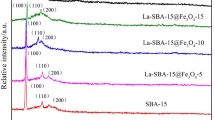
Abstract
In this study, mesoporous silica/iron oxide nanocomposite (MCM-Fe2O3) was synthesized via hydrothermal technique. The chemical synthesis of MCM-Fe2O3 nanocomposite was achieved at 18 h. The effect of concentration of tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) on nanocomposites properties was studied during synthesis process. For this purpose, 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, and 4.5 ml tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) were selected, respectively. The textural properties and microstructure of the nanocomposites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), N2 adsorption–desorption, and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) analysis. Results show that the nanocomposite with tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS)/cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) ratio of 5 exhibits large surface areas (461.19 m2·g−1). Furthermore, this nanocomposite shows superparamagnetic behavior under external magnetic field compared to other samples. Moreover, results of removal of metal ions indicate that adsorption of Ni(II), Cd(II), Cr(III), Zn(II), and Pb(II) ions on the surface of adsorbent (nanocomposite) increases with the increase in solution pH, contact time, and adsorbent dosage. Furthermore, the maximum removal rates of heavy metals ions reach 53.0 %, 79.0 %, 61.0 %, 89.0 %, and 99.5 % at pH of 5, time of 50 min, and the weight of adsorbent of 0.16 with 2.5 ml TEOS, respectively.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morales MA, Mascarenhas AJS, Gomes AMS, Leite CAP, Andrade HMC, De Castilho CMC, Galembeck F. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic mesoporous particles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;342(2):269.
Caparros C, Benelmekki M, Martins PM, Xuriguera E, Silva CJR, Martinez LIM, Lanceros-Mendez S. Hydrothermal assisted synthesis of iron oxide-based magnetic silica spheres and their performance in magnetophoretic water purification. Mater Chem Phys. 2012;135(2–3):510.
Parida KM, Dash SK. Adsorption of Cu2+ on spherical Fe-MCM-41 and its application for oxidation of Adamantane. J Hazard Mater. 2010;178(1–3):642.
Anbia M, Ghassemian Z. Removal of Cd(II) and Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using mesoporous silicate containing zirconium and iron. Chem Eng Res Des. 2010;89(12):2770.
Wang P, Lo IMC. Synthesis of mesoporous magnetic γ-Fe2O3 and its application to Cr(VI) removal from contaminated water. Water Res. 2009;43(15):3727.
Kim K, Lee J, Um W, Kim J, Joo J, Lee JH, Kwak JH, Kim JH, Lee CH, Lee H, Addleman SH, Hyeon T, Gui MB. Magnetic mesoporous materials for removal of environmental wastes. J Hazard Mater. 2011;193(3):1140.
Wang J, Zheng SH, Shao Y, Liu J, Xu ZH, Zhu D. Amino-Functionalized Fe3O4/SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;349(1):293.
Li G, Zhao Z, Liu J, Jiang G. Effective heavy metal removal from aqueous systems by thiol functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica. J Hazard Mater. 2011;277(1):277.
Xin X, Wei Q, Yang J, Yan L, Feng R, Chen G, Du B, Li H. Highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions by amine-functionalized mesoporous Fe3O4 nanosorbents. Chem Eng J. 2012;184(1):132.
Chen X, Lam KF, Yeung KL. Selective removal of chromium from different aqueous systems using magnetic MCM-41 nanosorbents. Chem Eng J. 2011;172(2–3):728.
Ursachi I, Stancu A, Vasile A. Magnetic α-Fe2O3/MCM-41 nanocomposites: preparation, characterization, and catalytic activity for methylene blue degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;377(1):184.
Xia M, Chen CH, Long M, Cai W, Zhou B. Magnetically separable mesoporous silica nanocomposite and its application in fenton catalysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011;145(1–3):217.
Guo SH, Li D, Zhang L, Li J, Wang E. Monodisperse mesoporous superparamagnetic single-crystal magnetite nanoparticles for drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2009;30(10):1881.
Sen T, Bruce IJ. Mesoporous silica-magnetite nanocomposites: fabrication, characterisation and applications in biosciences. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009;120(3):246.
Chen F, Shi R, Xue Y, Chen L, Wan QH. Templated synthesis of monodisperse mesoporous maghemite/silica microspheres for magnetic separation of genomic DNA. Magn Magn Mater. 2010;322(16):2439.
Wang CH, Ao Y, Wang P, Qian J, Hou J, Zhang S. A Simple method for preparation of superparamagnetic porous silica. J Alloys Compd. 2010;493(1–2):410.
Cornel RM, Schwertmann U. The Iron Oxides. Structure, Properties, Reactions and Uses. Weinheim: VCH Publishers; 1996. 573.
