Abstract
Objectives
To assess the association between Body Mass Index (BMI) and cause-specific mortality in older adults and to assess which BMI was associated with lowest mortality.
Design
Prospective study.
Setting
European towns.
Participants
1,980 older adults, aged 70–75 years from the SENECA (Survey in Europe on Nutrition and the Elderly: a concerted action) study.
Measurements
BMI, examined in 1988/1989, and mortality rates and causes of death during 10 years of follow-up.
Results
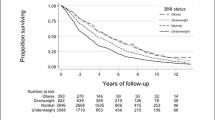
Cox proportional hazards model including both BMI and BMI2, accounting for sex, smoking status, educational level and age at baseline showed that BMI was associated with all-cause mortality (p<0.01), cardiovascular mortality (p<0.01) and mortality from other causes (p<0.01), but not with cancer or respiratory mortality (p>0.3). The lowest all-cause mortality risk was found at 27.1 (95%CI 24.1, 29.3) kg/m2, and this risk was increased with statistical significance when higher than 31.4 kg/m2 and lower than 21.1 kg/m2. The lowest cardiovascular mortality risk was found at 25.6 (95%CI 17.1, 28.4) kg/m2, and was increased with statistical significance when higher than 30.9 kg/m2.
Conclusion
In this study, BMI was associated with all-cause mortality risk in older people. This risk was mostly driven by an increased cardiovascular mortality risk, as no association was found for mortality risk from cancer or respiratory disease. Our results indicate that the WHO cut-off point of 25 kg/m2 for overweight might be too low in old age, but more studies are needed to define specific cut-off points.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branca F NH, Lobstein T. The challenge of obesity in the WHO European Region and the strategies for response. In: Organization DWH, ed Denmark: World Health Organization, 2007.
Janssen I, Mark AE. Elevated body mass index and mortality risk in the elderly. Obes Rev 2007;8(1):41–59.
Flicker L, McCaul KA, Hankey GJ, Jamrozik K, Brown WJ, Byles JE, Almeida OP. Body mass index and survival in men and women aged 70 to 75. J Am Geriatr Soc; 58(2):234–241.
Heiat A, Vaccarino V, Krumholz HM. An evidence-based assessment of federal guidelines for overweight and obesity as they apply to elderly persons. Arch Intern Med 2001;161(9):1194–1203.
Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB, Kipnis V, Mouw T, Ballard-Barbash R, Hollenbeck A, Leitzmann MF. Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N Engl J Med 2006;355(8):763–778.
Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH. Excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. Jama 2005;293(15):1861–1867.
Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH. Cause-specific excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA 2007;298(17):2028–2037.
Van’ t Hof MA, Hautvast JG, Schroll M, Vlachonikolis IG. Design, methods and participation. Euronut SENECA investigators. Eur J Clin Nutr 1991;45 Suppl 3:5–22.
De Groot C VSW. Nutrition and the elderly: manual of operations. (Report 11). In: Investigators TE-S, ed. Wageningen, the Netherlands, 1988.
Trichopoulou A, Costacou T, Bamia C, Trichopoulos D. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N Engl J Med 2003;348(26):2599–2608.
Knoops KT, de Groot LC, Kromhout D, Perrin AE, Moreiras-Varela O, Menotti A, van Staveren WA. Mediterranean diet, lifestyle factors, and 10-year mortality in elderly European men and women: the HALE project. Jama 2004;292(12):1433–1439.
Voorrips LE, Ravelli AC, Dongelmans PC, Deurenberg P, Van Staveren WA. A physical activity questionnaire for the elderly. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1991;23(8):974–979.
World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9). Geneva: World Health Organization, 1977.
Kivimaki M, Ferrie JE, Batty GD, Davey Smith G, Elovainio M, Marmot MG, Shipley MJ. Optimal form of operationalizing BMI in relation to all-cause and causespecific mortality: the original Whitehall study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16(8):1926–1932.
Manson JE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Rosner B, Monson RR, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH. A prospective study of obesity and risk of coronary heart disease in women. N Engl J Med 1990;322(13):882–889.
Willett WC, Dietz WH, Colditz GA. Guidelines for healthy weight. N Engl J Med 1999;341(6):427–434.
Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, Flint AJ, Hannan L, MacInnis RJ, Moore SC, Tobias GS, Anton-Culver H, Freeman LB, Beeson WL, Clipp SL, English DR, Folsom AR, Freedman DM, Giles G, Hakansson N, Henderson KD, Hoffman-Bolton J, Hoppin JA, Koenig KL, Lee IM, Linet MS, Park Y, Pocobelli G, Schatzkin A, Sesso HD, Weiderpass E, Willcox BJ, Wolk A, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Willett WC, Thun MJ. Body-mass index and mortality among 1.46 million white adults. N Engl J Med; 363(23):2211–2219.
van’t Hof MA, Burema J. Assessment of bias in the SENECA study. Eur J Clin Nutr 1996;50Suppl 2:S4–S8.
Sorkin JD, Muller DC, Andres R. Longitudinal change in height of men and women: implications for interpretation of the body mass index: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Am J Epidemiol 1999;150(9):969–977.
Zamboni M, Mazzali G, Zoico E, Harris TB, Meigs JB, Di Francesco V, Fantin F, Bissoli L, Bosello O. Health consequences of obesity in the elderly: a review of four unresolved questions. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005;29(9):1011–1029.
Al Snih S, Ottenbacher KJ, Markides KS, Kuo YF, Eschbach K, Goodwin JS. The effect of obesity on disability vs mortality in older Americans. Arch Intern Med 2007;167(8):774–780.
Locher JL, Roth DL, Ritchie CS, Cox K, Sawyer P, Bodner EV, Allman RM. Body mass index, weight loss, and mortality in community-dwelling older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2007;62(12):1389–1392.
Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Lennon L, Whincup PH. Decreased muscle mass and increased central adiposity are independently related to mortality in older men. Am J Clin Nutr 2007;86(5):1339–1346.
Baik I, Ascherio A, Rimm EB, Giovannucci E, Spiegelman D, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. Adiposity and mortality in men. Am J Epidemiol 2000;152(3):264–271.
Breeze E, Clarke R, Shipley MJ, Marmot MG, Fletcher AE. Cause-specific mortality in old age in relation to body mass index in middle age and in old age: follow-up of the Whitehall cohort of male civil servants. Int J Epidemiol 2006;35(1):169–178.
Dyer AR, Stamler J, Garside DB, Greenland P. Long-term consequences of body mass index for cardiovascular mortality: the Chicago Heart Association Detection Project in Industry study. Ann Epidemiol 2004;14(2):101–108.
Ni Mhurchu C, Rodgers A, Pan WH, Gu DF, Woodward M. Body mass index and cardiovascular disease in the Asia-Pacific Region: an overview of 33 cohorts involving 310 000 participants. Int J Epidemiol 2004;33(4):751–758.
Whitlock G, Lewington S, Sherliker P, Clarke R, Emberson J, Halsey J, Qizilbash N, Collins R, Peto R. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009;373(9669):1083–1096.
Engeland A, Bjorge T, Selmer RM, Tverdal A. Height and body mass index in relation to total mortality. Epidemiology 2003;14(3):293–299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Hollander, E., Van Zutphen, M., Bogers, R.P. et al. The impact of body mass index in old age on cause-specific mortality. J Nutr Health Aging 16, 100–106 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-011-0077-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-011-0077-6