Abstract
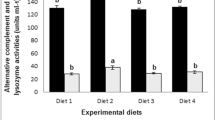
This study investigated the effect of dietary supplementation of probiotic Pedicoccus acidilactici and nucleotide (separately or combined) on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, hemato-immunological parameters, and immunity response in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Fish (average weight 5–6 g) were acclimatized and divided into eight experimental diets supplemented with P. acidilactici of different concentrations (0.1, 0.2, and 0.3% diet) and nucleotides (0 and 0.5% diet) for 6 months. Fish fed with experimental diets showed significant differences in terms of final weight, weight gain, feed conversion ratio, daily growth rate, and condition factor when compared to control diet (P < 0.05). Fish fed with probiotic (0.3%) separately and combined with nucleotide (0.5%) had highest RBC and WBC when compared to other diets (P < 0.05), while the highest values for Hb and Hct as well as total protein, glucose, albumin, and globulin were observed in probiotic (0.2%) and nucleotide (0.5%) combined diet. Serum lysozyme and anti-protease activities were significantly higher in probiotic (0.1 and 0.2%) and nucleotide (0.5%) combined diets. Similarly, these two diets combined showed the highest colonization of P. acidilactici when compared to other diets. In conclusion, combined dietary probiotic and nucleotide improve the growth performance, hemato-biochemical parameters, and intestine growth in C. auratus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vannuccini S (2004) Overview of fish production, utilization, consumption and trade. FAO, Fishery Information, Data and Statistics Unit. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome www.fao.org
Sinha A, Ghosh S, Singh D (2004) Probiotics and nutrient supplement in artificial feed of gold fish (Carassius auratus). J Indian Fish 31:139–144
Low C, Wadsworth S, Burrells C, Secombe CJ (2003) Expression of immune genes in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) fed a nucleotide-supplemented diet. Aquaculture 221:23–40
Mackie AM (1973) The chemical basis of food detection in the lobster Homarus gammarus. Mar Biol 21:103–108
Kiyohara S, Hidaka I, Tamura T (1975) Gustatory response in the puffer-II. Single fiber analysis. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 41:383–391
Mackie AM, Adron JW (1978) Identification of inosine and inosine 5V-monophosphate as the gustatory feeding stimulants for the turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Comp Biochem Physiol 60A:79–83
Li P, Gatlin DM (2006) Nucleotide nutrition in fish: current knowledge and future applications. Aquaculture 251:141–152
CAC (1997) General requirements (food hygiene). Supplement to Vol. 1. B. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, FAO, Rome
Fuller R (1989) Probiotics in man and animals. A review J Appl Microbiol 66:365–378
Gildberg A, Mikkelsen H, Sandaker E, Ring E (1997) Probiotic effect of lactic acid bacteria in the feed on growth and survival of fry of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Hydrobiologia 352:279–285
Nikoskelainen S, Ouwehand AC, Bylund G, Salminen S, Lilius E (2003) Immune enhancement in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by potential probiotic bacteria (Lactobacillus rhamnosus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 15:443–452
Stiles ME (1996) Biopreservation by lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 70:331–345
Jamuna M, Jeevaratnam K (2004) Isolation and partial characterization of bacteriocins from Pediococcus species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:433–439
Villamil L, Figueras A, Planas M, Novoa B (2010) Pediococcus acidilactici in the culture of turbot (Psetta maxima) larvae: administration pathways. Aquaculture 307:83–88
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) (1995) Official methods of analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 16th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington
Azarin H, Aramli MS, Imanpour MR, Rajabpour M (2015) Effect of a probiotic containing Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis and ferroin solution on growth performance, body composition and haematological parameters in kutum (Rutilus frisii kutum) fry. Probiotics and Antimicro Prot 7:31–37
Brett J, Groves T (1979) Physiological energetics. Fish Physiology 8:279–352
Merrifield DL, Bradley G, Harper GM, Baker RTM, Munn CB, Davies SJ (2011) Assessment of the effects of vegetative and lyophilized Pediococcus acidilactici on growth, feed utilization, intestinal colonization and health parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquac Nutr 17:73–79
Herigstad B, Hamilton M, Heersink J (2001) How to optimize the drop plate method for enumerating bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 44:121–129
