Abstract
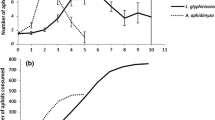
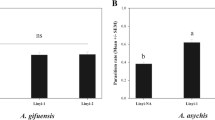
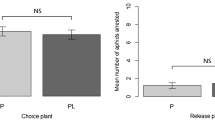
The use of a selective insecticide is highly recommended for Integrated Pest Management programs. Plenum (a.i.: pymetrozine; Syngenta Agro), a systemic insecticide, is regarded as a good candidate for use in situations where plant-sucking insects have to be controlled and where natural enemies can play a substantial role as biological control agents. In this context, the effects of Plenum on a host–endoparasitoid relationship were investigated. Potato aphids Macrosiphum euphorbiae were reared for 4 days on an artificial diet supplemented with a low concentration of Plenum (sublethal concentration inducing 15% aphid mortality) before parasitization by the endoparasitoid Aphidius ervi. The development of A. ervi larvae was negatively affected, especially during the early stages of development, and the sex ratio of the progeny was strongly male-biased. Moreover, the host-choice experiment showed that A. ervi was not able to discriminate between control and Plenum-contaminated aphids. These results show that Plenum may not be as selective as it was previously thought to be, and the observed effects need to be considered when developing IPM systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Tara, R., Samara, F., Gamal, M., Shalaby, F., Assaf, S., & Rostom, G. (2008). Impact of some pesticides on pupae of the parasitoid Eretmocerus mundus (Mercet) and Encarsia formosa (Gahan) under laboratory conditions. Egyptian Journal of Biological Pest Control, 18, 201–206.
Acheampong, S., & Stark, J. D. (2004a). Can reduced rates of pymetrozine and natural enemies control the cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae (Homoptera: Aphididae), on broccoli? International Journal of Pest Management, 50, 275–279.
Acheampong, S., & Stark, J. D. (2004b). Effects of the agricultural adjuvant Sylgard 309 and the insecticide pymetrozine on demographic parameters of the aphid parasitoid, Diaeretiella rapae. Biological Control, 31, 133–137.
Arthur, A. P. (1981). Host acceptance by parasitoids. In D. A. Nordlund, R. L. Jones, & W. J. Lewis (Eds.), Semiochemicals: Their role in pest control (pp. 97–120). New York, NY: Wiley.
Ausborn, J., Wolf, H., Mader, W., & Kayser, H. (2005). The insecticide pymetrozine selectively affects chordotonal mechanoreceptors. Journal of Experimental Biology, 208, 4451–4466.
Bloomquist, J. R. (1996). Ion channels as targets for insecticides. Annual Review of Entomology, 41, 163–190.
Croft, B. A. (1990). Arthropod biological control agents and pesticides. New York, NY: Wiley and Sons.
Desneux, N., Decourtye, A., & Delpuech, J.-M. (2007). The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annual Review of Entomology, 52, 81–106.
Desneux, N., Denoyelle, R., & Kaiser, L. (2006a). A multi-step bioassay to assess the effect of the deltamethrin on the parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi. Chemosphere, 65, 1697–1706.
Desneux, N., Ramirez-Romero, R., & Kaiser, L. (2006b). Multi step bioassay to predict recolonization potential of emerging parasitoids after a pesticide treatment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25, 2675–2682.
Down, R. E., Gatehouse, A. M. R., Hamilton, W. D. O., & Gatehouse, J. A. (1996). Snowdrop lectin inhibits development and decreases fecundity of the glasshouse potato aphid (Aulacorthum solani) when administered in vivo and via transgenic plants both in laboratory and glasshouse trials. Journal of Insect Physiology, 42, 1035–1045.
Febvay, G., Delobel, B., & Rahbé, Y. (1988). Influence of the amino acid balance on the improvement of an artificial diet for a biotype of Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 66, 2449–2453.
Ferron, P., & Deguine, J.-P. (2005). Vers une conception agroécologique de la protection des cultures. In C. Regnault-Roger (Ed.), Enjeux phytosanitaires pour l’agriculture et l’environnement (pp. 347–466). Paris, France: Lavoisier.
Flückiger, C. R., Kristinsson, H., Senn, R., Rindlisbacher, A., Buholzer, H., & Voss, G. (1992). CGA 215944—A novel agent to control aphids and whiteflies. Proceedings of the Brighton Crop Protection Conference – Pests and Diseases, 2–3, 43–50.
Godfray, H. C. J. (1994). Parasitoids—behavioral and evolutionary ecology. Princeton, NJ, USA: Princeton University Press.
Hågvar, E. B., & Hofsvang, T. (1991). Aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae): biology, host selection and use in biological control. Biocontrol News and Information, 12, 13–41.
