Abstract
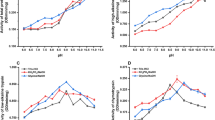
Digestive proteolytic activities were studied in the larval midgut of Papilio demoleus by using azocasein, specific substrates and inhibitors regarding enzymatic allocation in the alimentary canal. The highest proteolytic activity was found in the midgut rather than foregut and hindgut that highest proteolytic activity was observed in soluble fraction. All specific proteases were almost equally distributed in both the anterior and posterior midgut except for trypsin- and chymotrypsin-like proteases, which showed the highest activity in the anterior midgut. Two peaks were observed in alkaline and acidic pHs when general proteolytic activities were assayed using azocasein in soluble and membrane-bound fractions. Specific substrates revealed the presence of trypsin-like, chymotrypsin-like, elastase, cathepsins B and L as well as two exopeptidases. These findings were confirmed using specific inhibitors including PMSF, TLCK, TPCK, SBTI, cystatin, DTT, E-64, EDTA and phenanthroline. Determination and characterization of the insect’s digestive proteases will enable development of pest control by designing protease inhibitors. This procedure will help us to designate an efficient pest control method with the lowest impact on the environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, Z., Saleemuddin, M., & Siddiqui, M. (1980). Purification and characterisation of three alkaline proteases from the larvae of army worm Spodoptera litura. Insect Biochemistry, 10, 667–673.
Ajamhassani, M., Zibaee, A., Sendi, J. J., Askary, H., & Farrar, N. (2012). Proteolytic activity in the midgut of the Crimson Speckled moth, Utethsia pulchella L. (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Journal of Plant Protection Research, 52, 368–373.
Anwar, A., & Saleemudin, M. (2002). Purification and characterization of a digestive alkaline protease from the larvae of Spilosoma oblique. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 51, 1–12.
Atwal, A. S. (1979). Agricultural pests of India and South-East Asia. Delhi, India: Kalyani Publishers.
Badawi, A. (1981). Studies on some aspects of the biology and ecology of the citrus butterfly Papilio demoleus L. in Saudi Arabia (Papilionidae: Lepidoptera). Zeitschrift für Angewandte Entomologie, 91, 286–292.
Barrett, A. J., & Rawling, N. D. (1991). Types and families of endopeptidases. Biochemical Transactions, 19, 707–715.
Bernardi, B., Tedeschi, G., & Ronchi, S. (1996). Isolation and some molecular properties of a trypsin-like enzyme from larvae of European corn borer Ostrinia nubilalis Hübner (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 26, 883–889.
Biondi, A., Desneux, N., Siscaro, G., & Zappalà, L. (2012a). Using organic-certified rather than synthetic pesticides may not be safer for biological control agents: selectivity and side effects of 14 pesticides on the predator Orius laevigatus. Chemosphere, 87, 803–812.
Biondi, A., Mommaerts, V., Smagghe, G., Viñuela, E., Zappalà, L., & Desneux, N. (2012b). The non-target impact of spinosyns on beneficial arthropods. Pest Management Science, 68, 1523–1536.
Caldeira, W., Dias, A. B., Terra, W. R., & Ribeiro, A. F. (2007). Digestive enzyme compartmentalization and recycling and sites of absorption and secretion along the midgut of Dermestes maculatus (Coleoptera) larvae. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 64, 1–18.
Chapman, R. F. (1998). The insects: Structure and function (4th ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Chougle, N. P., Doyle, E., Fitches, E., & Gatehouse, J. A. (2008). Biochemical characterization of midgut digestive proteases from Mamestra brassicae (Cabbage moth; Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and effect of soybean Kunitz trypsin inhibitor (SKTI) in feeding assays. Journal of Insect Physiology, 54, 563–572.
Desneux, N., Decourtye, A., & Delpuech, J. M. (2007). The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annual Review of Entomology, 52, 81–106.
Ebeling, W. (1959). Subtropical fruit pests. Berkeley, CA, USA: Division of Agricultural Science, University of California.
Elpidina, E. N., Vinokurov, K. S., Gromenko, V. A., Rudenskaya, Y. A., Dunaevsky, Y. E., & Zhuzhikov, D. P. (2001). Compartmentalization of proteinases and amylases in Nauphoeta cinerea midgut. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 48, 206–216.
Foard, D. E., Murdock, L. L., & Dunn, P. E. (1983). Engineering of crop plants with resistance to herbivores and pathogens: An approach using primary gene products. Plant Molecular Biology, 2, 223–233.
Garcia-Carreno, F. L., Dimes, L. E., & Haard, N. F. (1993). Substrate–gel electrophoresis for composition and molecular weight of proteinases or proteinaceous protease inhibitors. Analytical Biochemistry, 214, 61–69.
Gatehouse, A. M. R., Norton, E., Davison, G. M., Babbe, S. M., Newell, C. A., & Gatehouse, J. A. (1999). Digestive proteolytic activity in larvae of tomato moth, Lacanobia oleracea; effects of plant protease inhibitors in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Insect Physiology, 45, 545–558.
Hegedus, D., Baldwin, D., O’Grady, M., Braun, L., Gleddie, S., Sharpe, A., et al. (2003). Midgut proteases from Mamestra configurata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae: Characterization, cDNA cloning, and expressed sequence tag analysis. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 53, 30–47.
Hilder, V. A., & Boulter, D. (1999). Genetic engineering of crop plants for insect resistance - a critical review. Crop Protection, 18, 177–191.
Hilder, V. A., Gatehouse, A. M. R., & Boulter, D. (1993). Transgenic plants conferring insect tolerance: protease inhibitor approach (pp. 317–338). In S. D. Inkung & R. Wu (Eds.), Transgenic plants. London, UK: Academic Press.
