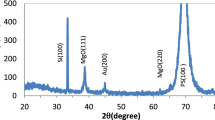
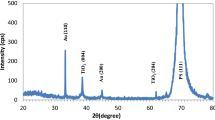
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to explore if nanostructured Au–TiO2 particles can replace traditional, bulkier materials in gas sensing applications. Then use a Nd-YAG laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm, number of shot 500 pulse, and 500 mJ, 660 mJ, and 820 mJ laser ablated energy, the pulsed laser deposition technique has been widely used to prepare and characterize Au–TiO2 nanoparticles on Porous Silicon substrate produced on n-type Silicon wafer. By using of drop casting method, the Au–TiO2 NPs have deposited on porous silicon (PS) layer with 15 drops of each specimen. The morphology of PS layer, Au:TiO2 NPs and Au–TiO2 NPs/PS specimens were reviewed using scanning electron microscopy, XRD pattern analysis, and transmission electron microscopy. We found that the Au:TiO2 NPs play important role to develop electrical properties and sensitivity to H2S and NO2.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
U.M. Nayef, M.W. Muayad, H.A. Khalaf, ZnO/PS/p-Si heterojunction properties. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 66, 20104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap/2014130470
D.H. Jwied, U.M. Nayef, F.A.-H. Mutlak, Preparation and characterization of C:Se nano-rods ablated on porous silicon. Optik 239, 166811 (2021)
F.A.-H. Mutlak, A.F. Ahmed, U.M. Nayef, Q. Al-zaidi, S.K. Abdulridha, Improvement of absorption light of laser texturing on silicon surface for optoelectronic application. Optik 237, 166755 (2021)
D.H. Jwied, U.M. Nayef, F.A.-H. Mutlak, Synthesis of C:Se (core:shell) nanoparticles via laser ablation on porous silicon for photodetector application. Optik 231, 166493 (2021)
T.M. Rashid, U.M. Nayef, M.S. Jabir, F.A.-H. Mutlak, Study of optical and morphological properties for Au–ZnO nanocomposite prepared by Laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1795(1), 012041 (2021)
N.A. Abdulkhaleq, U.M. Nayef, A.K.H. Albarazanchi, MgO nanoparticles synthesis via laser ablation stationed on porous silicon for photoconversion application. Optik 212, 164793 (2020)
U.M. Nayef, R.I. Kamel, Bi2O3 nanoparticles ablated on porous silicon for sensing NO2 gas. Optik 208, 164146 (2020)
N.A. Abdulkhaleqa, A.K. Hassan, U.M. Nayef, Enhancement of photodetectors devices for silicon nanostructure from study effect of etching time by photoelectrochemical etching technique. Optik 206, 164325 (2020)
B. Ding, M. Wang, J. Yu, G. Sun, Gas sensors based on electrospun nanofibers. Sensors 9, 1609–1624 (2009)
V.A. Sharadrao, V.L. Patil, N.S. Harale, S.A. Vhanalakar, M.G. Gang, J.Y. Kim, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Controlled growth of ZnO nanorod arrays via wet chemical route for NO2 gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 221, 1195–1201 (2015)
H. Ozoe, K. Okada, The effect of the direction of the external magnetic field on the three-dimensional natural convection in a cubical enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 32, 1939–1954 (1989)
J.C. Scaiano, F.L. Cozens, J. McLean, Model for the rationalization of magnetic field effects in vivo. Application of the radical-pair mechanism to biological systems. Photochem. Photobiol. 59, 585–589 (1994)
D. Horák, B. Rittich, A. Španová, M.J. Beneš, Magnetic microparticulate carriers with immobilized selective ligands in DNA diagnostics. Polymer 46, 1245–1255 (2005)
A. Jordan, R. Scholz, K. Maier-Hauff, M. Johannsen, P. Wust, J. Nadobny, H. Schirra et al., Presentation of a new magnetic field therapy system for the treatment of human solid tumors with magnetic fluid hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 225, 118–126 (2001)
J. Xie, S. Lee, X. Chen, Nanoparticle-based theranostic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 62, 1064–1079 (2010)
T. Van Nguyen, H. Bui, Nano porous silicon microcavity sensor for determination organic solvents and pesticide in water. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 5, 045003 (2014)
U.M. Nayef, H.T. Hussein, A.M. Abdul Hussien, Study of photoluminescence quenching in porous silicon layers that using for chemical solvents vapor sensor. Optik 172, 1134–1139 (2018)
H.T. Hussein, U.M. Nayef, A.M. Abdul Hussien, Synthesis of graphene on porous silicon for vapor organic sensor by using photoluminescence. Optik 180, 61–70 (2019)
S.S. Khudiar, U.M. Nayef, F.A.-H. Mutlak, Improvement of spectral responsivity of ZnO nanoparticles deposited on porous silicon via laser ablation in liquid. Optik 244, 167530 (2021)
U.M. Nayef, R.I. Kamel, Enhancement the electrical properties of porous silicon for photo-detectors applications by depositing Bi2O3 nanoparticles. Optik 207, 163847 (2020)
D.H. Jwied, U.M. Nayef, F.A.-H. Mutlak, Synthesis of C:Se nanoparticles via laser ablated with magnetic field on porous silicon for gas sensor applications. Optik 242, 167207 (2021)
R.I. Kamel, D.S. Ahmed, U.M. Nayef, Synthesis of Bi2O3 nanoparticles by laser ablation on porous silicon for photoconversion application. Optik 193, 163013 (2019)
U.M. Nayef, I.M. Khudhair, Synthesis of gold nanoparticles chemically doped with porous silicon for organic vapor sensor by using photoluminescence. Optik 154, 398–404 (2018)
U.M. Nayef, Improve the efficiency of UV-detector by modifying the Si and porous silicon substrate with ZnS thin films. Optik 130, 441–447 (2017)
F.A.H. Mutlak, A.B. Taha, U.M. Nayef, Synthesis and characterization of SnO2 on porous silicon for photoconversion. SILICON 10(3), 967–974 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9554-9
U.M. Nayef, I.M. Khudhair, Study of porous silicon humidity sensor vapors by photoluminescence quenching for organic solvents. Optik 135, 169–173 (2017)
N. Harb, F.A.-H. Mutlak, Production and characterization of porous silicon via laser-assisted etching: effect of gamma irradiation. Optik 246, 167800 (2021)
M. Aswad, F.A.-H. Mutlak, M. Jabir, S. Abdulridha, A. Ahmed, U.M. Nayef, Laser assisted hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1795, 012030 (2021)
A. Ahmed, M. Abdulameer, M. Kadhim, F. Mutlak, Plasma parameters of Au nano-particles ablated on porous silicon produced via Nd-YAG laser at 355 nm for sensing NH3 gas. Optik 249, 168260 (2022)
S.S. Khudiar, U.M. Nayef, F.A.-H. Mutlak, Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles via laser ablation for sensing NO2 gas. Optik 246, 167762 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jwar, A.J., Nayef, U.M. & Mutlak, F.A. Study effect of magnetic field on Au–TiO2 nanoparticles ablated on silicon nanostructures for gas sensors. J Opt 53, 747–755 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00987-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00987-w