Abstract
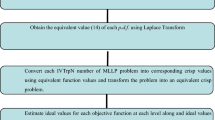
This paper addresses the general fully neutrosophic multi-level multiobjective programming problems i.e. ML-MOLPPs in which not only coefficients of each objective at each level but also all coefficients and parameters in the constraints are fully neutrosophic numbers in the form of trapezoidal neutrosophic numbers (NNs). From the point of view of complexity of the problem, it is proposed to apply ranking function of NNs to convert problem into equivalent ML-MOLPPs with crisp values of neutrosophic coefficients and parameters. Then suitable membership function for each objective and decision variable are formulated using lowest and highest value of each objective and decision variables of converted ML-MOLPP. Formulation of membership functions for decision variables (using corresponding values to maximum and minimum of objectives) will avoid decision deadlock in hierarchical structure. Accordingly, simple fuzzy goal programming strategy is applied to build FGP solution models. With the help of linear programming techniques on these solution models, compromise optimal solution of original fully neutrosophic ML-MOLPP is obtained. The proposed approach is a unique and simple method to provide compromise optimal solution to decision makers of general fully neutrosophic ML-MOLPP. The proposed approach is illustrated with numerical example to show its uniqueness and simplicity as solution technique. A case study is also discussed to demonstrate its applicability on real problems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lachhwani, K., Dwivedi, A.: Bi-level and multi-level programming problems: taxonomy of literature review and research issues. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 25, 847–877 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-017-9216-5
Bhati, D., Singh, P., Arya, R.: A taxonomy and review of the multi-objective fractional programming (MOFP) problems. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 3, 2695–2717 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-016-0261-9
Gzara, F.: A cutting plane approach for bilevel hazardous material transport network design. Oper. Res. Lett. 41, 40–46 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orl.2012.10.007
Fontaine, P., Minner, S.: Benders decomposition for discrete-continuous linear bilevel problems with application to traffic network design. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 70, 163–172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trb.2014.09.007
Kis, T., Kovács, A.: Exact solution approaches for bilevel lot-sizing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 226, 237–245 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2012.11.023
Wang, D., Du, G., Jiao, R.J., Wu, R., Yu, J., Yang, D.: A Stackelberg game theoretic model for optimizing product family architecting with supply chain consideration. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 172, 1–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.11.001
Camacho-Vallejo, J.-F., Cordero-Franco, Á.E., González-Ramírez, R.G.: Solving the bilevel facility location problem under preferences by a Stackelberg-evolutionary algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 1–14 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/430243
Kalashnikov, V., Matis, T.I., Camacho Vallejo, J.F., Kavun, S.V.: Bilevel programming, equilibrium, and combinatorial problems with applications to engineering. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 1–3 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/490758
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8, 338–353 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0019-9958(65)90241-x
Atanassov, K.T.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20, 87–96 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-0114(86)80034-3
Smarandache, F.: A unifying field in logics: neutrosophic logic. Neutrosophy, Neutrosophic set, neutrosophic probability and statistics. (1998)
Smarandache, F.: Introduction of neutrosophic statistics. Sitech and Education Publisher, Craiova (2013)
Smarandache, F.: (t, i, f)-Neutrosophic structures & I-neutrosophic structures (revisited). Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 8, 3–9 (2015)
Ye, J.: Multiple-attribute group decision-making method under a neutrosophic number environment. J. Intell. Syst. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/jisys-2014-0149
Deli, I., Şubaş, Y.: A ranking method of single valued neutrosophic numbers and its applications to multi-attribute decision making problems. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 8, 1309–1322 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0505-3
Deli, I., Şubaş, Y.: Some weighted geometric operators with SVTrN-numbers and their application to multi-criteria decision making problems. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 32, 291–301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-151677
Tanaka, H., Okuda, T., Asai, K.: Fuzzy mathematical programming. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control Eng. 9, 607–613 (1973). https://doi.org/10.9746/sicetr1965.9.607
Zimmermann, H.-J.: Fuzzy programming and linear programming with several objective functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1, 45–55 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(78)90031-3
Bharati, S.K., Singh, S.R.: A note on solving a fully intuitionistic fuzzy linear programming problem based on sign distance. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 119, 30–35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5120/21379-4347
Sidhu, S.K., Kumar, A.: A note on “Solving intuitionistic fuzzy linear programming problems by ranking function.” J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 30, 2787–2790 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3233/ifs-152033
Liu, Q., Yang, Y.: Interactive programming approach for solving multi-level multi-objective linear programming problem. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 35, 55–61 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-169566
Pramanik, S., Banerjee, D., Giri, B.: Multi-level multi-objective linear plus linear fractional programming problem based on FGP approach. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2, 171–177 (2015)
Baky, I.A.: Solving multi-level multi-objective linear programming problems through fuzzy goal programming approach. Appl. Math. Model. 34, 2377–2387 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2009.11.004
Lachhwani, K.: On solving multi-level multi objective linear programming problems through fuzzy goal programming approach. Opsearch 51, 624–637 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12597-013-0157-y
Lachhwani, K.: Modified FGP approach for multi-level multi objective linear fractional programming problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 266, 1038–1049 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2015.06.027
Osman, M.S., Emam, O.E., El Sayed, M.A.: Solving multi-level multi-objective fractional programming problems with fuzzy demands via FGP approach. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-017-0467-5
Pramanik, S., Roy, R., Roy, T.: Teacher selection strategy based on bidirectional projection measure in neutrosophic number environment. In: Neutrosophic operational research, pp. 29–53. Pons Publishing House/Pons asb, Bruxelles (2017)
Ye, J.: Neutrosophic number linear programming method and its application under neutrosophic number environments. Soft. Comput. 22, 4639–4646 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2646-z
Ye, J., Cui, W., Lu, Z.: Neutrosophic number nonlinear programming problems and their general solution methods under neutrosophic number environments. Axioms 7, 13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms7010013
Pramanik, S., Banerjee, D.: Neutrosophic number goal programming for multi-objective linear programming problem in neutrosophic number environment. MOJ Curr. Res. Rev. 1, 135–141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.15406/mojcrr.2018.01.00021
Pramanik, S., Dey, P.: Bi-level linear programming problem with neutrosophic numbers. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 21, 110–121 (2018)
Maiti, I., Mandal, T., Pramanik, S.: Neutrosophic goal programming strategy for multi-level multi-objective linear programming problem. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 11, 3175–3186 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01482-0
Abdel-Basset, M., Gunasekaran, M., Mohamed, M., Smarandache, F.: A novel method for solving the fully neutrosophic linear programming problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 31, 1595–1605 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3404-6
Mohamed, M., Abdel-Basset, M., Zaied, A., Smarandache, F.: Neutrosophic integer programming problem. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 15, 3–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.570944
Ganesan, K., Veeramani, P.: Fuzzy linear programs with trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Ann. Oper. Res. 143, 305–315 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-006-7390-1
Ebrahimnejad, A., Tavana, M.: A novel method for solving linear programming problems with symmetric trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Appl. Math. Model. 38, 4388–4395 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2014.02.024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lachhwani, K. Solving the general fully neutrosophic multi-level multiobjective linear programming problems. OPSEARCH 58, 1192–1216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12597-021-00522-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12597-021-00522-8