. Yang, L.X. Gai, et al., ZIF-67/CMC-derived 3D N-doped hierarchical porous carbon with in situ encapsulated bimetallic sulfide and Ni NPs for synergistic microwave absorption, Composites Part A, 149(2021), art. No. 106584.
Z.Q. Yan, Z.H. Sun, A.R. Li, et al., Vacancy and architecture engineering of porous FeP nanorods for achieving superior Li+ storage, Chem. Eng. J., 429(2022), art. No. 132249.
W.J. Ruan, C.P. Mu, B.C. Wang, et al., Metal—organic framework derived cobalt phosphosulfide with ultrahigh microwave absorption properties, Nanotechnology, 29(2018), No. 40, art. No. 405703.
J. Ouyang, Z.L. He, Y. Zhang, H.M. Yang, and Q.H. Zhao, Trimetallic FeCoNi@C nanocomposite hollow spheres derived from metal-organic frameworks with superior electromagnetic wave absorption ability, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11(2019), No. 42, p. 39304.
Q. Liao, M. He, Y.M. Zhou, et al., Highly cuboid-shaped heterobimetallic metal—organic frameworks derived from porous Co/ZnO/C microrods with improved electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10(2018), No. 34, p. 29136.
X.Y. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, F. Zhang, et al., MOF-derived NiFe2S4/Porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 610(2022), p. 610.
S.J. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, B. Cheng, Z.W. Zhao, F. Lu, and G.L. Wu, Recent progress of perovskite oxides and their hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption: A mini-review, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 5(2022), No. 3, p. 2440.
L. Wang, X.F. Yu, X. Li, J. Zhang, M. Wang, and R.C. Che, MOF-derived yolk—shell Ni@C@ZnO Schottky contact structure for enhanced microwave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 383(2020), art. No. 123099.
Y. Qiu, H.B. Yang, L. Ma, et al., In situ-derived carbon nanotube-decorated nitrogen-doped carbon-coated nickel hybrids from MOF/melamine for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 581(2021), p. 783.
Z.G. Gao, D. Lan, L.M. Zhang, and H.J. Wu, Simultaneous manipulation of interfacial and defects polarization toward Zn/Co phase and ion hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption, Adv. Funct. Mater., 31(2021), No. 50, art. No. 2106677.
Z.G. Gao, Z.H. Ma, D. Lan, et al., Synergistic polarization loss of MoS2-based multiphase solid solution for electromagnetic wave absorption, Adv. Funct. Mater., 32(2022), No. 18, art. No. 2112294.
S.J.G. Gift and B. Maundy, Semiconductor diode, [in] Electronic Circuit Design and Application, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2021, p. 1.
X.F. Zhang, L.L. Xu, J.T. Zhou, et al., Liquid metal-derived two-dimensional layered double oxide nanoplatelet-based coatings for electromagnetic wave absorption, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 4(2021), No. 9, p. 9200.
K.N. Alekseev, P. Pietiläinen, J. Isohätälä, A.A. Zharov, and F.V. Kusmartsev, Chaos and rectification of electromagnetic wave in a lateral semiconductor superlattice, Europhys. Lett., 70(2005), No. 3, p. 292.
L.N. Huang, C.G. Chen, X.Y. Huang, S.C. Ruan, and Y.J. Zeng, Enhanced electromagnetic absorbing performance of MOF-derived Ni/NiO/Cu@C composites, Composites Part B, 164(2019), p. 583.
R. Yang, J.Q. Yuan, C.H. Yu, et al., Efficient electromagnetic wave absorption by SiC/Ni/NiO/C nanocomposites, J. Alloys Compd., 816(2020), art. No. 152519.
Y.Z. Jiao, S.Y. Cheng, F. Wu, et al., MOF-Guest complex derived Cu/C nanocomposites with multiple heterogeneous interfaces for excellent electromagnetic waves absorption, Composites Part B, 211(2021), art. No. 108643.
Q.V. Thi, S. Park, J. Jeong, et al., A nanostructure of reduced graphene oxide and NiO/ZnO hollow spheres toward attenuation of electromagnetic waves, Mater. Chem. Phys., 266(2021), art. No. 124530.
M. del Rio, J.C. Grimalt Escarabajal, G. Turnes Palomino, and C. Palomino Cabello, Zinc/Iron mixed-metal MOF-74 derived magnetic carbon nanorods for the enhanced removal of organic pollutants from water, Chem. Eng. J., 428(2022), art. No. 131147.