Kong A, Wang H, Li J, Shan YK. Prepration of super paramagnetic crystalline mesoporous γ-Fe2O3 with high surface. Mater Lett. 2008;62(6–7):943.
Wagner AC, Martin W, Ulf S. Iron and copper immobilised on mesoporous MCM-41 molecular sieves as catalysts for the oxidation of cyclohexane. Orig J Mol Catal A Chem. 1999;144(1):91.
Bengoa JF, Cagnoli MV, Gallegos NG, Alvarez AM, Mogni LV, Moreno MS, Marchetti SG. Iron oxide nanoparticles inside the MCM-41 channels: study of the structural stability of the support. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005;84(1–3):153.
Mitra A, Vazquez-Vazquez C, Lopez-Quintela MA, Paul BK, Bhaumik A. Soft-templating approach for the synthesis of high surface area and superparamagnetic mesoporous iron oxide materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010;131(1–3):373.
Darezereshki E, Bakhtiari F, Alizadeh M, Yakylabad AB, Ranjbar M. Direct thermal decomposition synthesis and characterization of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2012;15(1):91.
Darezereshki E. Synthesis of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles by wet chemical method at room temperature. Mater Lett. 2010;64(13):1471.
Darezereshki E. One-step synthesis of hematite nanoparticles by direct thermal decomposition of maghemite. Mater Lett. 2011;65(4):642.
Khosroshahi ME, Ghazanfari L. Synthesis and functionalization of SiO2 coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with amine groups based on self-assembly. Mater Sci Eng, C. 2012;32(5):1043.
Ngomsik AF, Bee A, Draye M, Cote G, Cabuil V. Magnetic nano- and microparticles for metal removal and environmental applications: a review. C R Chim. 2005;8(6–7):963.
Crane RA, Scott TB. Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater. 2012;211(212):317.
Sidhaarth KRA. Comparative studies of removal of lead and zinc from industrial wastewater and aqueous solution by iron oxide nanoparticle: performance and mechanisms. Eur J Sci Res. 2012;70(2):169.
Al-Saad KA, Amr MA, Hadi DT, Arar RS, Al-Sulaiti MM, Abdulmalik TA, Alsahamary NM, Kwak JC. Iron oxide nanoparticles: applicability for heavy metal removal from contaminated water. Arab J Nucl Sci Appl. 2012;45(2):335.
Slowing II, Escoto JLV, Wu CHW, Lin VSY. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(1):1278.
Hudson SP, Padera RF, Langer R, Kohane DS. The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterial. 2008;29(30):4045.
Carrillo AI, Linares N, Serrano E, Martinez JG. Well-ordered mesoporous interconnected silica spheres prepared using extremely low surfactant concentrations. Mater Chem Phys. 2011;1299(1–2):261.
Du E, Yu SH, Zuo L, Zhang J, Huang X, Wang Y. Pb(II) sorption on molecular sieve analogues of MCM-41 synthesized from kaolinite and montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci. 2011;51(1):94.
Quintanilla DP, Sánchez A, Del Hierro I, Fajardo M, Sierra I. Preparation, characterization, and Zn2+ adsorption behavior of chemically modified MCM-41 with 5-mercapto-1-methyltetrazole. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007;313(2):551.
Heidari A, Younesi H, Mehraban Z. Removal of Ni(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) from a ternary aqueous solution by amino functionalized mesoporous and nano mesoporous silica. Chem Eng J. 2009;153(1–3):70.
Surowiec Z, Wiertel M, Budzynski M, Sarzynski J, Goworek J. Magnetite nanowires in MCM-41 type mesoporous silica templates. J Non Cryst Solids. 2008;354(35–39):4271.
Surowiec Z, Bierska-Piech B, Wiertel M, Budzynski M, Goworek J. Magnetic nanoparticles in MCM-41 type mesoporous silica. Acta Phys Pol, A. 2008;114(6):1605.
Yang H, Deng Y, Du CH. Synthesis and optical properties of mesoporous MCM-41 containing doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2009;339(1–3):111.
Sheng X, Gao J, Han L, Jia Y, Sheng W. One-pot synthesis of tryptophols with mesoporous MCM-41 silica catalyst functionalized with sulfonic acid groups. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011;143(1):73.
Yousefpour M, Taherian Z. The effects of ageing time on the microstructure and properties of mesoporous silica-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. Superlattices Microstruct. 2013;54:78.
Naghiloo M, Yousefpour M, Nourbakhsh MS, Taherian Z. Functionalization of SBA-16 silica particles for ibuprofen delivery. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol. 2015;74(2):537.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Semnan University Foundation of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalantari, S., Yousefpour, M. & Taherian, Z. Synthesis of mesoporous silica/iron oxide nanocomposites and application of optimum sample as adsorbent in removal of heavy metals. Rare Met. 36, 942–950 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0709-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0709-4