Abstract
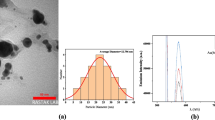
This work aims to control the random laser performance using magnetic-plasmonic nanoparticles including Fe3O4 and Au nanoparticles mixed with the active laser media R6G dye. For this purpose, Au nanoparticles were produced via the electrical exploding wire method and mixed with the Fe3O4 nanoparticles in the dye medium. After characterizing the samples through the transmission electron microscopy and the florescence spectra in the visible region, they were pumped by the second harmonic generation of the Nd: YAG laser where the random lasing action was detected by a spectrometer. These measurements were performed with and without external magnetic field at 35 mT. The results revealed a nice full width at half maximum of random laser efficiency in the samples exposed to the external magnetic field. In addition, using the external magnetic field, the coherency percentage of the random lasing action diminished because of the fixed direction of the magnetic field which was collinear to the cell direction that can affect the coherency loop due to nanoparticles’ arrangement direction in the dye medium.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Wang, L. Deng, Electrically controlled plasmonic lasing resonances with silver nanoparticles embedded in amplifying nematic liquid crystals. Laser Phys. Lett. 11, 115814–115818 (2014)
T. Nakamura, T. Takahashi, S. Adachi, Temperature-dependent random lasing from GaAs powders. Laser Reson. Beam Control XII, 75791J (2010)
T. Naruta, T. Akita, Y. Uchida, D. Lisjak, A. Mertelj, N. Nishiyama, Magnetically controllable random laser in ferromagnetic nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Express 27, 24427–24432 (2019)
C.-Y. Tsai, Y.-M. Liao, W.-C. Liao, Magnetically controllable random lasers. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2, 1700170–1700174 (2017)
H. Kaiju, J. Nishii, K. Sasaki, Magnetic response of random lasing modes in a ZnO nanoparticle film deposited on a NiFe thin fil. Appl. Phys. Lett. 113, 131108–131111 (2018)
V. Hoang, N.T. Phuong, N. Van Phu, Random Lasers: Characteristics, Applications and Some Research Results. Computational Methods in Science and Technology 2, 47–51 (2010)
R.G.S. El-Dardiry, R. Mooiweer, A. Lagendijk, Experimental phase diagram for random laser spectra. New J. Phys. 14, 1–11 (2012)
S.F. Haddawi, H. Hummud, S.M. Hamidi, Signature of plasmonic nanoparticles in multi-wavelength low power random lasing. Opt. Laser Technol. 121, 105770–105784 (2020)
S. Mujumdar, M. Ricci, R. Torre, D.S. Wiersma, Amplified extended modes in random lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 053903–053908 (2004)
A.O. Govorov, H.H. Richardson, Generating heat with metal nanoparticles. Nano Today 2, 30–38 (2007)
A.O. Govorov, W. Zhang, T. Skeini, H. Richardson, J. Lee, N.A. Kotov, Gold nanoparticle ensembles as heaters and actuators: Melting and collective plasmon resonances. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 1, 84–90 (2006)
J.B. Herzog, M.W. Knight, D. Natelson, Thermoplasmonics: Quantifying plasmonic heating in single nanowires. Nano Lett. 14, 499–503 (2014)
V. Kotaidis, C. Dahmen, G. von Plessen, F. Springer, A. Plech, Excitation of nanoscale vapor bubbles at the surface of gold nanoparticles in water. J. Chem. Phys 124, 184702–184706 (2006)
H.H. Richardson, M.T. Carlson, P.J. Tandler, P. Hernandez, A.O. Govorov, Experimental and theoretical studies of light-to-heat conversion and collective heating effects in metal nanoparticle solutions. Nano Lett. 9, 1139–1146 (2009)
M. Virk, K. Xiong, M. Svedendahl, M. Kall, A.B. Dahlin, A thermal plasmonic sensor platform: Resistive heating of nanohole arrays. Nano Lett. 14, 3544–3549 (2014)
A. Lenert, D.M. Bierman, Y. Nam, W.R. Chan, I. Celanovic, M. Soljacic, E.N. Wang, A nanophotonic solar thermophoto voltaicdevice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 126–130 (2014)
