Abstract
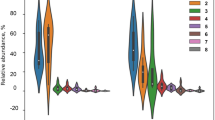
Gut microbiota has been proven to be of crucial importance in maintaining human health. However, the microbiota profile changes with aging, while the loss of microbiota diversity and the alterations in the optimal composition and quantity of beneficial microbes are believed to increase the risk of many diseases. Although the short-term modulatory impact of probiotics on gut microbiota has been revealed in various studies, no studies focused on longer time consumption of probiotics have been demonstrated. In this study, we found that microbial diversity in the probiotic group was similar to that in the control. We identified a panel of microbiota changes, such as Blautia (10.24 vs. 3.76%, P = 0.006), Streptococcus (7.38 vs. 1.16%, P = 0.004), and Enterococcus (0.13 vs. 0.00%, P = 0.030) were more abundant in the probiotic group. Faecalibacterium, a genus containing anti-inflammatory property, also had a higher abundance in the probiotic group in the gut. The microbiota architecture in the different probiotic dose groups was also revealed. No statistical difference was observed in regard to the short-chain fatty acid concentration between the groups. High-dose intake of probiotics resulted in lower microbial richness. The profile of inflammatory factors indicated that only the level of IL-1β was higher in the probiotic population. Taken together, our study demonstrated that the long-time intake of probiotics caused significant changes in the gut microbiota structure, including an increase in the composition of beneficial microorganisms, which might contribute to the maintenance of host health and homeostasis of microenvironment. More prospective cohorts were needed to illustrate the influences of probiotics on the gut microbiota.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plottel CS, Blaser MJ (2011) Microbiome and malignancy. Cell Host Microbe 10(4):324–335
Manichanh C, Borruel N, Casellas F, Guarner F (2012) The gut microbiota in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(10):599–608
Abreu MT, Peek RM Jr (2014) Gastrointestinal malignancy and the microbiome. Gastroenterology 146(6):1534–1546 e1533
Sears CL, Garrett WS (2014) Microbes, microbiota, and colon cancer. Cell Host Microbe 15(3):317–328
Garrett WS (2015) Cancer and the microbiota. Science 348(6230):80–86
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, Peng Y, Zhang D, Jie Z, Wu W, Qin Y, Xue W, Li J, Han L, Lu D, Wu P, Dai Y, Sun X, Li Z, Tang A, Zhong S, Li X, Chen W, Xu R, Wang M, Feng Q, Gong M, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Hansen T, Sanchez G, Raes J, Falony G, Okuda S, Almeida M, LeChatelier E, Renault P, Pons N, Batto JM, Zhang Z, Chen H, Yang R, Zheng W, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Nielsen R, Pedersen O, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490(7418):55–60
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444(7122):1027–1031
Qin N, Yang F, Li A, Prifti E, Chen Y, Shao L, Guo J, Le Chatelier E, Yao J, Wu L, Zhou J, Ni S, Liu L, Pons N, Batto JM, Kennedy SP, Leonard P, Yuan C, Ding W, Chen Y, Hu X, Zheng B, Qian G, Xu W, Ehrlich SD, Zheng S, Li L (2014) Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 513(7516):59–64
Zhu W, Gregory JC, Org E, Buffa JA, Gupta N, Wang Z, Li L, Fu X, Wu Y, Mehrabian M, Sartor RB, McIntyre TM, Silverstein RL, Tang WH, DiDonato JA, Brown JM, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL (2016) Gut microbial metabolite TMAO enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis risk. Cell 165(1):111–124
Schroeder BO, Backhed F (2016) Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat Med 22(10):1079–1089
Engen PA, Green SJ, Voigt RM, Forsyth CB, Keshavarzian A (2015) The gastrointestinal microbiome: alcohol effects on the composition of intestinal microbiota. Alcohol Res 37(2):223–236
Goodrich JK, Waters JL, Poole AC, Sutter JL, Koren O, Blekhman R, Beaumont M, Van Treuren W, Knight R, Bell JT, Spector TD, Clark AG, Ley RE (2014) Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159(4):789–799
