Abstract
Osteoporosis is a systemic condition of the skeleton that leads to diminished bone mass, a breakdown in the bone tissue’s microscopic architecture, and an elevated risk of breaking a bone. The elderly and women particularly after menopause are disproportionately affected, and the condition generally stays undiagnosed until a broken bone causes severe pain and immobility. Causes of osteoporosis include low bone mass, more than normal bone loss, changes in hormone levels (decreased estrogen or testosterone), certain diseases and therapies, and lifestyle factors like smoking and inactivity. The spine, hip, and forearm are particularly vulnerable to osteoporosis-related fractures. The purpose of this article is to present a thorough understanding of osteoporosis, including the disease’s connection to bone density in humans, and the major part played by genetic pathways and gut flora. The causes of osteoporosis, the effects of aging on bone density, and why some groups experience a higher incidence of the disease than others are investigated. The paper also includes animal and human experiments investigating the link between gut flora and osteoporosis. Finally, it looks to the future and speculates on possible developments in osteoporosis prevention and therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Demontiero O, Vidal C, Duque G (2012) Aging and bone loss: new insights for the clinician. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 4:61–76. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720X11430858
Office of the Surgeon General (US) (2004) Bone health and osteoporosis: a report of the surgeon general. Rockville (MD): Office of the Surgeon General (US) 2004
Sozen T, Ozisik L, Calik Basaran N (2017) An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol 4:46–56. https://doi.org/10.5152/eurjrheum.2016.048
Pouresmaeili F, Kamalidehghan B, Kamarehei M, Goh YM (2018) A comprehensive overview on osteoporosis and its risk factors. Ther Clin Risk Manag 14:2029–2049. https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S138000
Siddiqui JA, Partridge NC (2016) Physiological bone remodeling: systemic regulation and growth factor involvement. Physiology 31:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00061.2014
Tu KN, Lie JD, Wan CKV et al (2018) Osteoporosis: a review of treatment options. Pharm Ther 43:92–104
Salari N, Darvishi N, Bartina Y et al (2021) Global prevalence of osteoporosis among the world older adults: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 16:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02821-8
Rozenberg S, Bruyère O, Bergmann P et al (2020) How to manage osteoporosis before the age of 50. Maturitas 138:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.05.004
De Martinis M, Sirufo MM, Polsinelli M et al (2020) Gender differences in osteoporosis: a single-center observational study. World J Mens Health 38:2287–4690. https://doi.org/10.5534/WJMH.200099
Alswat KA (2017) Gender disparities in osteoporosis. J Clin Med Res 9:382–387. https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr2970w
Björnsdottir S, Clarke BL, Mannstadt M, Langdahl BL (2022) Male osteoporosis-what are the causes, diagnostic challenges, and management. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2022.101766
LeBoff MS, Greenspan SL, Insogna KL et al (2022) The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 33:2049–2102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-021-05900-y
Release notice (2021) Osteoporosis and related fractures in Canada: report from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System 2020
Hou J, He C, He W et al (2020) Obesity and bone health: a complex link. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.600181
Noel SE, Santos MP, Wright NC (2021) Racial and ethnic disparities in bone health and outcomes in the United States. J Bone Miner Res 36:1881–1905. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.4417
Cauley JA (2011) Defining ethnic and racial differences in osteoporosis and fragility fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:1891–1899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1863-5
Prada D, Zhong J, Colicino E et al (2017) Association of air particulate pollution with bone loss over time and bone fracture risk: analysis of data from two independent studies. Lancet Planet Heal 1:e337–e347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30136-5
Wright NC, Melton ME, Sohail M et al (2019) Race plays a role in the knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs of women with osteoporosis. J Racial Ethn Heal Disparities 6:707–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-019-00569-w
Föger-Samwald U, Dovjak P, Azizi-Semrad U et al (2020) Osteoporosis: pathophysiology and therapeutic options. Excli J 19:1017–1037. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2020-2591
Marini F, Brandi ML (2010) Genetic determinants of osteoporosis: common bases to cardiovascular diseases? Int J Hypertens 2010. https://doi.org/10.4061/2010/394579
Mäkitie RE, Costantini A, Kämpe A et al (2019) New insights into monogenic causes of osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00070
Trajanoska K, Rivadeneira F (2019) The genetic architecture of osteoporosis and fracture risk. Bone 126:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2019.04.005
Zhu X, Bai W, Zheng H (2021) Twelve years of GWAS discoveries for osteoporosis and related traits: advances, challenges and applications. Bone Res 9(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-021-00143-3
Hou-Feng Z, Vincenzo F, Yi-Hsiang H et al (2015) Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture. Nature 526:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14878
Alonso N, Albagha OME, Azfer A et al (2023) Genome-wide association study identifies genetic variants which predict the response of bone mineral density to teriparatide therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 985–991. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2022-223618
Seely KD, Kotelko CA, Douglas H et al (2021) The human gut microbiota: a key mediator of osteoporosis and osteogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179452
Chen Y, Wang X, Zhang C et al (2022) Gut microbiota and bone diseases: a growing partnership. Front Microbiol 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.877776
Ke K, Arra M, Abu-Amer Y (2019) Mechanisms underlying bone loss associated with gut inflammation. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246323
Yan Q, Cai L, Guo W (2022) New advances in improving bone health based on specific gut microbiota. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.821429
Behera J, Ison J, Tyagi SC, Tyagi N (2020) The role of gut microbiota in bone homeostasis. Bone 135:115317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2020.115317
Li S, Mao Y, Zhou F et al (2020) Gut microbiome and osteoporosis. Bone Jt Res 9:524–530. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.98.BJR-2020-0089.R1
