Abstract
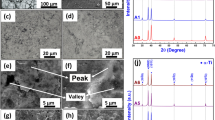
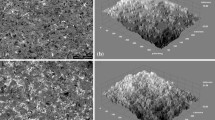
Surface modification is often performed using grit or shot blasting treatment for improving the performances of biomedical implants. The effects of blasting treatments using steel slag balls and spherical shots on the surface and subsurface of titanium were studied in this paper. The treatments were conducted for 60–300 s using 2–5 mm steel slag balls and 3.18 mm spherical shots. The surface morphology, roughness, and elemental composition of titanium specimens were examined prior to and after the treatments. Irregular and rough titanium surfaces were formed after the treatment with the steel slag balls instead of the spherical shots. The former treatment also introduced some bioactive elements on the titanium surface, but the latter one yielded a harder surface layer. In conclusion, both steel slag ball and shot blasting treatment have their own specialization in modifying the surface of metallic biomaterials. Steel slag ball blasting is potential for improving the osseointegration quality of implants; but the shot blasting is more appropriate for improving the mechanical properties of temporary and load bearing implants, such as osteosynthesis plates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Le Guéhennec, A. Soueidan, P. Layrolle, and Y. Amouriq,, Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration, Dent. Mater., 23(2007), No. 7, p. 844.
C.N. Elias, Y. Oshida, J.H. Lima, and C.A. Muller, Relationship between surface properties (roughness, wettability and morphology) of titanium and dental implant removal torque, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 1(2008), No. 3, p. 234.
H.J. Rønold, S.P. Lyngstadaas, and J.E. Ellingsen,, Analysing the optimal value for titanium implant roughness in bone attachment using a tensile test, Biomaterials, 24(2003), No. 25, p. 4559.
P.A. Ramires, A. Romito, F. Cosentino, and E. Milella, The influence of titania/hydroxyapatite composite coatings on in vitro osteoblasts behaviour, Biomaterials, 22(2001), No. 12, p. 1467.
L.P. Xu, F. Pan, G.N. Yu, L. Yang, E.L. Zhang, and K. Yang, In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the surface bioactivity of a calcium phosphate coated magnesium alloy, Biomaterials, 30(2009), No. 8, p. 1512.
W.D. Müeller, U. Gross, T. Fritz, C. Voigt, P. Fischer, G. Berger, S. Rogaschewski, and K.P. Lange,, Evaluation of the interface between bone and titanium surfaces being blasted by aluminium oxide or bioceramic particles, Clin. Oral Implants Res., 14(2003), No. 3, p. 349.
M. Piattelli, A. Scarano, M. Paolantonio, G. Iezzi, G. Petrone, and A. Piattelli, Bone response to machined and resorbable blast material titanium implants: an experimental study in rabbits, J. Oral Implantol., 28(2002), No. 1, p. 2.
D.D. Deligianni, N.D. Katsala, P.G. Koutsoukos, and Y.F. Missirlis, Effect of surface roughness of hydroxyapatite on human bone marrow cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation and detachment strength, Biomaterials, 22(2000), No. 1, p. 87.
K. Das, S. Bose, and A. Bandyopadhyay, Surface modifications and cell-materials interactions with anodized Ti, Acta Biomater., 3(2007), No. 4, p. 573.
M. Multigner, E. Frutos, C.L. Mera, J. Chao, and J.L. González-Carrasco,, Interrogations on the sub-surface strain hardening of grit blasted Ti-6Al-4V alloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 203(2009), No. 14, p. 2036.
A. Wennerberg, T. Albrektsson, C. Johansson, and B. Andersson, Experimental study of turned and grit-blasted screw-shaped implants with special emphasis on effects of blasting material and surface topography, Biomaterials, 17(1996), No. 1, p. 15.
X.P. Jiang, X.Y. Wang, J.X. Li, D.Y. Li, C.S. Man, M.J. Shepard, and T. Zhai, Enhancement of fatigue and corrosion properties of pure Ti by sandblasting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 429(2006), No. 1–2, p. 30.
M. Kern and V.P. Thompson, Effects of sandblasting and silica-coating procedures on pure titanium, J. Dent., 22(1994), No. 5, p. 300.
M. Multigner, S. Ferreira-Barragáns, E. Frutos, M. Jaafar, J. Ibáñez, P. Marín, M.T. Pérez-Prado, G. González-Doncel, A. Asenjo, and J.L. González-Carrasco, Superficial severe plastic deformation of 316 LVM stainless steel through grit blasting: effects on its microstructure and subsurface mechanical properties, Surf. Coat. Technol., 205(2010), No. 7, p. 1830.
H.I. Chung, S.K. Kim, Y.S. Lee, and J. Yu, Permeable reactive barrier using atomized slag material for treatment of contaminants from landfills, Geosci. J., 11(2007), No. 2, p. 137.
