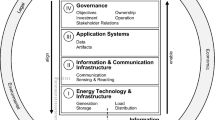
Abstract
Increasing regulatory requirements such as price cap regulation have increased the importance of strategic grid asset management. Empirical studies reveal that information supply and consolidation are error prone and long-term processes. The reason is the missing automation of extraction, transformation, and loading. The current gap does neither fulfill the requirements of regulatory nor the necessity of standardized reporting. Furthermore, a detailed planning is not enabled and the calculation of key figures is extensive. Currently, a framework that considers the coupling of financial and technical key figures, the coupling of strategic and operative key figures as well as the integration into information systems is not existent. Therefore, this paper addresses the design of a reference model as a recommendation for action to integrate the asset management within information systems. It is validated by expert interviews. Moreover, it provides information to integrate relevant financial and technical artifacts from distributed systems. Simultaneously, it provides recommendations for implementing a Business Intelligence architecture in the context of strategic decision support.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Long-term orientation and strategies are in conflict if a grid decision endures because of the long-term use of the assets (60 years). An operative decision (i.e. the choice of chain assemblies) always influences maintenance in the next 5 to 10 years and possibly determines replacements.
This means that the technical interdependencies between different parameters are the foundation for financial evaluation. Maintenance and replacement are primarily technical necessities, not financial ones, even though they affect OPEX and CAPEX.
The IEC Standard supports the compatibility of energy-generating tools and machinery. It measures parameters such as frequency, vibration curves, reactive power, or voltage changes in order to make them comparable independently of third party tools.
In the context of this paper, neither company names nor tools are mentioned.
References
Accenture (2005) Instandhaltungsstrategien im Netzbetrieb. http://tu-dresden.de/die_tu_dresden/fakultaeten/fakultaet_wirtschaftswissenschaften/bwl/ee2/lehrstuhlseiten/ordner_lehre/ordner_ss_06/ordner_energiewirtschaft_2_ss_06/html_energiewirtschaft_2_ss_06_ger. Accessed 2011-07-16
Anreizregulierungsverordnung (2007) ARegV – Verordnung über die Anreizregulierung der Energieversorgungsnetze
Bahadoorsingh S, Rowland SM (2007) The relationship between insulation aging and power network performance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference of solid dialectrics, Winchester, 8–13 July
Balzer G, Gaul A, Neumann C, Schorn C (2007) The general asset management process of power systems. In: Konferenzbeitrag CIGRE-Symposium, Osaka, 1–4 November
Braun R, Esswein W (2007) Classification of reference models. In: Proceedings of the 30th conference of the Gesellschaft für Klassifikation, Berlin
Bulos D (1996) OLAP database design. A new dimension. Database Programming and Design 9(6):33–37
Chamoni P, Gluchowski P (2006) Entwicklungslinien und Architekturkonzepte des On-Line Analytical Processing. In: Chamoni P, Gluchowski P (eds) Analytische Informationssysteme, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 143–176
Czotscher E (2009) Branchenkompass Energieversorger. Steria Mummert, Hamburg
Dietzsch A, Esswein W (1998) Wissensaustausch. auf der Grundlage von Referenzmodellen – Anforderungen und Möglichkeiten. ISI 1998, pp. 201–212
Elmasri R, Navathe S (2007) Fundamentals of database systems. 5th edn. Addison-Wesley, Boston
Energiewirtschaftsgesetz (2005) EnWG – Teil 2, 3, 4
Fette M (2008) Strategische Netzentwicklung und strategisches Asset-Management. http://www.samco-networks.de/fileadmin/data/publikationen/Samco_Strategisches_Asset_Management.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
Fette M (2009) Strategisches Asset- und Regulierungsmanagement – Nutzenbetrachtung. In: Mettenmeier Fachkongress Utility Solutions Essen, 27–29 April
Fettke P, Loos P (2004) Referenzmodellierungsforschung. WIRTSCHAFTSINFORMATIK 46(5):331–340
Frank U (2007) Relevance of research implies relevance to researchers. WIRTSCHAFTSINFORMATIK 49(5):404–405
Fuhrberg-Baumann J, Jeltsch K (2009) Blick in die Zukunft zahlt sich aus. Zeitung für kommunale Wirtschaft 12(09):8–9
Goes S (2003) Management Accounting von Stromnetzbetreibern. Dissertation. Gabler, Wiesbaden
Hahne M (2005) SAP Business Information Warehouse – Mehrdimensionale Datenmodellierung. Springer, Berlin
Inmon W (2005) Building the data warehouse, 4th edn. Wiley, Indianapolis
Jaeger U, Reinecke S (2009) Das Expertengespräch. In: Baumgarth C, Eisend M, Evanschitzky H (eds) Empirische Mastertechniken der Marketing- und Managementforschung. Gabler, Wiesbaden, pp 29–76
Kemper HG, Mehanna W, Unger C (2006) Business Intelligence Grundlagen und praktische Anwendungen, 2nd edn. Vieweg, Wiesbaden
