Abstract
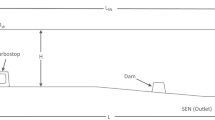
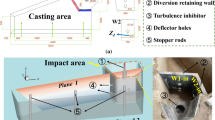
The metallurgical effect of a round tundish used to cast heavy steel ingots in machine works at present was evaluated through water modeling experiments. The flow control devices of the improved oval tundish, which was used instead of the round tundish, had been optimized. The results show that the residence time of the round tundish is short, its inclusion removal efficiency is too low, and it has more dead zones and an unreasonable flow field. Compared with the round tundish, the improved oval tundish with the optimized weir and dam has a better effect: its minimum residence time is prolonged by 38.1 s, the average residence time is prolonged by 233.4 s, its dead volume fraction decreases from 26% to 15%, and the ratio of plug volume fraction to dead volume fraction increases from 0.54 to 1.27. The inclusion removal efficiency also increases by 17.5%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.L. Jiang and M.F. Yu, Metallurgical technique for the heavy rotor ingot of high quality, Shanghai Met., 16(1994), No.5, p.23.
S. Susumu, S. Koreaki, and W. Juro, Application of advanced vacuum carbon dioxidized steels to heavy forging, [in] Effect of Melting and Process Variables on the Mechanical Property of Steel, Atlanta, 1997, p.89.
T.Y. Huang, X.G. Liu, J.W. Kang, et al., Situation and key technology on large steel casting production in China, Foundry, 56(2007), No.9, p.899.
L. Zhao, H.L. Liu, W.C. Cui, et al., Physical simulation research on the level fluctuate of intermediate ladle in die-casting, Heavy Cast. Forg., 9(2008), No.5, p.1.
Y.F. Wang, G.H. Wen, P. Tang, et al., Mathematical modeling of fluid flow, heat transfer and inclusion transport in a four strand tundish, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 14(2007), No.1, p.22.
M.M. Zhu, G.H. Wen, P. Tang, et al., Dissymmetric flow phenomenon in a multistrand tundish, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 14(2007), No.6, p.490.
L.C. Zhong, B.K. Li, Y.X. Zhu, et al., Fluid flow in a four-strand bloom continuous casting tundish with different flow modifiers, ISIJ Int., 47(2007), No.1, p.88.
X.J. Ruan, J.S. Li, J.B. Wang, et al., Optimizing of tundish structure in Xingcheng Special Steel, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing (in Chinese), 29(2007), Suppl.1, p.138.
Z.Y. Wei, Y.P. Bao, J.H. Liu, et al., Orthogonal analysis of water model study on the optimization of flow control devices in a six-strand tundish, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 14(2007), No.2, p.118.
A. Kumar, D. Mazumdar, and S.C. Koria, Modeling of fluid flow and residence time distribution in a four-strand tundish for enhancing inclusion removal, ISIJ Int., 48(2008), No.1, p.38.
J.G. Liu, H.C. Yan, L. Liu, and X.H. Wang, Water modeling of optimizing tundish flow field, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 14(2007), No.3, p.14.
Y. Sahai and T. Emi, Melt flow characterization in continuous casting tundishes, ISIJ Int., 36(1996), No.6, p.667.
H.Y. Tang, M. Yu, J.S. Li, et al., Numerical and physical simulation on inner structure optimization of a continuous casting tundish and its metallurgical effect (in Chinese), J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 31(2009), Suppl.1, p.38.
L.F. Zhang, S. Taniguchi, and K.K. Cai, Fluid flow and inclusion removal in continuous casting tundish, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 31(2000), p.253.
Y. Sahai and T. Emi, Physical modeling of melt flow in continuous casting tundishes, [in] Proceedings of the International Conference on Modelling and Simulation in Metallurgical Engineering and Materials Science, Beijing, 1996, p.11.
G.H. Wen, L.F. Zhang, P. Tang, et al., Modeling study on fluid flow and inclusion motion in 6-strand bloom caster tundishes, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 11(2004), No.4, p.310.
S.J. Zhang and M.Y. Zhu, Water model study of removal mechanism of inclusion in continuous casting tundish, Acta Metall. Sin., 43(2007), No.9, p.1004.
S.J. Zhang, S.G. Zheng, and M.Y. Zhu, Water model study on the mechanism of inclusion removal in a continuous casting tundish, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing (in Chinese), 29(2007), No.8, p.781.
J. Jiang, J.S. Li, and H.J. Wu, Water modeling of molten steel flow in a multi-strand tundish with gas blowing, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 17(2010), No.2, p.143.
S. Singh and S.C. Koria, Physical modeling of steel flow in continuous casting tundish, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 20(1993), No.3, p.222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was financially supported by the Key Special Project in the National Science & Technology Program during the Eleventh Five-Year Plan Period (No.2009ZX04014-061-7).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, Gh., Huang, Yf., Tang, P. et al. Improvement of tundish shape and optimization of flow control devices for sequence casting heavy steel ingots. Int J Miner Metall Mater 19, 15–20 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-012-0509-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-012-0509-2