Abstract
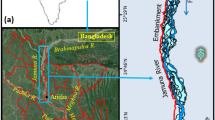
The Rapti a foothills-fed river is emerging from the Lesser Himalayan zone of southern Nepal. It has shifted its course at its foothills and middle reaches several times and has been affecting many localities in the last few decades. Keeping this in view a severely affected 94 km. long stretch of Rapti river flowing in the Shravasti district of eastern Uttar Pradesh was selected for the study of channel dynamics. In the present work, the geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing (RS) techniques were used to evaluate the river shifting and assessment of related effects on the adjacent landscapes between the years 1980 to 2020. Satellite image of Landsat and Sentinel was also used to determine the spatio-temporal changes occurring in the river channel for the last forty years. The river channels, their centre lines and bars were digitized in a GIS environment and all channels were divided into four reaches, viz. A, B, C and D. Twenty cross-sections perpendicular to the centre line representing the position of the channel in the year 1980 were drawn. The sinuosity index, measurements of the channel migration, channel width and bank line shift of the channel were calculated.
The sinuosity indices of the river channels for the years 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020 were computed as 1.52, 1.47, 1.47, 1.70 and 1.48, respectively. Temporal changes in sinuosity exhibit the meandering pattern of the river channel. Overlayed active channel centre lines of the years 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020 show the migrational trend of the river channel. The maximum migration has occurred along reaches A and D. The extensive migration and sedimentation in the channel also alter the channel width that varies significantly along reaches A and C. Apart from this, the geomorphic features viz. channel migration, bank line erosion, abandoned channels, expansion of meanders, oxbow lake, chute cut off, neck cut off, etc. were identified as indicators of active erosion on the flood plain of the Rapti. It has been observed that river migration and bank line erosion are severely affecting the many rural settlements situated in the active flood plain. This study infers that the Rapti river channel has been migrating frequently for the last forty years and is increasing the vulnerability of flood hazards in its active flood plains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhakal, L., Dubey, B., Sarma, A.K. (2005) Estimation of bank erosion in the river Brahmaputra near Agyathuri by Using Geographic Information System. Jour. Indian Soc. Rem. Sens., v.33(1), pp.81–84. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02989994
Bhatt S. C., Hussain A., Suresh M. and Balasooriya N. W. B. (2017) Geological structural control on Sukhnai Basin and Land Use/ Land Cover Pattern in Mauranipur and adjoining areas, Bundelkhand Craton, Central India. Jour. Geol. Soc. Sri Lanka, v.18 (2), pp.53–61.
Bhatt S.C., Rubal Singh, Ansari M.A., Bhatt, S. (2020) Quantitative Morphometric and Morphometric Analysis of Pahuj Catchment Basin, Central India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.96, pp.513–520 (2020). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1590-1
Bhatt, S.C., Singh, V.K. (2021) Tectonic Evolution of Babina-Prithvipur Crustal Shear Zones, Bundelkhand Craton, India: Implications of Shear Indicators. In: Shandilya, A.K., Singh, V.K., Bhatt, S.C., Dubey, C.S. (Eds.), Geological and Geo-Environmental Processes on Earth. Springer Natural Hazards. Springer, Singapore. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4122-0_11
Bhatt, S.C., Mishra, S., Singh, R., Bhatt, S. (2021) Morphometric Analysis of Rohni Watershed, Upper Betwa Basin, Bundelkhand Region, Central India. In: Shandilya, A.K., Singh, V.K., Bhatt, S.C., Dubey, C.S. (Eds.), Geological and Geo-Environmental Processes on Earth. Springer Natural Hazards. Springer, Singapore. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4122-0_18
Bhatt, S.C., Singh, R., Singh, R., Saif, M., Singh, M.M. (2021) A GIS-based Approach for Morphometric Analysis of Jamini Basin and Its Subwatersheds: Implication for Conservation of Soil and Water Resources. In: Shandilya, A.K., Singh, V.K., Bhatt, S.C., Dubey, C.S. (Eds.), Geological and Geo-Environmental Processes on Earth. Springer Natural Hazards. Springer, Singapore. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4122-0_16
