Abstract
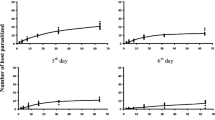
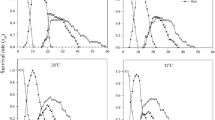
Aphelinus asychis has been used to control various species of aphids. Temperature is a crucial abiotic factor for the development and reproduction of insects. This study examined the influence of different constant temperatures (20, 25 and 30 °C) on the longevity, net reproductive rate (R0), intrinsic rate of increase (r), net killing rate (Z0) and finite killing rate (θ) of A. asychis parasitizing the cabbage pest Myzus persicae, and compared its control efficiency. The results showed that increasing temperature decreased the longevity of A. asychis significantly. The value of r was significantly higher at 30 °C than at 25 and 20o C. Similarly, θ was significantly higher at 30 °C (0.7163 aphids) than at 25 (0.5654 aphids) and 20o C (0.3522 aphids). Aphelinus asychis could produce progeny successfully within the range of 20-30 °C and its control efficiency was higher at high temperatures than at low temperatures. We discuss the implications of these results for the application of this parasitoid for the biological control of the cabbage aphid in greenhouse and field conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akköprü, E.P., Atl han, R., Okut, H., & Chi, H. (2015). Demographic assessment of plant cultivar resistance to insect pests: A case study of the dusky-veined walnut aphid (Hemiptera: Callaphididae) on five walnut cultivars. Journal of Economic Entomology, 108, 378–387.
Anstead, J. A., Mallet, J., & Denholm, I. (2007). Temporal and spatial incidence of alleles conferring knockdown resistance to pyrethroids in the peach-potato aphid, Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae), and their association with other insecticide resistance mechanisms. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 97, 243–252.
Bai, B., & Mackauer, M. (1990). Oviposition and host-feeding patterns in Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) at different aphid densities. Ecological Entomology, 15, 9–16.
Barbagallo, S., Cocuzza, G., Cravedi, P., & Komazaki, S. (2007). IPM case studies: Deciduous fruit trees, in aphids as crop pests. CABI, Wallingford, Oxon: 651–661.
Bass, C., Puinean, A. M., Zimmer, C. T., Denholm, I., Field, L. M., Foster, S. P., Gutbrod, O., Nauen, R., Slater, R., & Williamson, M. S. (2014). The evolution of insecticide resistance in the peach potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B Biological Sciences, 51, 41–51.
Blackman, R.L., & Eastop, V.F. (1985). Aphids on the world’s crops. In: An identification guide. John Wiley and Sons Press, Chichester, UK.
Byeon, Y. W., Tuda, M., Takagi, M., Kim, J. H., & Kim, Y. H. (2009). Non-reproductive host killing caused by Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), a parasitoid of cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae). Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture Kyushu University, 54, 369–372.
Byeon, Y. W., Tuda, M., Takagi, M., Kim, J. H., & Choi, M. Y. (2011). Life history parameters and temperature requirements for development of an aphid parasitoid Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Environmental Entomology, 40, 431–440.
Castle, S. J., & Berger, P. H. (1993). Rates of growth and increase of Myzus persicae on virus infected potatoes according to type of virus-vector relationship. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 69, 51–57.
Chi, H. (2017a). TWOSEX-MSChart: A computer program for the age-stage, two-sex life table analysis. http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan.
Chi, H. (2017b). CONSUME-MSChart: computer program for consumption rate analysis based on the age stage, two-sex life table (http://140.120.197.173/ecology/). National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan.
Chi, H. (2017c). TIMING: computer program for consumption rate analysis based on the age stage, two-sex life table (http://140.120.197.173/ecology/). National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan.
Chi, H., Mou, D.F., Allahyari, H., Yu, J.Z., Huang, Y.B., Yang, T.C., Farhadi, R., & Gholizadeh, M. (2011). Finite predation rate: A novel parameter for the quantitative measurement of predation potential of predator at population level. In: Nature Preceedings. Available from: <http://hdl.handle.net/10101/npre.2011.6651.1>.
Chi, H., & Liu, H. (1985). Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bulletin of Institute of Zoological Academy Sinica, 24, 225–240.
Chi, H. (1988). Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environmental Entomology, 17, 26–34.
Efron, B., & Tibshirani, R.J. (1993). An introduction to the bootstrap. New York: Chapman and Hall.
Flanders, S. E. (1953). Aphelinid biologies with implication for taxonomy. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 46, 84–94.
Foster, S. P., Denholm, I., Rison, J. L., Portillo, H. E., Margaritopoulis, J., & Slater, R. (2012). Susceptibility of standard clones and European field populations of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae, and the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae), to the novel anthranilic diamide insecticide cyantraniliprole. Pest Management Science, 68, 629–633.