B. Arifvianto, S.K.A. Wibisono, and M. Mahardika, Influence of grit blasting treatment using steel slag balls on the subsurface microhardness, surface characteristics and chemical composition of medical grade 316L stainless steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 210(2012), p. 176.
P. Dewo, Evaluation and Redesign of an Osteosynthesis Plate, Produced in Indonesia [Dissertation], University of Groningen, Groningen, 2011.
K. Dai, J. Villegas, Z. Stone, and L. Shaw, Finite element modeling of the surface roughness of 5052 Al alloy subjected to a surface severe plastic deformation process, Acta Mater., 52(2004), No. 20, p. 5771.
B. Arifvianto, Suyitno, M. Mahardika, P. Dewo, P.T. Iswanto, and U.A. Salim, Effect of surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) on microhardness, surface roughness and wettability of AISI 316L, Mater. Chem. Phys., 125(2011), No. 3, p. 418.
B. Arifvianto, Suyitno, and M. Mahardika, Effects of surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) on a rough surface of AISI 316L stainless steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 258(2012), No. 10, p. 4538.
A.S. Brentel, L.M.R. de Vasconcellos, M.V. Oliveira, M.L. de Alencastro Graça, L.G.O. de Vasconcellos, C.A.A. Cairo, and Y.R. Carvalho,, Histomorphometric analysis of pure titanium implants with porous surface versus rough surface, J. Appl. Oral. Sci., 14(2006), No. 3, p. 213.
K. Gotfredsen, A. Wennerberg, C. Johansson, L.T. Skovgaard, and E. Hjørting-Hansen,, Anchorage of TiO2-blasted, HA-coated, and machined implants: an experimental study with rabbits, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 29(1995), No. 10, p. 1223.
T. Jinno, S.K. Kirk, S. Morita, and V.M. Goldberg, Effects of calcium ion implantation on osseointegration of surface-blasted titanium alloy femoral implants in a canine total hip arthroplasty model, J. Arthroplasty, 19(2004), No. 1, p. 102.
M.M. Dewidar and J.K. Lim, Properties of solid core and porous surface Ti-6Al-4V implants manufactured by powder metallurgy, J. Alloys Compd., 454(2008) No. 1–2, p. 442.
R. Sabetrashekh, H. Tiainen, J.E. Reseland, J. Will, J.E. Ellingsen, S.P. Lyngstadaas, and H.J. Haugen, Impact of trace elements on biocompatibility of titaniumscaffolds, Biomed. Mater., 5(2010), No. 1, p. 1.
A. Citeau, J. Guicheux, C. Vinatier, P. Layrolle, T.P. Nguyen, P. Pilet, and G. Daculsi, In vitro biological effects of titanium rough surface obtained by calcium phosphate grid blasting, Biomaterials, 26(2005), No. 2, p. 157.
K. Anselme, P. Linez, M. Bigerelle, D. Le Maguer, A.L. Maguer, P. Hardouin, H.F. Hildebrand, A. Iost, and J.M. Leroy, The relative influence of the topography and chemistry of TiAl6V4 surfaces on osteoblastic cell behaviour, Biomaterials, 21(2000), No. 15, p. 1567.
C. Aparicio, F. Javier Gil, C. Fonseca, M. Barbosa, and J.A. Planell, Corrosion behaviour of commercially pure titanium shot blasted with different materials and sizes of shot particles for dental implant applications, Biomaterials, 24(2003), No. 2, p. 263.
T. Roland, D. Retraint, K. Lu, and J. Lu, Enhanced mechanical behavior of a nanocrystallised stainless steel and its thermal stability, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 445–446(2007), p. 281.
T. Roland, D. Retraint, K. Lu, and J. Lu, Fatigue life improvement through surface nanostructuring of stainless steel by means of surface mechanical attrition treatment, Scripta Mater., 54(2006), No. 11, p. 1949.
M. Wen, G. Liu, J.F. Gu, W.M. Guan, and J. Lu, The tensile properties of titanium processed by surface mechanical attrition treatment, Surf. Coat. Technol., 202(2008), No. 19, p. 4728.
P. Dewo, E.B. van der Houwen, P.K. Sharma, R. Magetsari, T.C. Bor, L.D. Vargas-Llona, J.R. van Horn, H.J. Busscher, and G.J. Verkerke, Mechanical properties of Indonesian-made narrow dynamic compression plate, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 13(2012), p. 93.
M. Baleani, M. Viceconti, and A. Toni, The effect of sandblasting treatment on endurance properties of titanium alloy hip prostheses, Artif. Organs, 24(2000), No. 4, p. 296.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arifvianto, B., Suyitno & Mahardika, M. Surface modification of titanium using steel slag ball and shot blasting treatment for biomedical implant applications. Int J Miner Metall Mater 20, 788–795 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0797-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0797-1