Abstract
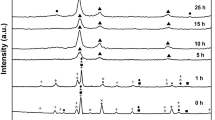
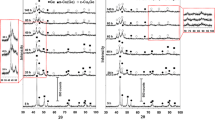
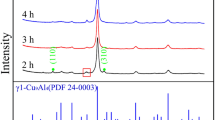
This work concerns the structural evolution of Cu70Nb20Al10 (at%) alloy processed by mechanical alloying using a planetary ball mill in air atmosphere for different times (4 to 200 h). The morphological, structural, micro structural, and thermal behaviors of the alloy were investigated by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and differential scanning calorimetry. X-ray diffraction patterns were examined using the Rietveld refinement technique with the help of the MAUD software. A disordered FCC-Cu(Nb,Al) solid solution was formed after 8 h of milling. The crystallite size, microstrain, and lattice parameter were determined by the Rietveld method. With increasing milling time, the crystallite size of the final product—ternary -phase FCC-Cu(Nb,Al)—is refined to the nanometer scale, reaching 12 nm after 200 h. This crystallographic structure combines good mechanical strength and good ductility. An increase in microstrain and partial oxidation were also observed with increasing milling time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.S. Benjamin, Dispersion strengthened superalloys by mechanical alloying, Metall. Trans., 1(1970), No. 10, p. 2943.
A.R. Yavari, P.J. Desre, and T. Banameur, Mechanically driven alloying of immiscible elements, Phys. Rev. Lett., 68(1992), No. 14, p. 2235.
K. Uenishi, K.F. Kobayashi, S. Nasu, H. Hatano, K.N. Ishibara, and P.H. Shingu, Mechanical alloying in the Fe-Cu system, Z. Metallkd., 83(1992), No. 2, p. 132.
J. Kuyama, H. Inui, S. Imaoka, K.N. Ishihara, and P.H. Shinhu, Nanometer-sized crystals formed by the mechanical alloying in the Ag-Fe system, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 30(1991), No. 5A, p. L854.
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical alloying and milling, Prog. Mater. Sci., 46(2001), No. 1–2, p. 1.
M.S. El-Eskandarany, Mechanical Alloying for Fabrication of Advanced Engineering Materials, Noyes Publications/William Andrew Publishing, Norwich, N.Y., 2001, p. 154.
M.S. Khoskhoo, S. Scudinio, J. Thomas, K.B. Sureddi, and J. Eckert, Grain and crystalline size evaluation of cryomilled pure copper, J. Alloys Compd., 509(2011), p. S343.
H. Abdoli, H. Farnoush, E. Salahi, and K. Pourazrang, Study of the densification of a nanostructured composite powder Part 1: effect of compaction pressure and reinforcement addition, Mater. Sci. Eng A, 486(2008), No. 1–2, p. 580.
J. Ghosh, S. Mazumdar, M. Das, S. Ghatak, and A.K. Basu, Microstructural characterization of amorphous and nanocrys-talline boron nitride prepared by high-energy ball milling, Mater. Res. Bull., 43(2008), No. 4, p. 1023.
J. Torrens-Serra, I. Peral, J. Rodriguez-Viejo, and M.T. Clavaguera-Mora, Micro structure evolution and grain size distribution in nanocrystalline FeNbBCu from synchrotron XRD and TEM analysis, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 358(2012), No. 1, p. 107.
F. Hadef, A. Otomani, A. Djekoun, and J.M. Greneche, Structural and microstructural study of nanostructured Fe50Al40Ni10 powders produced by mechanical alloying, Mater. Charact., 62(2011), No. 8,p. 751.
H. Dutta, A. Sen, J. Bhattacharjee, and S.K. Pradhan, Preparation of ternary Ti0.9Ni0.1C cermets by mechanical alloying: microstructure characterization by Rietveld method and electron microscopy, J. Alloys Compd., 493(2010), No. 1–2, p. 666.
A. Inoue, Bulk amorphous alloys, [in] Amorphous and Nanocrystalline Materials, Springer, Berlin, 2001, p. 1.
S.Z. Kou, L. Feng, Y.T. Ding, G.J. Xu, Z.F. Ding, and P.Q. La, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Cu-based amorphous alloys made by mechanical alloying, Intermetallics, 12(2004), No. 10–11, p. 1115.
