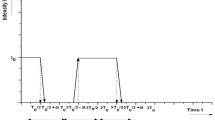
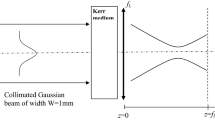
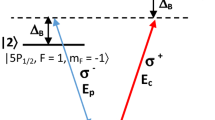
Abstract
Optical self-focusing and defocusing, optical switching activities and optical signal processing can be successfully done by using optical Kerr materials. Due to the nonlinear property of Kerr medium, this medium can be used to convert the frequency of the applied light signal passing through the medium. Here, in this paper, the authors propose a method of using optical Kerr medium for parametric generation of very low frequency electrical signal.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Chatterjee, S. Mukhopadhyay, A new method of obtaining an ultrashort optical pulse by the use of optical kerr material and a sawtooth optical pulse. Int. J. Electron. Commun. Technol. 6, 42–43 (2015)
A. Chatterjee, A. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, Method of frequency conversion of Manchester encoded data from a Kerr type of nonlinear medium. J. Opt. 46, 415–419 (2017)
J. Xu, X. Yu, W. Lu, F. Qu, N. Deng, Offset Manchester coding for rayleigh noise suppression in carrier distributed WDM-POMS. Opt. Commun. 346, 106–109 (2015)
J. Leuuthold, C.-S. Bres, All-optical pulse shaping for highest spectral efficiency. Springer Ser. Opt. Sci. 194, 217–260 (2015)
A.M. Cailean, B. Cagnea, L. Chassagne, Evaluation of the noise effects on visible light communications using Manchester and Miller coding, in Conference Proceedings, Development and Application System (DAS) (IEEE, 2014), pp. 85–89, 6842433. https://doi.org/10.1109/daa-s
B. Chakraborty, S. Mukhopadhyay, Alternative approach of conducting phase-modulated all optical logic gates. Opt. Eng. 48, 035201 (2009)
M. Vitek, I. Musevic, Nanosecond control and optical pulse shaping by stimulated emission depletion in a liquid crystal. Opt. Express 23, 16921–16932 (2015)
S. Dhar, S. Mukhopadhyay, All optical implementation of ASCII by use of nonlinear material for optical encoding of necessary symbols. Opt. Eng. 44, 065201 (2005)
D. Samanta, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical method for maintaining a fixed intensity level of a light signal in optical computation. Opt. Commun. 281, 4851–4853 (2008)
S.K. Chandra, S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, Phase encoded all-optical reconfigurable integrated multilogic unit using phase information processing of four wave mixing in semiconductor optical amplifier. IET Optoelectron. 10, 1–6 (2016)
S. Sen, S. Mukhopadhyay, Reduction of VP voltage of an electro-optic modulator by the oblique end cutting and multi-rotation. Opt. Laser Technol. 59, 19–23 (2014)
S. Bhattacharya, S.N. Patra, S. Mukhopadhyay, An all optical prototype neuron based on optical Kerr material. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 126, 13–18 (2015)
F.E. Robles, M.C. Fischer, W.S. Warren, Femtosecond pulse shaping enables detection of optical Kerr-effect (OKE) dynamics for molecular imaging. Opt. Lett. 39, 4788–4991 (2014)
S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-Optical approach for conversion of a binary number having a fractional part to its decimal equivalent to three places of decimal using single system optical tree architecture. J. Opt. 43, 122–129 (2014)
Y. Liu, F. Qin, F. Zhou, Q-b Meng, D-z Zhang, Z-y Li, Ultrafast optical switching in Kerr nonlinear photonic crystals. Front. Phys. Chin. 5, 220–244 (2010)
Z.-Y. Li, Z.-M. Meng, Polystyrene Kerr nonlinear photonic crystals for building ultrafast optical switching and logic devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 773–954 (2014)
L. Brzozowski, E.H. Sargent, Azobenzenes for photonic network applications: third-order nonlinear optical properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 12, 483–489 (2001)
B. Sarkar, S. Mukhopadhyay, Optoelctronic scheme for generation of time bound low-frequency electronic signal using multi-passing of light. J. Opt. Commu. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/joc
S. Mitra, S. Mukhopadhyay, An all optical scheme for implementing a NAND logic by dibit representation of squeezed states of light. J. Nonlinear Opt. Phys. Mater. 24, 1550048 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, A., Mukhopadhyay, S. Use of optical Kerr medium for parametric generation of very low frequency electrical signal. J Opt 48, 582–585 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-019-00570-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-019-00570-w