M.L. Dong, M.Y. Peng, W. Wei, H.J. Xu, C.T. Liu, and C.Y. Shen, Improved microwave absorption performance of double helical C/Co@CNT nanocomposite with hierarchical structures, J. Mater. Chem. C, 9(2021), No. 6, p. 2178.
L.N. Jin, X.S. Zhao, J. Ye, X.Y. Qian, and M.D. Dong, MOF-derived magnetic Ni-carbon submicrorods for the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol, Catal. Commun., 107(2018), p. 43.
Q. Wu, B.L. Wang, Y.G. Fu, Z.F. Zhang, P.F. Yan, and T. Liu, MOF-derived Co/CoO particles prepared by low temperature reduction for microwave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 410(2021), art. No. 128378.
X.Y. Xiao, W.J. Zhu, Z. Tan, et al., Ultra-small Co/CNTs nanohybrid from metal organic framework with highly efficient microwave absorption, Composites Part B, 152(2018), p. 316.
H.C. Wang, L. Xiang, W. Wei, et al., Efficient and light-weight electromagnetic wave absorber derived from metal organic framework-encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 9(2017), No. 48, p. 42102.
N.N. Wu, B.B. Zhao, J.Y. Liu, et al., MOF-derived porous hollow Ni/C composites with optimized impedance matching as lightweight microwave absorption materials, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 4(2021), No. 3, p. 707.
X. Li, Z.L. Wang, Z. Xiang, et al., Biconical prisms Ni@C composites derived from metal-organic frameworks with an enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption, Carbon, 184(2021), p. 115.
J.Q. Tao, L.L. Xu, L. Wan, et al., Cubic-like Co/NC composites derived from ZIF-67 with a dual control strategy of size and graphitization degree for microwave absorption, Nanoscale, 13(2021), No. 30, p. 12896.
L.F. Lyu, S.N. Zheng, F.L. Wang, Y. Liu, and J.R. Liu, High-performance microwave absorption of MOF-derived Co3O4@N-doped carbon anchored on carbon foam, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 602(2021), p. 197.
B. Wen, H.B. Yang, Y. Lin, L. Ma, Y. Qiu, F.F. Hu, and Y.N. Zheng, Synthesis of core—shell Co@S-doped carbon@ mesoporous N-doped carbon nanosheets with a hierarchically porous structure for strong electromagnetic wave absorption, J. Mater. Chem. A, 9(2021), No. 6, p. 3567.
B. Wen, H.B. Yang, Y. Lin, L. Ma, Y. Qiu, and F.F. Hu, Controlling the heterogeneous interfaces of S, Co co-doped porous carbon nanosheets for enhancing the electromagnetic wave absorption, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 586(2021), p. 208.
J.Y. Cheng, H.B. Zhang, M.Q. Ning, et al., Emerging materials and designs for low- and multi-band electromagnetic wave absorbers: The search for dielectric and magnetic synergy? Adv. Funct. Mater., 32(2022), No. 23, art. No. 2200123.
T. Wang, G. Chen, J.H. Zhu, H. Gong, L.M. Zhang, and H.J. Wu, Deep understanding of impedance matching and quarter wavelength theory in electromagnetic wave absorption, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 595(2021), p. 1.
Z.C. Wu, H.W. Cheng, C. Jin, B.T. Yang, C.Y. Xu, K. Pei, H.B. Zhang, Z.Q. Yang, and R.C. Che, Dimensional design and core—shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption, Adv. Mater., 34(2022), No. 11, art. No. 2107538.
X.F. Xu, S.H. Shi, Y.L. Tang, G.Z. Wang, M.F. Zhou, G.Q. Zhao, X.C. Zhou, S.W. Lin, and F.B. Meng, Growth of NiAl-layered double hydroxide on graphene toward excellent anti-corrosive microwave absorption application, Adv. Sci., 8(2021), No. 5, art. No. 2002658.
Z.G. Gao, J.Q. Zhang, S.J. Zhang, D. Lan, Z.H. Zhao, and K.C. Kou, Strategies for electromagnetic wave absorbers derived from zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-67) with ferrocene containing polymers, Polymer, 202(2020), art. No. 122679.
F. Chen, S.S. Zhang, B.B. Ma, et al., Bimetallic CoFe-MOF@Ti3C2Tx MXene derived composites for broadband microwave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 431(2022), p. 134007.