G.M. Wang, S.S. Fang, X.S. Xiao, Q. Hua, J.Z. Gu, and YD. Dong, Microstructure and properties of Zr65Al10Ni10Cu15 amorphous plates rolled in the supercooled liquid region, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 373(2004), No. 1–2, p. 217.
M. Gogebakan, The effect of Si addition on crystallization behaviour of amorphous Al-Y-Ni alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 13(2004), No. 4, p. 504.
R.S. Lei, M.P. Wang, H.P. Wang, and S.Q. Xu, New insights on the formation of supersaturated Cu-Nb solid solution prepared by mechanical alloying, Mater. Charact, 118(2016), p. 324.
M.A. Morris and D.G. Morris, Microstructure refinement and associated strength of copper alloys obtained by mechanical alloying, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 111(1989), p. 115.
A. Benghalem and D.G. Morris, Microstructure and mechanical properties of concentrated alloys prepared by mechanical alloying, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 161(1993), No. 2, p. 255.
E. Botcharova, M. Heilmaier, J. Freudenberger, G. Drew, D. Kudashow, U. Martin, and L. Schultz, Supersaturated solid solution of niobium in copper by mechanical alloying, J. Alloys Compd, 351(2003), No. 1–2, p. 119.
E. Botcharova, J. Freudenberger, and L. Schultz, Cu-Nb alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and subsequent heat treatment, J. Alloys Compd., 365(2004), No. 1–2, p. 157.
S. Mula, H. Bahmanpour, S. Mal, P.C. Kang, M. Atwater, W. Jian, R.O. Scattergood, and C.C. Koch, Thermodynamic feasibility of solid solubility extension of Nb in Cu and their thermal stability, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 539(2012), p. 330.
R.S. Lei, M.P. Wang, Z. Li, H.G. Wei, W.C. Yang, Y.L. Jia, and S. Gong, Structure evolution and solid solubility extension of copper-niobium powders during mechanical alloying, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 528(2011), No. 13–14, p. 4475.
M. Azabou, H.I. Gharsallah, L. Escoda, J.J. Sunol, A.W. Kolsi, and M. Khitouni, Mechanochemical reactions in nano-crystalline Cu-Fe system induced by mechanical alloying in air atmosphere, Powder Technol., 224(2012), p. 338.
M. Khitouni, R. Daly, M. Mhadhbi, and A. Kolsi, Structural evolution in nanocristalline Cu obtained by high energy mechanical milling: phases formation of copper oxides, J. Alloys Compd., 475(2009), No. 1–2, p. 581.
S.M. Yoon, C. Nagarjuna, D.W. Shin, C.H. Lee, B. Madava-li, S.J. Hong, and K.H. Lee, Influence of milling atmosphere on thermoelectric properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te based alloys by mechanical alloying, J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst, 24(2017), No. 5, p. 357.
Z.Q. Zhao, Z. Xiao, Z. Li, M.N. Zhu, and Z.Q. Yang, Characterization of dispersion strengthened copper alloy prepared by internal oxidation combined with mechanical alloying, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 26(2017), No. 11, p. 5641.
M. do Carmo Amorim da Silva and S.J.G. de Lima, Evolution of mechanical alloying to obtain Cu-Al-Nb shape memory alloy, Mater. Res., 8(2005), No. 2, p. 169.
L. Lutterotti, S. Matthies, and H. R. Wenk, MAUD: a friendly Java program for material analysis using diffraction, IUCr: Newsletter of the CPD, 21(1999), p.14.
J. Eckert, J.C. Holzer, and W.L. Johnson, Thermal stability and grain growth behavior of mechanically alloyed nano-crystalline Fe-Cu alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 73(1993), No. 1, p. 131.
F.A. Mohamed, A dislocation model for the minimum grain size obtainable by milling, Acta Mater, 51(2003), No. 14, p. 4107.
T. Bachaga, R. Daly, L. Escode, J.J. Suñol, and M. Khitouni, Amorphization of Al50(Fe2B)30Nb20 mixture by mechanical alloying, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 44(2013), No. 10, p. 4718.