P. Li, B. Liu, Y. Ni, K.K. Liew, J. Sze, S. Chen, S. Shen, Large-scale nanophotonic solar selective absorbers for high-efficiency solar thermal energy conversion. Adv. Mater. 27, 4585–4591 (2015)
K.T. Lin, H.L. Chen, Y.S. Lai, C.C. Yu, Y.C. Lee, P.Y. Su, Y.T. Yen, B.Y. Chen, Loading effect–induced broadband perfect absorber based on single-layer structured metal film. Nano Energy 37, 61–73 (2017)
J.W. Schwede, I. Bargatin, D.C. Riley, B.E. Hardin, S.J. Rosenthal, Y. Sun, F. Schmitt, P. Pianetta, R.T. Howe, Z.X. Shen, N.A. Melosh, Photon-enhanced thermionic emission for solar concentrator systems. Nat. Mater. 9, 762–767 (2010)
A. Kosuga, Y. Yamamoto, M. Miyai, A high performance photothermal film with spherical shell-type metallic nanocomposites for solar thermoelectric conversion. Nanoscale 7, 7580–7584 (2015)
M. Fedoruk, M. Meixner, S. Carretero-Palacios, T. Lohmuller, J. Feldmann, Nanolithography by plasmonic heating and optical manipulation of gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 7, 7648–7653 (2013)
C.M. Cobley, L. Au, J. Chen, Y. Xia, Targeting gold nanocages to cancer cells for photothermal destruction and drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 7, 577–587 (2010)
L. Gao, R. Liu, F. Gao, Y. Wang, X. Jiang, X. Gao, Plasmon mediated generation of reactive oxygen species from near infrared light excited gold nanocages for photodynamic therapy in vitro. ACS Nano 8, 7260–7271 (2014)
R. Huschka, J. Zuloaga, M.W. Knight, L.V. Brown, P. Nordlander, N.J. Halas, Light-induced release of DNA from gold nanoparticles: nanoshells and nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 12247–12255 (2011)
M.A. Mackey, M.R. Ali, L.A. Austin, R.D. Near, M.A. ElSayed, The most effective gold nanorod size for plasmonic photothermal therapy: theory and in vitro experiments. J. Phys. Chem. B 118, 1319–1326 (2014)
Y. Wang, K.C.L. Black, H. Luehmann, Comparison study of gold nanohexapods, nanorods, and nanocages for photothermal cancer treatment. ACS Nano 7, 2068–2077 (2013)
J. Yang, D. Shen, L. Zhou, W. Li, X. Li, C. Yao, R. Wang, A.M. Toni, F. Zhang, D. Zhao, Spatially confined fabrication of core–shell gold nanocages@mesoporous silica for near-infrared controlled photothermal drug release. Chem. Mat. 25, 3030–3037 (2013)
M.S. Yavuz, Y. Cheng, J. Chen et al., Gold nanocages covered by smart polymers for controlled release with near-infrared light. Nat. Mater. 8, 935–939 (2009)
L. Zhou, S. Zhuang, C. He, Y. Tan, Z. Wang, J. Zhu, Self assembled spectrum selective plasmonic absorbers with tunable bandwidth for solar energy conversion. Nano Energy 32, 195–200 (2017)
L. Zhou, Y. Tan, J. Wang, W. Xu, Y. Yuan, W. Cai, S. Zhu, J. Zhu, 3D self-assembly of Aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination. Nat. Photonics 10, 393–398 (2016)
S.H. Tsao, D. Wan, Y.S. Lai, H.M. Chang, C.C. Yu, K.T. Lin, H.L. Chen, White-light-induced collective heating of gold nanocomposite/bombyxmori silk thin films with ultrahigh broadband absorbance. ACS Nano 9, 12045–12059 (2015)
K.T. Lin, H.L. Chen, Y.S. Lai, Filter-free, junctionless structures for color sensing. Nanoscale 8, 16936–16946 (2016)
A.S. Wasfi, H.R. Humud, N.K. Fadhil, Synthesis of core-shell Fe3O4-Au nanoparticles by electrical exploding wire technique combined with laser pulse shooting. Opt. Laser Technol. 111, 720–726 (2019)
Q. Li, C.W. Kartikowati, S. Horie, T. Ogi, T. Iwaki, K. Okuyama, Correlation between particle size/ domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 7, 9894–9899 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
A-Jarah, N.H., Wasfi, A.S. & Hamidi, S.M. Random laser performance by magneto-plasmonic nanoparticles. J Opt 52, 1381–1387 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00974-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00974-1