Konnov A (2007) Zuverlässigkeitsberechnung und vorbeugende Wartung von komplexen technischen Systemen mittels modifizierter Markov-Methode. Dissertation. University of Karlsruhe
Lehr D (2006) Kundenbindungsmanagement und Sanierungserfolg – Explorative Analyse der Wirkungszusammenhänge. Gabler, Wiesbaden
Microsoft (2008) Regulierung des Marktes verschärft Kostendruck für die Energiewirtschaft. http://microsoft.com/germany/dynamics/branchen/energie-entsorgung/trends/regulierung-energiemarkte.aspx. Accessed 2011-07-16
Nguyen H (2010) Revolution der Stromnetze – Expansion der neuen Energien erfordert massive Investitionen in den Netzumbau. Deutsche Bank Research. http://www.dbresearch.de/prod/dbr_internet_de-prod/prod0000000000255690.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
Obergünner M, Schwan M, Krane C, von Sengbusch K, Bock C, Quadflieg D (2002) Ermittlung von Eingangsdaten für Zuverlässigkeitsberechnungen aus der VDN-Störungsstatistik. Energiewirtschaft 103(15):32–36
Osztermayer J (2004) Neue Ansätze im Asset-Management von elektrischen Betriebsmitteln. In: Micafil Symposium, Stuttgart, 24–25 March. http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/ieh/forschung/veroeffentlichungen/2004_micafil_osztermayer.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
Osztermayer J (2007) Zustandsabhängiges, risikobasiertes Asset-Management in der Energieversorgung. Dissertation. University of Stuttgart
na (2011a) http://www.ventyx.com/network-management/network-manager-SCADA-EMS.asp. Accessed 2011-07-16
na (2011b) http://www.abb.com/product/seitp334/bb06198da13c99eb8525719a004f4187.aspx?productLanguage=ge&country=DE&tabKey=7. Accessed 2011-07-16
na (2011c) http://www.netz-und-raum.de/PDF_dokumente/PDF%206318.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
na (2011d) http://www-05.ibm.com/de/energy/pdf/8020_gt12-7016-00.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
na (2011e) http://www.ge-energy.com/products_and_services/products/energy_consulting_software/concorda_software_suite.jsp. Accessed 2011-07-16
na (2011f) http://www.samco-networks.de/fileadmin/img/simulationswerkzeuge/TWA-Seite/Samco_Technisch-wirtschaftliches_Anlagenregister_TWA.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
na (2011g) http://www.sag-rcm.de/466.0.html. Accessed 2011-07-16
Panko RR (2009) Revising the Panko-Halverson taxonomy of spreadsheet risks. In: Proceedings of the 42th HICSS, Waikoloa, 5–8 January
Safirov J, Kamphans K (2010) Smarte Tools ermöglichen integriertes “regulatorisches Asset Management”. Energiewirtschaftliche Tagesfragen 60(1/2):94–95
Schneider J, Gaul A, Neumann C, Hogräfer J, Wellßow W, Schnettler A (2005) Asset management techniques. In: PSCC, Liege, 22–26 August
Schreiner W, Rieder T, Haslauer F, Wagner O, Heinz F (2002) Risikoorientiertes Anlagenmanagement. Energiewirtschaftliche Tagesfragen 52(11):776–779
Schütte R (1997) Grundsätze ordnungsgemäßer Referenzmodellierung – Konstruktion konfigurations- und anpassungsorientierter Modelle. Dissertation. Universität Münster. Gabler, Wiesbaden
Spitzer H, Engels C (2009) Dynamic Asset Simulation – Risk Management am Beispiel der Energieversorgung. In: RiskConf, München, 5th November
Stender A (2008) Netzinfrastruktur-Management. Dissertation. Gabler, Wiesbaden
Theil G, Demiri B (2007) Ermittlung der Lebensdauerverteilungsfunktionen von ausgewählten Betriebsmitteln elektrischer MS-Netze zwecks Anwendung in der Instandhaltungsplanung. Elektrotechnik & Informationstechnik 124(6):209–214
Thurner E, Dal Cin M, SchneeweißW (1998) Verläßlichkeitsbewertung komplexer Systeme. Informatik-Spektrum 21:318–327
Totok A, Jaworski R (1998) Modellierung von multidimensionalen Datenstrukturen mit ADAPT – Ein Fallbeispiel. http://home.arcor.de/andreas.totok/pdf/Arbeitsbericht_ADAPT.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
Wellßow WH (2006) Asset-Management-Strategien in Verteilnetzen. Siemens AG. http://www.life-needs-power.de/2006/26-04-2006_Mittwoch/060426_13-30_AM%20in%20VNetzen%20-%20Wellssow%20v03.pdf. Accessed 2011-07-16
Wenzler V (2005) Development of an asset management strategy for a network utility company. Lessons from a dynamic business simulation approach Simulation and Gaming 36(1):75–90
Zdrallek M (2005) TÜV für Netze. Systematische Zustandsbewertung von MS- und NS-Netzen. In: Fachtagung Netzbetrieb der Zukunft, Pfaffendorf, 16th July
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Accepted after one revision by Prof. Dr. Terzidis.
This article is also available in German in print and via http://www.wirtschaftsinformatik.de: Felden C, Buder JJ (2012) Integrierte Informationsversorgung zur Entscheidungsunterstützung in Netzgesellschaften. WIRTSCHAFTSINFORMATIK. doi: 10.1007/s11576-011-0306-y.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felden, C., Buder, J.J. Integrated Information Supply for Decision Support in Grid Companies. Bus Inf Syst Eng 4, 15–29 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12599-011-0198-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12599-011-0198-9