Geraylou Z, Souffreau C, Rurangwa E, De Meester L, Courtin CM, Delcour JA et al (2013) Effects of dietary arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides (AXOS) and endogenous probiotics on the growth performance, non-specific immunity and gut microbiota of juvenile Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:766–775
Blaxhall PC, Daisley KW (1973) Routine haematological methods for use with fish blood. J Fish Biol 5:771–781
Collier HB (1994) The standardization of blood hemoglobin determinations. Can Med Assoc J 50:550–552
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Shahsavani D, Mohri M, Gholipour K (2010) Determination of normal values of some blood serum enzymes in Acipenser stellatus Pallas. Fish Physiol Biochem 36:39–43
Ellis TA (1990) Lysozyme assays. In: Stolen JS, Fletcher TC, Anderson DP, Roberson BS, Van Muiswinkel WB (eds) Techniques in fish immunology. SOS Publications, Fair Haven, pp 101–103
Magnadóttir B, Jónsdóttir H, Helgason S, Björnsson B, Jørgensen TØ, Pilström L (1999) Humoral immune parameters in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.): the effects of environmental temperature. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 122(2):173–180
Zuo X, Woo PTK (1997) Natural anti-proteases in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss and brook charr, Salvelinus fontinalis and the in vitro neutralization of fish α2-macroglobulin by the metalloprotease from the pathogenic haemoflagellate, Crytobia salmositica. Parasitology 114(4):375–381
Hoseinifar SH, Mirvaghefi A, Mojazi Amiri B, Rostami HK, Merrifield DL (2011) The effects of oligofructose on growth performance, survival and autochthonous intestinal microbiota of beluga (Huso huso) juveniles. Aquac Nutr 17:498–504
Rawling MD, Merrifield DL, Davies SJ (2009) Preliminary assessment of dietary supplementation of Sangrovit on red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth performance and health. Aquaculture 294:118–122
Kongnum K, Hongpattarakere T (2012) Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from digestive tract of wild shrimp on growth and survival of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) challenged with Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:170–177
Dash G, Prakash Raman R, Pani Prasad K, Makesh M, Pradeep MA, Sen S (2015) Evaluation of paraprobiotic applicability of Lactobacillus plantarumin improving the immune response and disease protection in giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man, 1879). Fish Shellfish Immunol 43:167–174
Son VM, Chang CC, Wu MC, Guu YK, Chiu CH, Cheng W (2009) Dietary administration of the probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum, enhanced the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:691–698
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015) Interaction effects of dietary supplementation of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum and β-glucan on growth performance, digestibility and immune response of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45(1):33–42
Kim D, Beck BR, Saet BH, Kim J, Kim HD, Lee SM et al (2013) Lactococcus lactis BFE920 activates the innate immune system of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), resulting in protection against Streptococcus iniae infection and enhancing feed efficiency and weight gain in large-scale field studies. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:1585–1590
Pirarat N, Pinpimai K, Endo M, Katagiri T, Ponpornpisit A, Chansue N et al (2011) Modulation of intestinal morphology and immunity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Res Vet Sci 91(3):92–97
Li P, Gatlin DM III, Neill WH (2007) Dietary supplementation of a purified nucleotide mixture transiently enhanced growth and feed utilization of juvenile red drum, Sciaenops ocellatus. J World Aquacult Soc 38:281–286
Tahmasebi-Kohyani A, Keyvanshokooh S, Nematollahi A, Mahmoudi N, Pasha-Zanoosi H (2011) Dietary administration of nucleotides to enhance growth, humoral immune responses, and disease resistance of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fingerlings. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:189–193
Abtahi B, Yousefi M, Abedian Kenari A (2013) Influence of dietary nucleotides supplementation on growth, body composition and fatty acid profile of beluga sturgeon juveniles (Huso huso). Aquac Res 44:254–260
Metailler R, Cadena-Roa M, Person-Le Ruyet J (1983) Attractive chemical substances for the weaning of dover sole (Solea vulgaris): qualitative and quantitative approach. J World Maric Soc 14:679–684
Li P, Lewi DH, Gatlin DM III (2004) Dietary oligonucleotide from yeast RNA influences immune responses and resistance of hybrid striped bass (Morone chrysops × M. saxatilis) to Streptococcus iniae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 16:561–569
Barros MM, Giumaraes IG, Pezzato LE, Orsi ROD, Junior ACF, Teixeira CP et al (2015) The effect of dietary nucleotide mixture on growth performance, hematological and immunological parameters of Nile tilapia. Aqua Res 46:987–993