M. Krifa, M. Mhadhbi, L. Escoda, J. Saurina, J.J. Suñol, N. Llorca-Isern, C. Artieda-Guzmán, and M. Khitouni, Phase transformation during mechanical alloying of Fe-30% Al-20% Cu, Powder Technol, 246(2013), p. 117.
H.I. Gharsallah, T. Makhlouf, L. Escoda, J.J. Suñol, and M. Khitouni, Magnetic and microstructural proprieties of nano-crystalline Fe-25at% Al and Fe-25at% Al + 0.2at% B alloys prepared by mechanical alloying process, Eur. Phys. J. Plus, 131(2016), No. 7, p. 119.
S. Bergheul, H. Tafat, and M. Azzaz, Formation and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe60Co40 alloys produced by mechanical alloying, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 15(2006), No. 3, p. 349.
D.Y. Ying, and D.L. Zhang, Processing of Cu-Al2O3 metal matrix nanocomposite materials by using high energy ball milling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 286(2000), No. 1, p. 152.
M. Gherib, A. Otmani, A. Djekoun, A. Bouasla, M. Poulain, and M. Legouira, Study of nanocrystalline NiAl alloys prepared by mechanical alloying, Defect Diffus. Forum, 329(2012), p. 19.
Y.C. Zhang, J.Y. Tang, G.L. Wang, M. Zhang, and X.Y. Hu, Facile synthesis of submicron Cu2O and CuO crystallites from a solid metallorganic molecular precursor, J. Cryst. Growth, 294(2006), No. 2, p. 278.
M.D. Abad, S. Parker, D. Kiene, M.M. Primorac, and P. Hosemann, Mcrostructure and mechanical properties of CUxNb1-x. alloys prepared by ball milling and high pressure torsion compacting, J. Alloys Compd., 630(2015), p. 117.
W. Pfeiler, Alloy Physics: A Comprehensive Reference, John Wileys and Sons, New York, 2008.
R.S. Lei, S.Q. Xu, M.P. Wang, and H.P. Wang, Mcrostructure and properties of nanocrystalline copper-niobium alloy with high strength and high conductivity, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 586(2013), p. 367.
M. Slimi, M. Azabou, L. Escoda, J.J. Sunol, and M. Khitouni, Stacking faults and structural characterization of mechanically alloyed Ni50Cu(Fe2B)10P30 powders, Eur. Phys. J. Plus, 130(2015), No. 4, p. 72.
S. Sivasankaran, K. Sivaprasad, R. Narayanasamy, and P.V. Satyanarayana, X-ray peak broadening analysis of AA 6061100-x-x wt.% A12O3 nanocomposite prepared by mechanical alloying, Mater. Charact, 62(2011), No. 7, p. 661.
Y.H. Zhao, HW. Sheng, and K. Lu, Mcrostructure evolution and thermal properties in nanocrystalline Fe during mechanical attrition, Acta Mater, 49(2001), No. 2, p. 365.
C. Slama and M. Abdellaoui, Mcrostructure characterization of nanocrystalline (Ti0.9W0.1) C prepared by mechanical alloying, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater, 54(2016), p. 270.
M. Slimi, M. Azabou, L. Escoda, J.J. Sunol, and M. Khitouni, Structural and microstructural properties of nanocrystalline Cu-Fe-Ni powders produced by mechanical alloying, Powder Technol., 266(2014), p. 262.
I. Hideaki, M. Toshiyuki, and N. Keiji, Measurement of enthalpies of formation of niobium oxides at 920 K in a Tian-Calvet-type calorimeter, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 16(1984), No. 5, p. 411.
K.T. Jacob, C. Shekhar, M. Vinay, and Y. Waseda, Thermodynamic properties of niobium oxides, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 55(2010), No 11, p. 4854.
R. Novakovic, Thermodynamics, surface properties and microscopic functions of liquid Al-Nb and Nb-Ti alloys, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 356(2010), No. 31–32, p. 1593.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaara, K., Chemingui, M., Optasanu, V. et al. Solid solution evolution during mechanical alloying in Cu-Nb-Al compounds. Int J Miner Metall Mater 26, 1129–1139 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1820-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1820-y