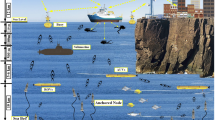
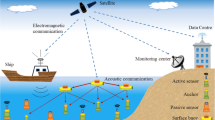
Abstract
Oceans cover about 72 percent of the Earth’s atmosphere. Owing to distinct incredible aquatic activities the Oceans remain unclear and deep-seated to investigate. “Underwater wireless communication” (UWC) plays an important role in sea species tracking, water contamination, oil and gas production, natural hazard control, maritime security, naval military activities, and in detecting improvements in the aquatic environment. To achieve these applications in an efficient way, a new era name Internet of Underwater Things (IoUT) is introduced. IoUT is a scientific development that could bring a new phase for research, business, and underwater military applications. It also severs as an important feature of 5G and 6G networking systems. The up-coming fifth (5G)- and sixth (6G)-generation connectivity networks are supposed to make tremendous improvement relative to the current fourth-generation systems with some essential and general problems about 5G coverage performance, 6G and high-ability networking networks, huge coverage, low latency, high protection, low power usage, strong knowledge, and stable networking. To encounter the obstacles in 5G networks, innovations like optical (OWC) communication by means of wireless means is utilized. Innovations such as optical wireless communication (OWC) are used to tackle the obstacles in 5G networks. OWC is a better employee for operation in 5G network specifications than other wireless technologies. This paper explains how the OWC strategy would be the best and most effective approach to effectively implement 5G, 6G, and IoUT networks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Saeed, A. Celik, T.Y. Al-Naffouri, M.-S. Alouini, Underwater optical wireless communications, networking, and localization: a survey. Ad Hoc Netw 94, 101935 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2019.101935
A. Celik, N. Saeed, B. Shihada, T.Y. Al-Naffouri, M. Alouini, A software-defined opto-acoustic network architecture for internet of underwater things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 58, 88–94 (2020)
M. Erol-Kantarci, H.T. Mouftah, S. Oktug, A survey of architectures and localization techniques for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 13, 487–502 (2011)
Z. Ghassemlooy, S. Arnon, M. Uysal, Z. Xu, J. Cheng, Emerging optical wireless communications-advances and challenges. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 33, 1738–1749 (2015)
Z. Xu, B.M. Sadler, Ultraviolet communications: potential and state-of-the-art. IEEE Commun. Mag. 46, 67–73 (2008)
J.M. Kahn, J.R. Barry, Wireless infrared communications. Proc. IEEE 85, 265–298 (1997)
P.H. Pathak, X. Feng, P. Hu, P. Mohapatra, Visible light communication, networking, and sensing: a survey, potential and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 17, 2047–2077 (2015)
M. Shafi, A.F. Molisch, P.J. Smith, T. Haustein, P. Zhu, P. De Silva, F. Tufvesson, A. Benjebbour, G. Wunder, 5g: A tutorial overview of standards, trials, challenges, deployment, and practice. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 35, 1201–1221 (2017)
J.G. Andrews, S. Buzzi, W. Choi, S.V. Hanly, A. Lozano, A.C.K. Soong, J.C. Zhang, What will 5g be? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 32, 1065–1082 (2014)
W.A. Hassan, H. Jo, A.R. Tharek, The feasibility of coexistence between 5g and existing services in the imt-2020 candidate bands in malaysia. IEEE Access 5, 14867–14888 (2017)
A. Ijaz, L. Zhang, M. Grau, A. Mohamed, S. Vural, A.U. Quddus, M.A. Imran, C.H. Foh, R. Tafazolli, Enabling massive iot in 5g and beyond systems: phy radio frame design considerations. IEEE Access 4, 3322–3339 (2016)
K. David, H. Berndt, 6g vision and requirements: Is there any need for beyond 5g? IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 13, 72–80 (2018)
F. Tariq, M. Khandaker, K.-K. Wong, M. Imran, M. Bennis, M. Debbah, A speculative study on 6g (2019).
S.J. Nawaz, S.K. Sharma, S. Wyne, M.N. Patwary, M. Asaduzzaman, Quantum machine learning for 6g communication networks: state-of-the-art and vision for the future. IEEE Access 7, 46317–46350 (2019)
R.-A. Stoica, G. Abreu, 6g: the wireless communications network for collaborative and ai applications (2019)
W. Saad, M. Bennis, M. Chen, A vision of 6g wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems. IEEE Network 34, 134–142 (2020)
D. Tsonev, S. Videv, H. Haas, Towards a 100 gb/s visible light wireless access network. Opt. Express 23, 1627 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.23.001627
M. Chowdhury, M.T. Hossan, M.K. Hasan, Y.M. Jang, Integrated rf/optical wireless networks for improving qos in indoor and transportation applications. Wireless Pers. Commun. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5971-3
S. Dimitrov, H. Haas, Principles of LED Light Communications: Towards Networked Li-Fi (2015). doi:10.1017/CBO9781107278929
H. Haas, L. Yin, Y. Wang, C. Chen, What is lifi? J. Lightwave Technol. 34, 1533–1544 (2016)
M.K. Hasan, M. Chowdhury, M. Shahjalal, Y.M. Jang, Fuzzy based network assignment and link-switching analysis in hybrid occ/lifi system. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2870518
H. Lu, C. Li, H. Chen, C. Ho, M. Cheng, Z. Yang, C. Lu, A 56 gb/s pam4 vcsel-based lifi transmission with two-stage injection-locked technique. IEEE Photonics J. 9, 1–8 (2017)
M.T. Hossan, M. Chowdhury, M.K. Hasan, M. Shahjalal, T. Nguyen, N.-T. Le, Y.M. Jang, A new vehicle localization scheme based on combined optical camera communication and photogrammetry. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2018, 14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8501898
M. Shahjalal, M. T. Hossan, M. K. Hasan, M. Z. Chowdhury, N. T. Le, Y. M. Jang, An implementation approach and performance analysis of image sensor based multilateral indoor localization and navigation system, CoRR abs/1810.02600 (2018).