Abedian-Kenari A, Mahmoudi N, Soltani M, Abedian-Kenari S (2012) Dietary nucleotide supplements influence the growth hemato-immunological parameters and stress responses in endangered Caspian brown trout (Salmo trutta caspius Kessler, 1877). Aqua Nutr 938:1365–2095
Yaghobi M, Paykan Heyrati F, Akhlaghi M, Dorafshan S, Mahmoudi N (2014) Intestinal microbiota of striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878) fed on dietary nucleotide. Iran J Ichthyol 1(4):274–280
Xu L, Ran C, He S, Zhang J, Hu J, Yang Y et al (2015) Effects of dietary yeast nucleotides on growth, non-specific immunity, intestine growth and intestinal microbiota of juvenile hybrid tilapia Oreochromis niloticus ♀ Oreochromis aureus ♂. Animal Nutrition 1:244–251
Ferguson RMW, Merrifield DL, Harper GM, Rawling MD, Mustafa S, Picchietti S et al (2010) The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici on the gut microbiota and immune status of on-growing red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Appl Microbiol 109(3):851–862
Rawls JF, Mahowald MA, Ley RE, Gordon JI (2006) Reciprocal gut microbiota transplants from zebrafish and mice to germ-free recipients reveal host habitat selection. Cell 127:423–433
Svobodova Z, Fravda D, Palakova J (1991) Unified methods of haematological examination of fish. Research Institute of Fish Culture and Hydrobiology. Czechoslovakia, Vodnany
Irianto A, Austin B (2002) Use of probiotics to control furunculosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 25:333–342
Brunt J, Austin B (2005) Use of a probiotic to control lactococcosis and streptococcosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 28:693–701
Yaghobi M, Dorafshan S, Paykan Heyrati F, Mahmoudi N (2014) Growth performance and some haematological parameters of ornamental striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) fed on dietary nucleotide. IJVR 15(3):262–265
Burrells C, Williams PD, Forno PF (2001) Dietary nucleotides: a novel supplement in fish feeds: 1. Effects on resistance to disease in salmonids. Aquaculture 199:159–169
Welker TL, Lim C, Yildirim-Aksoy M, Klesius PH (2011) Effects of dietary supplementation of a purified nucleotide mixture on immune function and disease and stress resistance in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Aquac Res 42:1878–1889
Jha AK, Pal AK, Sahu NP, Kumar S, Mukherjee SC (2007) Haematoimmunological responses to dietary yeast RNA, ω-3 fatty acid and b-carotene in Catla catla juveniles. Fish Shell Immunol 23:917–927
Yousefi M, Abtahi B, Abedian Kenari M (2012) Hematological, serum biochemical parameters, and physiological responses to acute stress of beluga sturgeon (Huso huso, Linnaeus 1785) juveniles fed dietary nucleotide. Comp Clin Pathol 21:1043–1048
Pourgholam MA, Khara H, Safari R, Yazdani Sadat MA, Aramli MS (2017) Influence of Lactobacillus plantarum inclusion in the diet of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) on performance and hematological parameters. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 17(1):1–5
Wang Y-B, Tian Z-Q, Yao J-T, Li W-F (2008) Effect of probiotics, Enteroccus faecium, on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth performance and immune response. Aquaculture 277:203–207
Panigrahi A, Kiron V, Kobayashi T, Puangkaew J, Satoh S, Sugita H (2004) Immune responses in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss induced by a potential probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus JCM 1136. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 102:379–388
Sakai M, Taniguchi K, Mamoto K, Ogawa H, Tabata M (2001) Immunostimulant effects of nucleotide isolated from yeast RNA on carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J Fish Dis 24:433–438
Cheng Z, Buentello A, Gatlin DM III (2011) Dietary nucleotides influence immune responses and intestinal morphology of red drum Sciaenops ocellatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:143–147
Standen BT, Rawling MD, Davies SJ, Castex M, Foey A, Gioacchini G et al (2013) Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici modulates both localised intestinal and peripheral-immunity in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:1097–1104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All fish manipulations were conducted in accordance with the guidelines on the care and use of animals for scientific purposes (National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehdinejad, N., Imanpour, M.R. & Jafari, V. Combined or Individual Effects of Dietary Probiotic Pedicoccus acidilactici and Nucleotide on Growth Performance, Intestinal Microbiota, Hemato-biochemical Parameters, and Innate Immune Response in Goldfish (Carassius auratus). Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 10, 558–565 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9297-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9297-3