Abstract
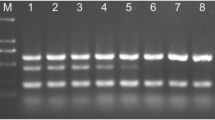
Wheat stem rust, wheat leaf rust, and wheat powdery mildew are three of the most economically damaging fungal diseases of wheat in China, caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici, Puccinia triticina, and Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici, respectively. In this study, single-step multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was developed for the simultaneous detection of the three pathogens. Three sets of specific primers were selected, followed by optimization of the annealing temperature and the dNTPs, Taq DNA polymerase, and primer concentrations for multiplex PCR to establish a method for the simultaneous detection of P. graminis f. sp. tritici, P. triticina, and B. graminis f. sp. tritici at an early stage of infection. The specificity and sensitivity of the multiplex PCR were tested. We observed three specific bands of 395 bp, 151 bp, and 464 bp on amplification with a three-reaction system. The detection sensitivity of the multiplex PCR was 1 ng DNA for P. graminis f. sp. tritici, 10 pg DNA for P. triticina, and 10 pg DNA for B. graminis f. sp. tritici. This study pioneered the use of the triplex PCR system for simultaneous detection of P. graminis f. sp. tritici, P. triticina, and B. graminis f. sp. tritici in infected plant tissues. This novel PCR-based method provides a simple and rapid method for detecting various pathogens in wheat, which will assist in the simultaneous diagnosis and monitoring of multiple plant diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abebe, T., Woldeab, G., & Dawit, W. (2012). Distribution and physiologic races of wheat stem rust in Tigray, Ethiopia. Journal of Plant Pathology and Microbiology, 3, 142.
Aldrich, J., & Cullis, C. A. (1993). RAPD analysis in flax: optimization of yield and reproducibility using Klen Taq I DNA polymerase, Chelex 100, and gel purification of genomic DNA. Plant Molecular Biology Reports, 11, 128–141.
Ballabio, A., Ranier, J. E., Chamberlain, J. S., Zollo, M., & Caskey, C. T. (1990). Screening for steroid sulfatase (STS) gene deletions by multiplex DNA amplification. Human Genetics, 84, 571–573.
Bates, J. A., Taylor, E. J. A., Kenyon, D. M., & Thomas, J. E. (2001). The application of real-time PCR to the identification, detection and quantification of Pyrenophora species in barley seed. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2, 49–57.
Bohm, J., Hahn, A., Schubert, R., Bahnweg, G., Adler, N., Nechwatal, J., et al. (1999). Real-time quantitative PCR: DNA determination in isolated spores of the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae and monitoring of Phytophthora infestans and Phytophthora citricola in their respective host plants. Journal of Phytopathology, 147, 409–416.
Cao, L. H., Xu, S. C., Chen, W. Q., Liu, T. G., & Lin, R. M. (2007). Molecular diagnosis and detection of Puccinia triticina in China. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 34, 561-566. (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Cao, Y. Y., Yu, J. C., Liu, Q., & Wei, S. H. (2005). Studies on preservation method for pure isolates of wheat powdery mildew. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 32, 271-272. (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Capote, N., Pastrana, A. M., Aguado, A., & Sánchez-Torres, P. (2012). Molecular tools for detection of plant pathogenic fungi and fungicide resistance. In C. J. R. Cumagun (Ed.), Plant pathology (pp. 151–202). Rijeka, Croatia: Intech.
Chen, H. G., Fang, Z., Chen, H. D., Lin, L., & Wang, Y. Z. (2005a). Comparison of Wheat sharp spot pathogenic isolates based on the internal transcribed spacer sequence. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 35, 24-29. (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Chen, M. J., Fang, T., Ke, T., Xiong, Z. Y., & He, G. Y. (2005b). Multiplex PCR – a molecular biotechnique of high efficiency and speed. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 27, 33–36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Côté, M.-J., Tardif, M.-C., & Meldrum, A. J. (2004). Identification of Monilinia fructigena, M. fructicola, M. laxa, and Monilia polystroma on inoculated and naturally infected fruit using multiplex PCR. Plant Disease, 88, 1219–1225.
Cullen, D. W., Lees, A. K., Toth, I. K., & Duncan, J. M. (2001). Conventional PCR and real-time PCR detection of Helminthosporium solani in soil and on potato tubers. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 107, 387–398.
Edwards, M. C., & Gibbs, R. A. (1994). Multiplex PCR: advantages, development, and applications. Genome Research, 3, S65–S75.
Fraaije, B. A., Lovell, D. J., Coelho, J. M., Baldwin, S., & Hollomon, D. W. (2001). PCR-based assays to assess wheat varietal resistance to blotch (Septoria tritici and Stagonospora nodorum) and rust (Puccinia striiformis and Puccinia recondita) diseases. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 107, 905–917.