Homziak, T., Nicholas, T., & Homziak, J. (2006). Papilio demoleus (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae): A new record for the United States, Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. Florida Entomologist, 89, 485–488.
Isman, M. B. (2000). Plant essential oils for pest and disease management. Crop Protection, 19, 603–608.
Jongsma, M. A., Stiekema, W. J., & Bosch, D. (1996). Combating inhibitor insensitive proteases of insect pests. Trends in Biotechnology, 14, 331–333.
Josephrajkumar, A., Chakrabarty, R., & Thomas, G. (2006). Midgut proteases of the cardamom shoot and capsule borer Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and their interaction with aprotinin. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 96, 91–98.
Koiwa, R. E., Shade, K., Zhu-Satzman, L., Subramanian, L. L., Murdock, S. S., Nielsen, R. A., et al. (1998). Phage display selection can differentiate insecticidal activity of soybean cystatins. The Plant Journal, 14, 371–379.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Larsen, T. B. (1984). The zoogeographical composition and distribution of the Arabian butterflies (Lepidoptera: Rhopalocera). Journal of Biogeography, 11, 119–158.
Laskowski, J. R., & Kato, M. (1980). Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annual Review of Botany, 49, 593–626.
Lee, M. J., & Anstee, J. H. (1995). Endoproteases from the midgut of larval Spodoptera littoralis include a chymotrypsin-like enzyme with an extended binding site. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 25, 49–61.
Lorito, M., Brodway, R. M., Hayes, C. K., Woo, S. L., Noviello, C., Williams, D. L., et al. (1994). Proteinase inhibitors from plants as a novel class of fungicide. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 7, 525–527.
Marchetti, S., Chiaba, C., Chisa, F., Bandiera, A., & Pitotti, A. (1998). Isolation and partial characterization of two trypsins from the larval midgut of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisduval). Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 28, 449–458.
Mehrabadi, M., & Bandani, A. R. (2011). Secretion and formation of perimicrovilar membrane in the digestive system of the Sunn pest, Eurygaster integriceps Puton (Hemiptera: Scutelleridae) in response to feeding. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 78, 190–200.
Mohammadi, D., PourAbad, R. F., Rashidi, M. R., & Mohammadi, S. A. (2010). Activity and some properties of Helicoverpa armigera Hübner and Spodoptera exigua Hübner (Lep.: Noctuidae) midgut protease. Munis Entomology and Zoology, 5, 697–706.
Murdock, L. L., Brookhart, G., Dunn, P. E., Foard, D. E., Kelley, S., Kitch, L., et al. (1987). Cysteine digestive proteinases in Coleoptera. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. B, 87, 783–787.
Oppert, B. (1999). Protease interactions with Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxins. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 42, 1–12.
Reek, G., Oppert, B., Denton, M., Kanost, M., Baker, J., & Kramer, K. (1999). Insect proteinases (pp. 125–148). In V. Turk (Ed.), Proteases: new perspectives. Basel, Switzerland: Birkhauser-Verlag
Ryan, C. A. (1981). Proteinase inhibitors. New York, NY: Academic Press.
Saadati, F., & Bandani, A. R. (2011). Effects of serine protease inhibitors on growth and development and digestive serine proteinases of the Sunn pest, Eurygaster integriceps. Journal of Insect Science, 11, 72. available online: insectscience.org/11.72.
Shaaya, E., Kostyukovski, M., Eilberg, J., & Sukprakarn, C. (1997). Plant oils as fumigants and contact insecticides for the control of stored-product insects. Journal of Stored Products Research, 33, 7–15.
Srinivasan, A., Giri, A., Harsulkar, A. M., Gatehouse, J. A., & Gupta, V. S. (2005). A Kunitz trypsin inhibitor from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) that exerts anti-metabolic effect on pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera) larvae. Plant Molecular Biology, 57, 359–374.
Teo, L. H., & Woodring, J. P. (1985). Digestive enzymes in the house cricket Acheta domesticus with special reference to amylase. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. B, 82, 871–877.
Terra, W. R., & Ferreira, C. (1983). Further evidence that enzymes involved in the final stages of digestion by Rhynchosciara americana do not enter the endoperitrophic space. Insect Biochemistry, 13, 143–150.
Terra, W. R., & Ferreira, C. (1994). Insect digestive enzymes: properties, compartmentalization and function. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. B, 109, 1–62.
Terra, W. R., & Ferreira, C. (2005). Biochemistry of digestion (pp. 171–224). In L. I. Gilbert, K. Iatrou, & S. S. Gill (Eds.), Comprehensive molecular insect science. vol. 3. San Diego, CA, USA: Elsevier.
Terra, W. R., Ferreira, C., Jordao, B. P., & Dillon, R. J. (1996). Digestive enzymes (pp. 153–193). In M. J. Lehane & P. F. Billingsley (Eds.), Biology of the insect midgut. London, UK: Chapman and Hall.
Weisenburger, D. D. (1993). Human health effects of agrichemicals use. Human Pathology, 24, 571–576.
Wyniger, R. (1962). Pests of crops in warm climates and their control. Basel, Switzerland: Verlag für Recht und Gesellschaft.
Zibaee, A. (2012). Proteolytic profile in the larval midgut of Chilo suppressalis Walker (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Entomological Research, 42, 142–150.
Zibaee, A., Bandani, A. R., & Ramzi, S. (2009). Characterization of α- and β-glucosidases in midgut and salivary glands of Chilo suppressalis Walker (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), rice striped stem borer. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 332, 633–641.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by a grant of the Elite Foundation of Iran and University of Guilan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazdani, E., Zibaee, A. & Sendi, J.J. Digestive proteases of Papilio demoleus : Compartmentalization and characterization. Phytoparasitica 42, 121–133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0323-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0323-z