S.J. Zhang, B. Cheng, Z.G. Gao, et al., Two-dimensional nanomaterials for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption: An overview of recent advances and prospects, J. Alloys Compd., 893(2022), art. No. 162343.
Z.G. Gao, J.Q. Zhang, D. Lei, et al., Ferrocene decorative phenolic epoxy resin as lightweight thermal-stable dielectric relaxor for electromagnetic wave absorption, Compos. Commun., 22(2020), art. No. 100472.
S.J. Zhang, B. Cheng, Z.R. Jia, et al., The art of framework construction: Hollow-structured materials toward high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 5(2022), No. 3, p. 1658.
M.S. Cao, X.X. Wang, M. Zhang, et al., Electromagnetic response and energy conversion for functions and devices in low-dimensional materials, Adv. Funct. Mater., 29(2019), No. 25, art. No. 1807398.
X.Y. Zhu, H.F. Qiu, P. Chen, G.Z. Chen, and W.X. Min, Anemone-shaped ZIF-67@CNTs as effective electromagnetic absorbent covered the whole X-band, Carbon, 173(2021), p. 1.
H.B. Zhang, J.Y. Cheng, H.H. Wang, et al., Initiating VB-group laminated NbS2 electromagnetic wave absorber toward superior absorption bandwidth as large as 6.48 GHz through phase engineering modulation, Adv. Funct. Mater., 32(2022), art. No. 2108194.
X. Zhang, J. Cheng, Z. Xiang, L. Cai, and W. Lu, A hierarchical Co @ mesoporous C/macroporous C sheet composite derived from bimetallic MOF and oroxylum indicum for enhanced microwave absorption, Carbon, 187(2022), p. 477.
Z.G. Gao, Z.H. Zhao, D. Lan, K.C. Kou, J.Q. Zhang, and H.J. Wu, Accessory ligand strategies for hexacyanometallate networks deriving perovskite polycrystalline electromagnetic absorbents, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 82(2021), p. 69.
P.F. Yin, L.M. Zhang, Y.T. Tang, and J.C. Liu, Earthwormlike (Co/CoO)@C composite derived from MOF for solving the problem of low-frequency microwave radiation, J. Alloys Compd., 881(2021), art. No. 160556.
X.Y. Zhou, J. Wang, L.L. Zhou, Y.G. Wang, and D.S. Yao, Structure, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of NiZnMn ferrite ceramics, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 534(2021), art. No. 168043.
Z.W. Zhang, Z.H. Cai, Z.Y. Wang, et al., A review on metal-organic framework-derived porous carbon-based novel microwave absorption materials, Nano Micro Lett., 13(2021), No. 1, p. 1.
W. Wei, X.G. Liu, W.L. Lu, et al., Light-weight gadolinium hydroxide@polypyrrole rare-earth nanocomposites with tunable and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11(2019), No. 13, p. 12752.
W. Liu, P.T. Duan, C. Mei, et al., Optimizing the size-dependent dielectric properties of metal-organic framework-derived Co/C composites for highly efficient microwave absorption, Inorg. Chem. Front., 8(2021), No. 8, p. 2042.
W. Liu, L. Liu, Z.H. Yang, J.J. Xu, Y.L. Hou, and G.B. Ji, A versatile route toward the electromagnetic functionalization of metal-organic framework-derived three-dimensional nanoporous carbon composites, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 10(2018), No. 10, p. 8965.
Z.G. Gao, Y.H. Song, S.J. Zhang, et al., Electromagnetic absorbers with Schottky contacts derived from interfacial ligand exchanging metal-organic frameworks, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 600(2021), p. 288.
W.H. Huang, W.M. Gao, S.W. Zuo, et al., Hollow MoC/NC sphere for electromagnetic wave attenuation: Direct observation of interfacial polarization on nanoscale hetero-interfaces, J. Mater. Chem. A, 10(2022), No. 3, p. 1290.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51872238, 21806129, and 52074227), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 3102018zy045 and 3102019AX11), and the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Nos. 2020JM-118 and 2017JQ5116). The authors acknowledge the support from The Analytical & Testing Center of Northwestern Polytechnical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Yang, K., Zhao, Z. et al. Design principles in MOF-derived electromagnetic wave absorption materials: Review and perspective. Int J Miner Metall Mater 30, 405–427 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2555-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2555-8