Abstract
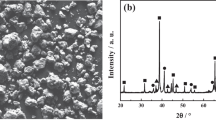
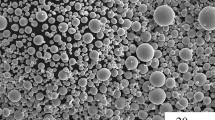
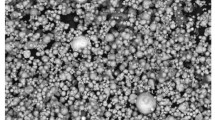
The ceramic injection molding technique was used in the gas-pressure sintering of ultra-fine Si3N4 powder. The feedstock’s flowability, debinding rate, defect evolution, and microstructural evolution during production were explored. The results show that the solid volume loading of less than 50vol% and the surfactant mass fraction of 6wt% result in a perfect flowability of feedstock; this feedstock is suitable for injection molding. When the debinding time is 8 h at 40°C, approximately 50% of the wax can be solvent debinded. Defects detected during the preparation are traced to improper injection parameters, mold design, debinding parameters, residual stress, or inhomogeneous composition distribution in the green body. The bulk density, Vickers hardness, and fracture toughness of the gas-pressure-sintered Si3N4 ceramic reach 3.2 g/cm3, 16.5 GPa, and 7.2 MPa·m1/2, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.P. Doğan and J.A. Hawk, Microstructure and abrasive wear in silicon nitride ceramics, Wear, 250(2001), No. 1-12, p. 256.
M.H. Bocanegra-Bernal and B. Matovic, Mechanical properties of silicon nitride-based ceramics and its use in structural applications at high temperatures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 6, p. 1314.
X.L. Ni, H.Q. Yin, L. Liu, S.J. Yi, and X.H. Qu, Injection molding and debinding of micro gears fabricated by micro powder injection molding, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 20(2013), No. 1, p. 82.
Z.W. Xu, C.C. Jia, C.J. Kuang, and X.H. Qu, Fabrication and sintering behavior of high-nitrogen nickel-free stainless steels by metal injection molding, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 17(2010), No. 4, p. 423.
S.J. Yi, H.Q. Yin, K. Chen, D.F. Khan, Q.J. Zheng, and X.H. Qu, Microstructure and properties of nano-TiN modified Ti(C,N)-based cermets fabricated by powder injection molding and die pressing, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 20(2013), No. 11, p. 1115.
M.H. Bocanegra-Bernal and B. Matovic, Dense and near-net-shape fabrication of Si3N4 ceramics, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 500(2009), No. 1-2, p. 130.
V.L. Wiesner, J.P. Youngblood, and R.W. Trice, Roomtemperature injection molding of aqueous alumina-polyvinylpyrrolidone suspensions, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 34(2014), No. 2, p. 453.
J. Hidalgo, C. Abajo, A. Jiménez-Morales, and J.M. Torralba, Effect of a binder system on the low-pressure powder injection moulding of water-soluble zircon feedstocks, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 33(2013), No. 15-16, p. 3185.
L. Gorjan, T. Kosmač, and A. Dakskobler, Single-step wick-debinding and sintering for powder injection molding, Ceram. Int., 40(2014), No. 1, p. 887.
S.M. Ani, A. Muchtar, N. Muhamad, and J.A. Ghani, Binder removal via a two-stage debinding process for ceramic injection molding parts, Ceram. Int., 40(2014), No. 2, p. 2819.
D. Bleyan, P. Svoboda, and B. Hausnerov, Specific interactions of low molecular weight analogues of carnauba wax and polyethylene glycol binders of ceramic injection moulding feedstocks, Ceram. Int., 41(2015), No. 3, p. 3975.
J. Hidalgo, A. Jiménez-Morales, and J.M. Torralba, Thermal stability and degradation kinetics of feedstocks for powder injection moulding: a new way to determine optimal solid loading? Polym. Degrad. Stab., 98(2013), No. 6, p. 1188.
S.M. Ani, A. Muchtar, N. Muhamad, and J.A. Ghani, Fabrication of zirconia-toughened alumina parts by powder injection molding process: Optimized processing parameters, Ceram. Int., 40(2014), No. 1, p. 273.
J. Lenz, R.K. Enneti, S.J. Park, and S.V. Atre, Powder injection molding process design for UAV engine components using nanoscale silicon nitride powders, Ceram. Int., 40(2014), No. 1, p. 893.
R.K. Enneti, T.S. Shivashankar, S.J. Park, R.M. German, and S.V. Atre, Master debinding curves for solvent extraction of binders in powder injection molding, Powder Technol., 228(2012), p. 14.
J.P. Choi, H.G. Lyu, W.S. Lee, and J.S. Lee, Investigation of the rheological behavior of 316L stainless steel micro-nano powder feedstock for micro powder injection molding, Powder Technol., 261(2014), p. 201.
X.F. Yang, C. Jia, Z.P. Xie, W. Liu, and Q.C. Liu, Water- soluble binder system based on poly-methyl methacrylate and poly-ethylene glycol for injection molding of large-sized ceramic parts, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 10(2013), No. 2, p. 339.
J.L. Fan, Y. Han, T. Liu, H.C. Cheng, Y. Gao, and J.M. Tian, Influence of surfactant addition on rheological behaviors of injection-molded ultrafine 98W–1Ni–1Fe suspension, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 23(2013), No. 6, p. 1709.
X.F. Yang, Z.P. Xie, G.W. Liu, and Y. Huang, Dynamics of water debinding in ceramic injection moulding, Adv. Appl. Ceram., 108(2009), No. 5, p. 295.
T.S. Shivashankar and R.M. German, Effective length scale for predicting solvent-debinding times of components produced by powder injection molding, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 82(1999), No. 5, p. 1146.
T.S. Wei and R.M. German, Two-stage Fast Debinding of Injection Molding Powder Compacts, US Patent, Appl.5028367, 1991.
P. Dvorak, T. Barriere, and J.C. Gelin, Direct observation of mould cavity filling in ceramic injection moulding, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 28(2008), No. 10, p. 1923.
W. Liu, X.F. Yang, Z.P. Xie, C. Jia, and L.L. Wang, Novel fabrication of injection-moulded ceramic parts with large section via partially water-debinding method, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 32(2012), No. 10, p. 2187.
S. Krug, J.R.G. Evans, and J.H.H. ter Maat, Residual stresses and cracking in large ceramic injection mouldings subjected to different solidification schedules, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 20(2000), No. 14-15, p. 2535.
X.F. Yang, Z.P. Xie, and Y. Huang, Influence of the compacts homogeneity on the incidence of cracks during thermal debinding in ceramic injection molding, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 25(2009), No. 2, p. 264
S.D. Yang, R.J. Zhang, and X.H. Qu, X-ray analysis of powder- binder separation during SiC injection process in L-shaped mould, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 35(2015), No. 1, p. 61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Xf., Yang, Jh., Xu, Xw. et al. Injection molding of ultra-fine Si3N4 powder for gas-pressure sintering. Int J Miner Metall Mater 22, 654–659 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1119-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1119-6