Harrewijn, P., & Kayser, H. (1997). Pymetrozine, a fast-acting and selective inhibitor of aphid feeding. In-situ studies with electronic monitoring of feeding behaviour. Pesticides Science, 49, 130–140.
Hsiech, C. Y., & Allen, W. W. (1986). Effects of insecticides on emergence, survival, longevity and fecundity of the parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) from mummified Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 79, 1599–1602.
Kaufmann, L., Schürmann, F., Yiallouros, M., Harrewijn, P., & Kayser, H. (2004). The serotonergic system is involved in feeding inhibition by pymetrozine. Comparative studies on a locust (Locusta migratoria) and an aphid (Myzus persicae). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 138, 469–483.
Kouamé, K. L., & Mackauer, M. (1991). Influence of aphid size, age and behaviour on host choice by the parasitoid wasp Ephedrus californicus: a test of host-size models. Oecologia, 88, 197–203.
Larocca, A., Fanti, P., Romano, V. A., Marsicovetere, E., Isodoro, N., Romani, R., et al. (2007). Functional bases of host-acceptance behaviour in the aphid parasitoid Aphidius ervi. Physiological Entomology, 32, 305–312.
Longley, M. A. (1999). A review of pesticide effects upon immature aphid parasitoids within mummified hosts. International Journal of Pest Management, 45, 139–145.
Longley, M. A., & Jepson, P. C. (1996). Effects of honeydew and insecticide residues on the distribution of foraging aphid parasitoids under glasshouse and field conditions. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 81, 189–198.
Longley, M. A., & Stark, J. D. (1996). Analytical techniques for quantifying direct, residual, and oral exposure of an insect parasitoid to an organophosphate insecticide. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination Toxicology, 57, 683–690.
Mackauer, M., Michaud, J. P., & Völkl, W. (1996). Host choice by aphidiid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae): host recognition, host quality and host value. Canadian Entomologist, 128, 959–980.
Medina, P., Morales, J. J., Budia, F., Adan, A., Del Estal, P., & Vinuela, E. (2007). Compatibility of endoparasitoid Hyposoter didymator (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) protected stages with five selected insecticides. Journal of Economic Entomology, 100, 1789–1796.
Preetha, G., Stanley, J., Suresh, S., Kuttalam, S., & Samiyappan, R. (2009). Toxicity of selected insecticides to Trichogramma chilonis: assessing their safety in the rice ecosystem. Phytoparasitica, 37, 209–215.
Sabahi, Q., Rasekh, A., Sangaki, A. H., & Sheikhi, A. (2009). The persistence toxicity of three insecticides against adult of a thelytokous parasitoid, Lysiphlebus fabarum (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Communications in Agricultural and Applied Biological Sciences, 74, 159–164.
Sechser, B., Bourgeois, F., & Reber, B. (2002). Pymetrozine: Selectivity spectrum to beneficial arthropods and fitness for integrated pest management. Journal of Pesticide Science, 75, 72–77.
Stapel, J. O., Cortesero, A. M., & Lewis, W. J. (1999). Disruptive sublethal effects of insecticides on biological control: altered foraging ability and life span of a parasitoid after feeding on extrafloral nectar of cotton treated with systemic insecticides. Biological Control, 17, 243–249.
Süss, L. (1983). Survival of pupal stage of Aphidius ervi Hal. in mummified Sitobion avenae F. to pesticide treatment. In R. Cavallaro (Ed.), Aphid antagonists (pp. 129–134). Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Balkema.
Torres, J. B., Silva-Torres, C. S. A., & Vargas de Oliveira, J. (2003). Toxicity of pymetrozine and thiamethoxam to Aphelinus gossypii and Delphastus pusillus. Pesquisa Agropecuaria Brasileira, 38, 459–466.
Tran, D. H., Takagi, M., & Takasu, K. (2005). Toxicity of selective insecticides to Neochrysocharis formosa (Westwood) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), a parasitoid of the American serpentine leafminer Lyriomyza trifolii (Burgess) (Diptera: Agrizomydae). Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture Kyushu University, 50, 109–118.
Acknowledgments
We thank Syngenta Agro (St. Cyr l’Ecole, France) for supplying Plenum; the UMR203 INRA-INSA (Villeurbanne, France) for providing aphids; the “Comité Nord Plants de Pommes de Terre” (France) for providing potato tubers; and Dr. Alice Mauchline for her advice on the use of the English language in the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, JR., Ameline, A. & Couty, A. Effects on the aphid parasitoid Aphidius ervi of an insecticide (Plenum®, pymetrozine) specific to plant-sucking insects. Phytoparasitica 39, 35–41 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-010-0134-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-010-0134-4