Cooney OD, Nagareddy PR, Murphy AJ, Lee MKS (2021) Healthy gut, healthy bones: targeting the gut microbiome to promote bone health. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.620466
Wu HJ, Wu E (2012) The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 3:4–14. https://doi.org/10.4161/gmic.19320
Zheng D, Liwinski T, Elinav E (2020) Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res 30:492–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0332-7
Chen Y, Xu J, Chen Y (2021) Regulation of neurotransmitters by the gut microbiota and effects on cognition in neurological disorders. Nutrients 13:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062099
Li J, Ho WTP, Liu C et al (2021) The role of gut microbiota in bone homeostasis. Bone Jt Res 10:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.101.BJR-2020-0273.R1
Okoro PC, Orwoll ES, Huttenhower C et al (2023) A two-cohort study on the association between the gut microbiota and bone density, microarchitecture, and strength. Front Endocrinol 14:1237727. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1237727
Cronin O, Lanham-New SA, Corfe BM et al (2022) Role of the microbiome in regulating bone metabolism and susceptibility to osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int 110:273–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-021-00924-2
Lorenzo J (2021) From the gut to bone: connecting the gut microbiota with Th17 T lymphocytes and postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Clin Invest 131:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI146619
Chevalier C, Kieser S, Çolakoğlu M et al (2020) Warmth prevents bone loss through the gut microbiota. Cell Metab 32:575-590.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.012
Wei H, Xu Y, Wang Y et al (2020) Identification of fibroblast activation protein as an osteogenic suppressor and anti-osteoporosis drug target. Cell Rep 33:108252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108252
Zhang J, Lu Y, Wang Y et al (2018) The impact of the intestinal microbiome on bone health. Intractable Rare Dis Res 7:148–155. https://doi.org/10.5582/irdr.2018.01055
Zemanova N, Omelka R, Mondockova V et al (2022) Roles of gut microbiome in bone homeostasis and its relationship with bone-related diseases. Biology (Basel) 11:1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101402
Li C, Pi G, Li F (2021) The role of intestinal flora in the regulation of bone homeostasis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.579323
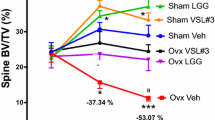
Jansson PA, Curiac D, Lazou Ahrén I et al (2019) Probiotic treatment using a mix of three Lactobacillus strains for lumbar spine bone loss in postmenopausal women: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Rheumatol 1:e154–e162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(19)30068-2
Jones RM, Mulle JG, Pacifici R (2018) Osteomicrobiology: the influence of gut microbiota on bone in health and disease. Bone 115:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2017.04.009
Takayanagi H (2007) Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol 7:292–304. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2062
Yan J, Herzog JW, Tsang K et al (2016) Gut microbiota induce IGF-1 and promote bone formation and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E7554–E7563. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1607235113
Chen Z, Cai Z, Zhuang P et al (2023) Living probiotic biomaterials for osteoporosis therapy. Biomed Technol 1:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmt.2022.11.007
Mutuş R, Kocabaǧli N, Alp M et al (2006) The effect of dietary probiotic supplementation on tibial bone characteristics and strength in broilers. Poult Sci 85:1621–1625. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/85.9.1621
Rodrigues FC, Castro ASB, Rodrigues VC et al (2012) Yacon flour and bifidobacterium longum modulate bone health in rats. J Med Food 15:664–670. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2011.0296
Tomofuji T, Ekuni D, Azuma T et al (2012) Supplementation of broccoli or Bifidobacterium longum-fermented broccoli suppresses serum lipid peroxidation and osteoclast differentiation on alveolar bone surface in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Nutr Res 32:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2012.03.006
Mccabe LR, Irwin R, Schaefer L, Britton RA (2013) Probiotic use decreases intestinal inflammation and increases bone density in healthy male but not female mice. J Cell Physiol 228:1793–1798. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24340
Kruger MC, Fear A, Chua WH et al (2009) The effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 on mineral absorption and bone health in growing male and ovariectomised female rats. Dairy Sci Technol 89:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1051/dst/2009012
Favazzo LJ, Hendesi H, Villani DA et al (2020) The gut microbiome-joint connection: Implications in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 32:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000681
Wei J, Zhang C, Zhang Y et al (2021) Association between gut microbiota and symptomatic hand osteoarthritis: data from the Xiangya Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheumatol 73:1656–1662. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41729
Chiang SS, Pan TM (2011) Antiosteoporotic effects of lactobacillus-fermented soy skim milk on bone mineral density and the microstructure of femoral bone in ovariectomized mice. J Agric Food Chem 59:7734–7742. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2013716
Kim JG, Lee E, Kim SH et al (2009) Effects of a Lactobacillus casei 393 fermented milk product on bone metabolism in ovariectomised rats. Int Dairy J 19:690–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.06.009
Liu H, Gu R, Li W et al (2019) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG attenuates tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-induced bone loss in male mice via gut-microbiota-dependent anti-inflammation. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 10:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622319860653
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. J. A.: conceptualization, writing original draft, review and editing. V. K. and A. R.: writing original draft, review and editing. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
J. J. A. was employed by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Limited. Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories had no direct and indirect role in the design/analysis/writing/publication of this review article. Other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahire, J.J., Kumar, V. & Rohilla, A. Understanding Osteoporosis: Human Bone Density, Genetic Mechanisms, Gut Microbiota, and Future Prospects. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 16, 875–883 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-023-10185-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-023-10185-0