Ekmekciu I, von Klitzing E, Fiebiger U, Neumann C, Bacher P, Scheffold A, Bereswill S, Heimesaat MM (2017) The probiotic compound VSL#3 modulates mucosal, peripheral, and systemic immunity following murine broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:167
Gareau MG, Sherman PM, Walker WA (2010) Probiotics and the gut microbiota in intestinal health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(9):503–514
Varankovich NV, Nickerson MT, Korber DR (2015) Probiotic-based strategies for therapeutic and prophylactic use against multiple gastrointestinal diseases. Front Microbiol 6:685
Redman MG, Ward EJ, Phillips RS (2014) The efficacy and safety of probiotics in people with cancer: a systematic review. Ann Oncol 25(10):1919–1929
Le Barz M, Anhe FF, Varin TV, Desjardins Y, Levy E, Roy D, Urdaci MC, Marette A (2015) Probiotics as complementary treatment for metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metab J 39(4):291–303
Panwar H, Rashmi HM, Batish VK, Grover S (2013) Probiotics as potential biotherapeutics in the management of type 2 diabetes—prospects and perspectives. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 29(2):103–112
Moayyedi P, Ford AC, Talley NJ, Cremonini F, Foxx-Orenstein AE, Brandt LJ, Quigley EM (2010) The efficacy of probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review. Gut 59(3):325–332
Wasilewski A, Zielinska M, Storr M, Fichna J (2015) Beneficial effects of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and psychobiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 21(7):1674–1682
Hempel S, Newberry SJ, Maher AR, Wang Z, Miles JN, Shanman R, Johnsen B, Shekelle PG (2012) Probiotics for the prevention and treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 307(18):1959–1969
Spaiser SJ, Culpepper T, Nieves C Jr, Ukhanova M, Mai V, Percival SS, Christman MC, Langkamp-Henken B (2015) Lactobacillus gasseri KS-13, Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1, and Bifidobacterium longum MM-2 ingestion induces a less inflammatory cytokine profile and a potentially beneficial shift in gut microbiota in older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. J Am Coll Nutr:1–11
Wang J, Tang H, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Derrien M, Rocher E, van-Hylckama Vlieg JE, Strissel K, Zhao L, Obin M, Shen J (2015) Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. ISME J 9(1):1–15
Hulston CJ, Churnside AA, Venables MC (2015) Probiotic supplementation prevents high-fat, overfeeding-induced insulin resistance in human subjects. Br J Nutr 113(4):596–602
Tytgat HL, Douillard FP, Reunanen J, Rasinkangas P, Hendrickx AP, Laine PK, Paulin L, Satokari R, de Vos WM (2016) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG outcompetes enterococcus faecium via mucus-binding pili: evidence for a novel and heterospecific probiotic mechanism. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(19):5756–5762
Petrof EO, Kojima K, Ropeleski MJ, Musch MW, Tao Y, De Simone C, Chang EB (2004) Probiotics inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B and induce heat shock proteins in colonic epithelial cells through proteasome inhibition. Gastroenterology 127(5):1474–1487
Ciorba MA, Riehl TE, Rao MS, Moon C, Ee X, Nava GM, Walker MR, Marinshaw JM, Stappenbeck TS, Stenson WF (2012) Lactobacillus probiotic protects intestinal epithelium from radiation injury in a TLR-2/cyclo-oxygenase-2-dependent manner. Gut 61(6):829–838
Perdigon G, de Moreno de LeBlanc A, Valdez J, Rachid M (2002) Role of yoghurt in the prevention of colon cancer. Eur J Clin Nutr 56(Suppl 3):S65–S68
Kato K, Mizuno S, Umesaki Y, Ishii Y, Sugitani M, Imaoka A, Otsuka M, Hasunuma O, Kurihara R, Iwasaki A, Arakawa Y (2004) Randomized placebo-controlled trial assessing the effect of bifidobacteria-fermented milk on active ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20(10):1133–1141
Ohigashi S, Sudo K, Kobayashi D, Takahashi O, Takahashi T, Asahara T, Nomoto K, Onodera H (2013) Changes of the intestinal microbiota, short chain fatty acids, and fecal pH in patients with colorectal cancer. Dig Dis Sci 58(6):1717–1726
Li J, Sung CY, Lee N, Ni Y, Pihlajamaki J, Panagiotou G, El-Nezami H (2016) Probiotics modulated gut microbiota suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(9):E1306–E1315