Fray, L. M., Leather, S. R., Powell, G., Slater, R., McIndoe, E., & Lind, R. J. (2014). Behavioural avoidance and enhanced dispersal in neonicotinoid-resistant Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Pest Management Science, 70, 88–96.
Gavkare, O., Kumar, S., & Japoshvili, G. (2014). Effectiveness of native parasitoids of Myzus persicae in greenhouse environments in India. Phytoparasitica, 42, 141–144.
Gerling, D., Roitberg, B. D., & Mackauer, M. (1990). Instar-specific defense of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum - influence on oviposition success of the parasite Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Journal of Insect Behavior, 3, 501–514.
Hayat, M. (1983). The genera of Aphelinidae (Hymenoptera) of the world. Systematic Entomology, 8, 63–102.
Huang, Z., Ren, S. X., & Musa, P. D. (2008). Effects of temperature on development, survival, longevity, and fecundity of the Bemisia tabaci Gennadius (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) predator, Axinoscymnus cardilobus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biological Control, 46, 209–215.
Inward, D. J. G., Wainhouse, D., & Peace, A. (2012). The effect of temperature on the development and life cycle regulation of the pine weevil Hylobius abietis and the potential impacts of climate change. Agricultural & Forest Entomology, 14, 348–357.
Jackson, H. B., & Eikenbary, R. D. (1971). Bionomics of Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) an introduced parasite of sorghum greenbug. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 64, 81–85.
Japoshvili, G., & Karaca, I. (2009). A review of the species of Aphelinus Dalman, 1820 (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) from Georgia. Journal of Entomological Research Society, 11, 41–52.
Kang, E. J., Byeon, Y. W., Kim, J. H., Choi, M. Y., & Choi, Y. S. (2012). The effect of temperatures on the biological characteristics of two aphid parasitoids Aphelinus asychis (Walker) and Aphelinus varipes (Forster) (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) on two aphid hosts. Korean Journal of Applied Entomology, 51, 397–403.
Kumar, S., Kashyap, S., & Soni, S. (2019). The foraging behaviour of Aphelinus asychis Walker (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) and Aphidius ervi (Haliday) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Phytoparasitica, 47, 351–360.
Li, W. X., Yang, Y. T., Xie, W., Wu, Q. J., Xu, B. Y., Wang, S. L., Zhu, X., Wang, S. J., & Zhang, Y. J. (2015). Effects of temperature on the age-stage, two-sex life table of Bradysia odoriphaga (Diptera: Sciaridae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 108, 126–134.
McClay, A. S., & Hughes, R. B. (2007). Temperature and host-plant effects on development and population growth of Mecinus janthinus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), a biological control agent for invasive Linaria spp. Biological Control, 40, 405–410.
Nauen, R., & Denholm, I. (2005). Resistance of insect pests to neonicotinoid insecticides: Current status and future prospects. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 58, 200–215.
Needham, P. H., & Sawicki, R. M. (1971). Diagnosis of resistance to organophosphorus insecticides in Myzus persicae. Nature, 230, 125–126.
Panini, M., Anaclerio, M., Puggioni, V., Stagnati, L., Nauen, R., & Mazzoni, E. (2015). Presence and impact of allelic variations of two alternative s-kdr mutations, M918T and M918L, in the voltage-gated sodium channel of the green peach aphid Myzus persicae. Pest Management Science, 71, 878–884.
Piyaphongkul, J., Pritchard, J., & Bale, J. (2014). Effects of acclimation on the thermal tolerance of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Agriculture & Forest Entomology, 16, 174–183.
Qiu, B., de Barro, P. J., Xu, C., & Ren, S. (2006). Effect of temperature on the life history of Encarsia bimaculata (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), a parasitoid of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). European Journal of Entomology, 103, 787–792.
Ralec, A. L., Anselme, C., Outreman, Y., Poirié, M., van Baaren, J., Lann, C. L., & van Alphen, J. J. M. (2010). Evolutionary ecology of the interactions between aphids and their parasitoids. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 333, 554–565.
Raney, H. G., Coles, L. W., Eikenbary, R. D., Morrison, R. D., & Starks, K. (1971). Host preference, longevity, developmental period and sex ratio of Aphelinus asychis with three sorghum-fed species of aphids held at controlled temperatures. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 64, 169–176.
Romo, C. M., & Tylianakis, J. M. (2013). Elevated temperature and drought interact to reduce parasitoid effectiveness in suppressing hosts. PLoS One, 8, e58136.
Schirmer, S., Sengonca, C., & Blaeser, P. (2008). Influence of abiotic factors on some biological and ecological characteristics of the aphid parasitoid Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) parasitizing Aphis gossypii (Sternorrhyncha: Aphididae). European Journal of Entomology, 105, 121–129.