P. Luo, S. Zvanovec, Optical Camera Communications, pp. 547–568 (2016).
Y. Goto, I. Takai, T. Yamazato, H. Okada, T. Fujii, S. Kawahito, S. Arai, T. Yendo, K. Kamakura, A new automotive vlc system using optical communication image sensor. IEEE Photonics J. 8, 1–17 (2016)
A. Malik, P. Singh, Free space optics: current applications and future challenges. Int. J. Opt. 2015, 1–7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/945483
M.-A. Khalighi, M. Uysal, Survey on free space optical communication: A communication theory perspective. IEEE Commun. Surv. Amp Tutor. 16, 2231–2258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2014.2329501
H. Kaushal, G. Kaddoum, Optical communication in space: Challenges and mitigation techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 19, 57–96 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2016.2603518
Z. Zeng, S. Fu, H. Zhang, Y. Dong, J. Cheng, A survey of underwater optical wireless communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 19, 204–238 (2017)
N. Saeed, A. C¸ elik, T. Al-Naffouri, M.-S. Alouini, Underwater optical wireless communications, networking, and localization: a survey (2018).
C. Gussen, P. Diniz, M. Campos, W. Martins, F. Costa, J. Gois, A survey of underwater wireless communication technologies. J. Commun. Inf. Syst. 31, 242–255 (2016). https://doi.org/10.14209/jcis.2016.22
H. Kaushal, G. Kaddoum, Underwater optical wireless communication. IEEE Access 4, 1518–1547 (2016)
I. Akyildiz, D. Pompili, T. Melodia, Underwater acoustic sensor networks: research challenges. Ad HocNetworks 3, 257–279 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2005.01.004
M. Rhodes, Electromagnetic propagation in sea water and its value in military systems, 2007.
M. Domingo, An overview of the internet of underwater things. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 35, 1879–1890 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2012.07.012
D. Bandyopadhyay, J. Sen, Internet of things: applications and challenges in technology and standardization, CoRR abs/1105.1693 (2011).
I. Akyildiz, P. Wang, S.-C. Lin, Softwater: software-defined networking for next-generation underwater communication systems, Ad Hoc Networks 46 (2016). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2016.02.016.
R. Smith, K. Baker, Optical properties of the clearest natural waters (200–800 nm). Appl. Opt. 20, 177–184 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.20.000177
Z. Zhu, W. Guan, L. Liu, S. Li, S. Kong, Y. Yan, A multi-hop localization algorithm in underwater wireless sensor networks, in 2014 6th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, WCSP 2014 (2014). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/WCSP.2014.6992019.
I. Akyildiz, D. Pompili, T. Melodia, Challenges for efficient communication in underwater acoustic sensor networks, ACM SIGBED Review 1 (2004). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/1121776.1121779.
A. Zoksimovski, C. Rappaport, D. Sexton, M. Stojanovic, Underwater electromagnetic communications using conduction—channel characterization, vol. 34 (2012). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/2398936.2398962.
M. Z. Chowdhury, M. Shahjalal, S. Ahmed, Y. M. Jang, 6g wireless communication systems: Applications, requirements, technologies, challenges, and research directions (2019).
K. David, H. Berndt, 6g vision and requirements: Is there any need for beyond 5g? IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 13(3), 72–80 (2018)
J.N. Syed, S.K. Sharma, S. Wyne, M. Patwary, M. Asaduzzaman, Quantum machine learning for 6g communication networks: state-of-the-art and vision for the future. IEEE Access 7, 46317–46350 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2909490
R.-A. Stoica, G. Abreu, 6g: the wireless communications network for collaborative and ai applications (2019).
W. Saad, M. Bennis, M. Chen, A vision of 6g wireless systems: applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems (2019).
S. Mumtaz, J. Jornet, J. Aulin, W. Gerstacker, X. Dong, B. Ai, Terahertz communication for vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 66, 5617–5625 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2017.2712878
L. Lov´en, T. Lepp¨anen, E. Peltonen, J. Partala, E. Harjula, P. Porambage, M. Ylianttila, J. Riekki, Edgeai:A vision for distributed, edge-native artificial intelligence in future 6g networks (2019).