Sivan A, Corrales L, Hubert N, Williams JB, Aquino-Michaels K, Earley ZM, Benyamin FW, Lei YM, Jabri B, Alegre ML, Chang EB, Gajewski TF (2015) Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science 350(6264):1084–1089
Kristensen NB, Bryrup T, Allin KH, Nielsen T, Hansen TH, Pedersen O (2016) Alterations in fecal microbiota composition by probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Genome Med 8(1):52
Charbonneau D, Gibb RD, Quigley EM (2013) Fecal excretion of Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 and changes in fecal microbiota after eight weeks of oral supplementation with encapsulated probiotic. Gut Microbes 4(3):201–211
Alberda C, Gramlich L, Meddings J, Field C, McCargar L, Kutsogiannis D, Fedorak R, Madsen K (2007) Effects of probiotic therapy in critically ill patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 85(3):816–823
Madden JA, Hunter JO (2002) A review of the role of the gut microflora in irritable bowel syndrome and the effects of probiotics. Br J Nutr 88(Suppl 1):S67–S72
Kruis W, Fric P, Pokrotnieks J, Lukas M, Fixa B, Kascak M, Kamm MA, Weismueller J, Beglinger C, Stolte M, Wolff C, Schulze J (2004) Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 53(11):1617–1623
Woodcock NP, McNaught CE, Morgan DR, Gregg KL, MacFie J (2004) An investigation into the effect of a probiotic on gut immune function in surgical patients. Clin Nutr 23(5):1069–1073
Simren M, Ohman L, Olsson J, Svensson U, Ohlson K, Posserud I, Strid H (2010) Clinical trial: the effects of a fermented milk containing three probiotic bacteria in patients with irritable bowel syndrome—a randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 31(2):218–227
Steed H, Macfarlane GT, Blackett KL, Bahrami B, Reynolds N, Walsh SV, Cummings JH, Macfarlane S (2010) Clinical trial: the microbiological and immunological effects of synbiotic consumption—a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study in active Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 32(7):872–883
Delzenne NM, Neyrinck AM, Backhed F, Cani PD (2011) Targeting gut microbiota in obesity: effects of prebiotics and probiotics. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7(11):639–646
Zhang Q, Wu Y, Fei X (2016) Effect of probiotics on glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicina 52(1):28–34
Urbanska M, Gieruszczak-Bialek D, Szajewska H (2016) Systematic review with meta-analysis: Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for diarrhoeal diseases in children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43(10):1025–1034
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Xu J, Xue Z, Zhang M, Pang X, Zhang X, Zhao L (2015) Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine and metformin during the treatment of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. Sci Rep 5:14405
Ferrario C, Taverniti V, Milani C, Fiore W, Laureati M, De Noni I, Stuknyte M, Chouaia B, Riso P, Guglielmetti S (2014) Modulation of fecal Clostridiales bacteria and butyrate by probiotic intervention with Lactobacillus paracasei DG varies among healthy adults. J Nutr 144(11):1787–1796
Quevrain E, Maubert MA, Michon C, Chain F, Marquant R, Tailhades J, Miquel S, Carlier L, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Pigneur B, Lequin O, Kharrat P, Thomas G, Rainteau D, Aubry C, Breyner N, Afonso C, Lavielle S, Grill JP, Chassaing G, Chatel JM, Trugnan G, Xavier R, Langella P, Sokol H, Seksik P (2016) Identification of an anti-inflammatory protein from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a commensal bacterium deficient in Crohn’s disease. Gut 65(3):415–425
Heinken A, Khan MT, Paglia G, Rodionov DA, Harmsen HJ, Thiele I (2014) Functional metabolic map of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a beneficial human gut microbe. J Bacteriol 196(18):3289–3302
Eloe-Fadrosh EA, Brady A, Crabtree J, Drabek EF, Ma B, Mahurkar A, Ravel J, Haverkamp M, Fiorino AM, Botelho C, Andreyeva I, Hibberd PL, Fraser CM (2015) Functional dynamics of the gut microbiome in elderly people during probiotic consumption. MBio 6(2):e00231–e00215