Sengonca, C., Schirmer, S., & Blaeser, P. (2008). Life table of the aphid parasitoid Aphelinus asychis (Walker) (Hymenoptera, Aphelinidae) parasitizing different age groups of Aphis gossypii glover (Homoptera, Aphididae). Journal of Plant Disease and Protection, 115, 122–128.
Shi, P. J., Wang, B., Ayres, M. P., Ge, F., Zhong, L., & Li, B. L. (2012). Influence of temperature on the northern distribution limits of Scirpophaga incertulas Walker (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in China. Journal of Thermal Biology, 37, 130–137.
Slater, R., Paul, V. L., Andrews, M., Garbay, M., & Camblin, P. (2011). Identifying the presence of neonicotinoid resistant peach-potato aphid (Myzus persicae) in the peach growing regions of southern France and northern Spain. Pest Management Science, 68, 634–638.
Speight, R. M., D. M. Hunter, D. A. Watt. (1999). Ecology of insects: Concepts and applications. Blackwell Science, UK.
Syller, J. (1994). The effects of temperature on the availability and acquisition of potato leaf roll luteovirus by Myzus persicae. Annals of Applied Biology, 124, 141–149.
Tang, Y. Q., & Yokomi, R. K. (1996). Biology of Aphelinus spiraecolae (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), a parasitoid of the Spirea aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environmental Entomology, 25, 519–523.
Tatsumi, E., & Takada, H. (2005). Evaluation of Aphelinus asychis and Aphelinus albipodus (Hym., Aphelinidae) as biological control agents against three pest aphids. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 40, 379–385.
Unruh, T., Knight, A., & Bush, M. R. (1996). Green peach aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) resistance to endosulfan in peach and nectarine orchards in Washington state. Journal of Economic Entomology, 89, 1067–1073.
van Nieuwenhove, G. A., Frías, E. A., & Virla, E. G. (2016). Effects of temperature on the development, performance and fitness of the corn leafhopper Dalbulus maidis (DeLong) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae): Implications on its distribution under climate change. Agriculture & Forest Entomology, 18, 1–10.
Wang, Q. B., Fang, Z. Y., Yang, L. M., Zhuang, M., Zhang, Y. Y., Liu, Y. M., Sun, P. T., & Lü, H. H. (2013). Survey and pedigree analysis of cabbage varieties released in China. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 40, 869–886.
Wang, S. Y., Chi, H., & Liu, T. X. (2016). Demography and parasitic effectiveness of Aphelinus asychis reared from Sitobion avenae as a biological control agent of Myzus persicae reared on chili pepper and cabbage. Biological Control, 92, 111–119.
Yano, E. (2003). Arthropod natural enemies: the ecology and use in biological pest control (pp. 296). Tokyo, Japan: Yokendo Co. Ltd.
Yu, J. Z., Chi, H., & Chen, B. H. (2013). Comparison of the life tables and predation rates of Harmonia dimidiata (F.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) fed on Aphis gossypii glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) at different temperatures. Biological Control, 64, 1–9.
Zhang, S. Z., Cao, Z., Zhang, F., & Liu, T. X. (2014). Exposing eggs to high temperatures affects the development, survival and reproduction of Harmonia axyridis. Journal of Thermal Biology, 39, 40–44.
Zhou, Z. S., Guo, J. Y., Chen, H. S., & Wan, F. H. (2010). Effects of temperature on survival, development, longevity, and fecundity of Ophraella communa (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a potential biological control agent against Ambrosia artemisiifolia (Asterales: Asteraceae). Environmental entomology, 39, 1021–1027.
Zhu, Y. C., & Fang, Q. Q. (2009). The phylogenetic relationships of introduced Aphelinus (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) biological control agents of the Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). Insect Sci., 16, 277–285.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Open Foundation of key laboratory for comprehensive management against crop pests at Northwest Loess Plateau of Agriculture Department (KFJJ20180109), Scientific Natural Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LGN19C140007), Developing Foundation of Zhejiang A&F University (2017FR007), China National Basic Research 973 Program (Grant No. 2013CB127604-3) and China Natural Science Foundation (31272089 and 31701848). We thank James Ridsdill-Smith (Entomologist, School of Animal Biology and Institute of Agriculture, University of Western Australia) for comments and language assistance on an earlier draft of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest among all authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S.Y., Zhang, D. & Liu, TX. Influence of temperature on the demographics and control efficiency of Aphelinus asychis, a parasitoid of the cabbage pest, Myzus persicae. Phytoparasitica 48, 767–783 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-020-00822-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-020-00822-7