He, J. M., Song, Y. L., Zhang, Z. S., & He, W. L. (1998). Prevention and control of wheat powdery mildew I. The distribution symptoms and harm of wheat powdery mildew. Henan Agricultural Science, 1, 17-18. (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Huang, Y. H., Hu, X. X., & Xu, W. Z. (2003). The factors affecting the efficiency of multiplex PCR. Hereditas, 25, 65-68. (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Ito, T., Ieki, H., & Ozaki, K. (2002). Simultaneous detection of six citrus viroids and Apple stem grooving virus from citrus plants by multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Virological Methods, 106, 235–239.
Johnson, J. R. (2000). Development of polymerase chain reaction-based assays for bacterial gene detection. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 41, 201–209.
Lefeuvre, P., Hoareau, M., Delatte, H., Reynaud, B., & Lett, J. M. (2007). A multiplex PCR method discriminating between the TYLCV and TYLCV-Mld clades of Tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Journal of Virological Methods, 144, 165–168.
Lievens, B., & Thomma, B. P. H. J. (2005). Recent developments in pathogen detection arrays: Implications for fungal plant pathogens and use in practice. Phytopathology, 95, 1374–1380.
Markoulatos, P., Siafakas, N., & Moncany, M. (2002). Multiplex polymerase chain reaction: A practical approach. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis, 16, 47–51.
McCartney, H. A., Foster, S. J., Fraaije, B. A., & Ward, E. (2003). Molecular diagnostics for fungal plant pathogens. Pest Management Science, 59, 129–142.
Nakamura, T., Vrinten, P., Saito, M., & Konda, M. (2002). Rapid classification of partial waxy wheat using PCR-based markers. Genome, 45, 1150–1156.
Periasamy, M., Niazi, F. R., & Malathi, V. G. (2006). Multiplex RT-PCR, a novel technique for the simultaneous detection of the DNA and RNA viruses causing rice tungro disease. Journal of Virological Methods, 134, 230–236.
Schoske, R., Vallone, P. M., Ruitberg, C. M., & Butler, J. M. (2003). Multiplex PCR design strategy used for the simultaneous amplification of 10 Y chromosome short tandem repeat (STR) loci. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 375, 333–343.
Sun, Z. G., Cao, Y. Y., Han, J. D., & Chen, W. S. (2010). Comparison of different methods for extraction of DNA of wheat stem rust urediospores. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 49, 1281–1284.
Thompson, J. R., Wetzel, S., Klerks, M. M., Vašková, D., Schoenb, C. D., Špak, J., et al. (2003). Multiplex RT-PCR detection of four aphid-borne strawberry viruses in Fragaria spp. in combination with a plant mRNA specific internal control. Journal of Virological Methods, 111, 85–93.
Uga, H., & Tsuda, S. (2005). A one-step reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction system for the simultaneous detection and identification of multiple tospovirus infection. Phytopathology, 95, 166–171.
Wang, N., Wang, J., Yin D. H., Gao, G. P., & Wang, W. (2010). Triplex PCR detection of Botrytis cinerea, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Verticillium dahliae in infected strawberry plant tissues. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 43, 4392–4400.
Wang, X., Liu, T. G., Xiang, W. S., & Chen, W. Q. (2011). Development of a SSR molecular marker for Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 44, 4593–4599. (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Ward, E., Foster, S. J., Fraaije, B. A., & McCartney, H. A. (2004). Plant pathogen diagnostics: immunological and nucleic acid-based approaches. Annals of Applied Biology, 145, 1–16.
Winton, L. M., & Hansen, E. M. (2001). Molecular diagnosis of Phytophthora lateralis in trees, water, and foliage baits using multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Forest Pathology, 31, 275–283.
Winton, L. M., Stone, J. K., Watrud, L. S., & Hansen, E. M. (2002). Simultaneous one-tube quantification of host and pathogen DNA with real-time polymerase chain reaction. Phytopathology, 92, 112–116.
Wittwer, C. T., Herrmann, M. G., Moss, A. A., & Rasmussen, R. P. (1997). Continuous fluorescence monitoring of rapid cycle DNA amplification. Biotechniques, 22, 130–138.
Wu, Y. S., & Huang, Z. T. (1987). Racial identification and dynamics analysis of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici for past 20 years in China. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 18, 105-138.
Xie, Z. X., Fadl, A. A., Girshick, T., & Khan, M. I. (1997). Amplification of avian reovirus RNA using the reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Avian Diseases, 41, 654–660.
Zeng, X. W., Luo, Y., Zhou, Y. L., & Duan, X. Y. (2008). PCR detection of Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici based on the sequences of rDNA ITS. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 38, 211–214.
Zhao, Y. G., Gao, C. Y., Wang, J. H., Wang, M., Xing, D. F., & Zhao, Q. S. (2003). How to avoid inhibiting by the inhibitor in PCR. Natural Sciences Journal of Harbin Normal University, 19, 81–84.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127701), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31171829), and the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201303016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Cao, Yy., Li, Ty. et al. Simultaneous detection of three wheat pathogenic fungal species by multiplex PCR. Phytoparasitica 43, 449–460 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-014-0442-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-014-0442-1