Kajander K, Krogius-Kurikka L, Rinttila T, Karjalainen H, Palva A, Korpela R (2007) Effects of multispecies probiotic supplementation on intestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26(3):463–473
Liu Z, Qin H, Yang Z, Xia Y, Liu W, Yang J, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Yang Z, Wang Y, Zheng Q (2011) Randomised clinical trial: the effects of perioperative probiotic treatment on barrier function and post-operative infectious complications in colorectal cancer surgery—a double-blind study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 33(1):50–63
Persborn M, Gerritsen J, Wallon C, Carlsson A, Akkermans LM, Soderholm JD (2013) The effects of probiotics on barrier function and mucosal pouch microbiota during maintenance treatment for severe pouchitis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 38(7):772–783
Odamaki T, Sugahara H, Yonezawa S, Yaeshima T, Iwatsuki K, Tanabe S, Tominaga T, Togashi H, Benno Y, Xiao JZ (2012) Effect of the oral intake of yogurt containing Bifidobacterium longum BB536 on the cell numbers of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis in microbiota. Anaerobe 18(1):14–18
Sun J, Buys N (2015) Effects of probiotics consumption on lowering lipids and CVD risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Med 47(6):430–440
Azad MB, Coneys JG, Kozyrskyj AL, Field CJ, Ramsey CD, Becker AB, Friesen C, Abou-Setta AM, Zarychanski R (2013) Probiotic supplementation during pregnancy or infancy for the prevention of asthma and wheeze: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 347:f6471
Sanders ME, Guarner F, Guerrant R, Holt PR, Quigley EM, Sartor RB, Sherman PM, Mayer EA (2013) An update on the use and investigation of probiotics in health and disease. Gut 62(5):787–796
Sung V, Collett S, de Gooyer T, Hiscock H, Tang M, Wake M (2013) Probiotics to prevent or treat excessive infant crying: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr 167(12):1150–1157
Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ (2016) Fecal microbiota, fecal metabolome, and colorectal cancer interrelations. PLoS One 11(3):e0152126
Falony G, Joossens M, Vieira-Silva S, Wang J, Darzi Y, Faust K, Kurilshikov A, Bonder MJ, Valles-Colomer M, Vandeputte D, Tito RY, Chaffron S, Rymenans L, Verspecht C, De Sutter L, Lima-Mendez G, D'Hoe K, Jonckheere K, Homola D, Garcia R, Tigchelaar EF, Eeckhaudt L, Fu J, Henckaerts L, Zhernakova A, Wijmenga C, Raes J (2016) Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation. Science 352(6285):560–564
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the great cooperation of the individuals who voluntarily participated in this study. We also thank major biomedicine technology co., LTD for their technical assistance.
Funding
This study was supported by projects from the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81730102, 81230057, 81472262), Emerging Cutting-Edge Technology Joint Research projects of Shanghai (nos. SHDC12017112, 12012106), and Tongji University Subject Pilot Program (no. 162385).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The experiments were conceived and designed by H.L.Q. The study was performed by R.Y.G. and R.R.S. The data was analyzed by R.Y.G., X.H.Z, and L.S.H. Finally, R.Y.G. and H.L.Q. were responsible for writing the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This study has been approved by the ethical committees of Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital.
Informed Consent
All the participants provided informed consents.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary Figure 1
The rarefaction curves of the detected samples. (GIF 96.1 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
The rarefaction estimation by shannon of all the samples. (GIF 55.8 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, R., Zhang, X., Huang, L. et al. Gut Microbiota Alteration After Long-Term Consumption of Probiotics in the Elderly. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 11, 655–666 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9403-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9403-1