Abstract
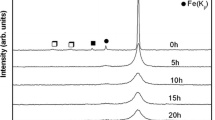
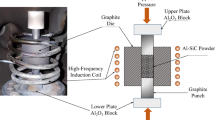
Fe-WC nanocomposites were successfully fabricated by high-frequency induction heated sintering of ball milled nanostructure powders. The ball milled powders were characterized by X-ray diffraction. Density measurements by the Archimedes method show that all sintered samples have the relative density higher than 95%. Studies on the effects of WC content, milling speed, and milling time indicate that a higher milling speed and a more WC content lead to the improvement of mechanical properties. There is a very good distribution of WC particles in the Fe matrix at the milling speed of 650 r/min. For the sintered sample 20-5-650 (20wt% WC, milling time of 5 h, and milled speed of 650 r/min), the maximum Brinell hardness and yield stress are obtained to be 3.25 GPa and 858 MPa, respectively. All sintered samples have brittle fracture during compression test except the sample 20-5-650.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Aldas and M.D. Mat, Experimental and theoretical analysis of particle distribution in particulate metal matrix composites, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 160(2005), No. 3, p. 289.
J. Hashim, L. Looney, and M.S.J. Hashmi, Particle distribution in cast metal matrix composites: Part I, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 123(2002), No. 2, p. 251.
I.J. Shon, B.R. Kim, J.M. Doh, and J.K. Yoon, Consolidation of binderless nanostructured titanium carbide by high-frequency induction heated sintering, Ceram. Int., 36(2010), No. 6, p. 1797.
H. Romanus, V. Cimalla, J. Schaefer, L. Spie G. Ecke, and J. Pezoldt, Preparation of single phase tungsten carbide by annealing of sputtered tungsten-carbon layers, Thin Solid Films, 359(2000), No. 2, p. 146.
L. Niu, M. Hojamberdiev, and Y.H. Xu, Preparation of in situ-formed WC/Fe composite on gray cast iron substrate by a centrifugal casting process, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 210(2010), No. 14, p. 1986.
A.M. Do Nascimento, V. Ocelík, M.C.F. Ierardi, and J.Th.M. De Hosson, Microstructure of reaction zone in WCp/duplex stainless steels matrix composites processing by laser melt injection, Surf. Coat. Technol., 202(2008), No. 10, p. 2113.
M.H. Korkut, O. Yilmaz, and S. Buytoz, Effect of aging on the microstructure and toughness of the interface zone of a gas tungsten arc (GTA) synthesized Fe-Cr-Si-Mo-C coated low carbon steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 157(2002), No. 1, p. 5.
K. Miyazaki, S. Ito, N. Koura, N. Yoneda, and K. Asaka, Preparation of tungsten carbide-iron composite using HIP, J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall., 37(1990), No. 2, p. 219.
Q.C. Jiang, X.L. Li, and H.Y. Wang, Fabrication of TiC particulate reinforced magnesium matrix composites, Scripta Mater., 48(2003), No. 6, p.713.
W.H. Jiang, J. Fei, and X.L. Han, Synthesis of titanium and tungsten carbides in iron matrices, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 20(2001), No. 3, p. 283.
M. Razavi, M.R. Rahimipour, and R. Yazdani-Rad, Synthesis of Fe-WC nanocomposite from industrial ferrotungsten via mechanical alloying method, Adv. Appl. Ceram., 110(2011), No. 6, p. 367.
K. Chu, C.C. Jia, X.B. Liang, and H. Chen, Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and thermal conductivity of Al/diamond composites prepared by spark plasma sintering, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 17(2010), No. 2, p. 234.
K. Chu, Z.F. Liu, C.C. Jia, H. Chen, X.B. Liang, W.J. Gao, W.H. Tian, and H. Guo, Thermal conductivity of SPS consolidated Cu/diamond composites with Cr-coated diamond particles, J. Alloys Compd., 490(2010), No. 1–2, p. 453.
J.H. Park, J.K. Yoon, J.M. Doh, B.S. Lee, and I.J. Shon, Simultaneous high-frequency induction heated combustion synthesis and consolidation of nanostructured HfSi2-SiC composite, Ceram. Int., 35(2009), No. 4, p. 1677.
K.D. Woo, B.R. Kim, E.P. Kwon, D.S. Kang, and I.J. Shon, Properties and rapid consolidation of nanostructured TiC-based hard materials with various binders by a high-frequency induction heated sintering, Ceram. Int., 36(2010), No. 1, p. 351.
M. Dewidar, Microstructure and mechanical properties of biocompatible high density Ti-6Al-4V/W produced by high frequency induction heating sintering, Mater. Des., 31(2010), No. 8, p. 3964.
N.R. Park, D.M. Lee, I.Y. Ko, J.K. Yoon, and I.J. Shon, Rapid consolidation of nanocrystalline Al2O3 reinforced Ni-Fe composite from mechanically alloyed powders by high frequency induction heated sintering, Ceram. Int., 35(2009), No. 8, p. 3147.
H.C. Kim, D.K. Kim, K.D. Woo, I.Y. Ko, and I.J. Shon, Consolidation of binderless WC-TiC by high frequency induction heating sintering, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 26(2008), No. 1, p. 48.
H.C. Kim, H.K. Park, I.K. Jeong, I.Y. Ko, and I.J. Shon, Sintering of binderless WC-Mo2C hard materials by rapid sintering process, Ceram. Int., 34(2008), No. 6, p. 1419.
I.J. Shon, I.K. Jeong, I.Y. Ko, J.M. Doh, and K.D. Woo, Sintering behavior and mechanical properties of WC-10Co, WC-10Ni and WC-10Fe hard materials produced by high-frequency induction heated sintering, Ceram. Int., 35(2009), No. 1, p. 339.
H.M. Rietveld, A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2(1969), No. 2, p. 65.
J. Shackelford, W. Alexander, and J. Park, CRC Handbook of Materials Science & Engineering, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakeri, M., Zanganeh, T. & Najafi, A. High-frequency induction heated sintering of ball milled Fe-WC nanocomposites. Int J Miner Metall Mater 20, 693–699 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0785-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0785-5