F. Clazzer, A. Munari, G. Liva, F. Lazaro, Stefanovi´c, P. Popovski, From 5g to 6g: Has the time for modern random access come? (2019).
M. Giordani, M. Polese, M. Mezzavilla, S. Rangan, M. Zorzi, Towards 6g networks: Use cases and technologies (2019).
L. G. J.-D. Lee, Juho, 5g: Vision and requirements for mobile communication system towards year 2020, Chinese Journal of Engineering (2016). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5974586.
P. Hu, P. Pathak, A. Das, Z. Yang, P. Mohapatra, Plifi: hybrid wifi-vlc networking using power lines, pp. 31–36 (2016). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/2981548.2981549.
Z. Du, W. Chunxi, S. Youming, G. Wu, Context-aware indoor vlc/rf heterogeneous network selection: Reinforcement learning with knowledge transfer, IEEE Access PP (2018). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2844882.
T. Koonen, Indoor optical wireless systems: technology, trends and applications. J. Lightwave Technol. pp. 1–1 (2017). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2017.2787614.
C. Danakis, M. Afgani, G. Povey, I. Underwood, H. Haas, Using a cmos camera sensor for visible light communication, pp. 1244–1248 (2012). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOMW.2012.6477759.
H.-M. Tsai, H.-M. Lin, H.-Y. Lee, Demo: Rollinglight—universal camera communications for single led (2014). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1145/2639108.2641748.
M. Chowdhury, M. Shahjalal, M.K. Hasan, Y.M. Jang, The role of optical wireless communication technologies in 5g/6g and iot solutions: Prospects, directions, and challenges. Appl. Sci. 9, 4367 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204367
T. Perera, D. N. Jayakody, S. K. Sharma, S. Chatzinotas, J. Li, Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (swipt): Recent advances and future challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. PP (2018). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2783901.
X. Chen, D. W. K. Ng, H.-H. Chen, Secrecy wireless information and power transfer: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Wireless Commun. 23 (2015). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/MWC.2016.7462485.
I.-J. Yoon, Wireless power transfer in the radiating near-field region, pp. 344–344 (2015). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/USNC- URSI.2015.7303628.
B. Srujana, P. Neha, H. Mathews, Govindan, Multi-source energy harvesting system for underwater wireless sensor networks. Procedia Computer Science 46, 1041–1048 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.01.015
A.-N. T. A. M. Saeed N, Celik A, Energy harvesting hybrid acoustic-optical underwater wireless sensor networks localization, Sensors (Basel) (2017).
W. Ding, B. Song, M. Zhaoyong, K. Wang, Experimental investigation on an ocean kinetic energy harvester for underwater gliders, pp. 1035–1038 (2015). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ECCE.2015.7309802.
D. Gesbert, M. Kountouris, R. Heath, C.-B. Chae, T. S¨alzer, From single user to multiuser communications: Shifting the mimo paradigm, IEEE Signal Process. Mag. vol 24 (2007).
J. Cheon, H.-S. Cho, Power allocation scheme for non-orthogonal multiple access in underwater acoustic communications. Sensors 17, 2465 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112465
C. Geldard, J. Thompson, W. Popoola, A study of non-orthogonal multiple access in underwater visible light communication systems, pp. 1–6(2018). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/VTCSpring.2018.8417835.
D. Wan, M. Wen, F. Ji, H. Yu, F. Chen, Non-orthogonal multiple access for cooperative com—munications: challenges, opportunities, and trends. IEEE Wireless Commun. vol 25 (2018). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/MWC.2018.1700134.
Y. Zhang, S. Xiao, L. Liu, D. Sun, Analysis and estimation of the underwater acoustic millimeter-wave communication channel, pp. 1–5 (2016). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/COA.2016.7535740.
M. S. Leeson, M. D. Higgins, Optical wireless and millimeter waves for 5G access networks, (2019).
Y. Niu, Y. Li, D. Jin, L. Su, A. Vasilakos, A survey of millimeter wave (mmwave) communications for 5g: Opportunities and challenges, Wireless Netw. vol. 21 (2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0942-z.
G. Su, J. Jin, Y. Gu, J. Wang, Performance analysis of norm constraint least mean square algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. TSP 60 (2012). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2012.2184537.
M. Xu, L. Liu, Sender-receiver role-based energy-aware scheduling for internet of underwater things. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. pp. 1–1 (2016). Doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/TETC.2016.2632749.
T.S. Rappaport, Y. Xing, O. Kanhere, S. Ju, A. Madanayake, S. Mandal, A. Alkhateeb, G.C. Trichopoulos, Wireless communications and applications above 100 ghz: opportunities and challenges for 6g and beyond. IEEE Access 7, 78729–78757 (2019)
Y. Ping, Y. Xiao, M. Xiao, S. Li, 6g wireless communications: vision and potential techniques. IEEE Network 33, 70–75 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2019.1800418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menaka, D., Gauni, S., Manimegalai, C.T. et al. Vision of IoUT: advances and future trends in optical wireless communication. J Opt 50, 439–452 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-021-00722-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-021-00722-x