Bhatt, S.C., Singh, R., Singh, R., Singh, V.K., Patel, A. (2021) Morphometric and Morphotectonic Studies of Sindh Basin, Central India, Using Advance Techniques of Remote Sensing and GIS. In: Shandilya, A.K., Singh, V.K., Bhatt, S.C., Dubey, C.S. (eds) Geological and Geo-Environmental Processes on Earth. Springer Natural Hazards. Springer, Singapore. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4122-0_17
Bhatt, S. C., Singh, R., Taiyab, M., Bhatt, S. (2021) Quantitative Morphometric Analysis of Watershed of Upper Pahuj Basin, Bundelkhand Region, Central India. In: Geological and Geo-Environmental Processes on Earth (pp. 293–304). Springer, Singapore doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4122-0_19
Bhowmik, M., Das (Pan), N. (2014) Qualitative Assessment of Bank Erosion Hazard in a Part of the Haora River, West Tripura District. In: Singh, M., Singh, R., Hassan, M. (Eds.), Landscape Ecology and Water Management. Advances in Geographical and Environmental Sciences. Springer, Tokyo. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-54871-3_14
Chakraborty, S., Mukhopadhyay, S. (2015) An assessment on the nature of channel migration of River Diana of the sub-Himalayan West Bengal using field and GIS techniques. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.8, pp.5649–5661. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1594-5
Das, N., Bhowmik, M. (2013) Qualitative assessment of river bank erosion risk in Jirania rural development block, Tripura. Indian Jour. Appl. Res., v.3(6), pp.274–276. doi: https://doi.org/10.15373/2249555X/JUNE2013/91
Debnath, J., Pan, N. D., Ahmed, I., Bhowmik, M. (2017) Channel migration and its impact on land use/land cover using RS and GIS: A study on Khowai River of Tripura, North-East India. The Egyptian Jour. Rem. Sens. Space Sci., v.20(2), pp.197–210. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2017.01.009
Desai, A.J., Naik, S.D., Shah, R.D. (2012) Study on the channel migration pattern of Jia-Bhareli, Puthimari and Pagladiya tributaries of the Brahmaputra River using Remote Sensing Technology. http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/XXXVI/part4/ Pages from RS-GEO-14.pdf District Gazetteers, Bahraich, 1988.
Gaurav Singh, V., Singh, S.K. (2022) Analysis of geo-morphometric and topo-hydrological indices using COP-DEM: a case study of Betwa River Basin, Central India. Geology, Ecology, and Landscapes, pp.1–28. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2022.2097376
Gogoi, C., Goswami, D.C. (2013) A study on bank erosion and bank line migration pattern of the Subansiri River in Assam using remote sensing and GIS technology. Internat. Jour. Engg. Sci., v.2(9), pp.1–6.
Goswami, D. C. (2002) Channel pattern, Sediment transport and Bed regime of the Brahmaputra River, Assam. In: S.K. Tandon and B. Thakur (Eds.), Recent Advances in Geomorphology, Quaternary Geology and Environmental Geosciences: Indian Case Studies. Manisha Publications, New Delhi, pp.143–156.
Islam, Z., Singh, S. K. (2021) Geospatial Analysis of the Impact of Flood and Drought Hazards on Crop Land and its Relationship with Human Migration at the District Level in Uttar Pradesh, India. Geomatics Environ. Eng., v.15(4), pp.117–127. doi:https://doi.org/10.7494/geom.2021.15.4.117
Kotoky, P., Bezbaruah, D., Baruah, J., Sarma, J.N. (2005) Nature of bank erosion along the Brahmaputra River channel, Assam, India. Curr. Sci., v.88(4), pp.634–640. https://www.jstor.org/stable/24110266
Kumar Pradhan, R., Srivastava, P.K., Maurya, S., Kumar Singh, S., Patel, D.P. (2020) Integrated framework for soil and water conservation in Kosi River Basin. Geocarto Internat., v.35(4), pp.391–410. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1520921
Kumar, N., Singh, S.K. (2021) Soil erosion assessment using earth observation data in a trans-boundary river basin. Natural Hazards, v.107(1), pp.1–34. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04571-6
Kummu, M., Lub, X.X., Rasphonec, A., Sarkkulad, J., Koponen, J. (2008) River bank Changes along the Mekong River: Remote Sensing Detection in the Vientiane-Nong Khai Area. Quaternary Internat., v.186 (1), pp.100–112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2007.10.015
Lane, E.W. (1957) A study of the shape of channels formed by natural streams flowing in erodible material: U. S. Army Corps of Engineers (Omaha), Missouri River Div. Sediment Series No.9, 106p.
Leopold, L.B., Wolman, M.G. (1957) River channel patterns: braided, meandering, and straight. USGS. Prof. Paper 282-B.
Leopold, L.B., Wolman, M.G., Miller, J.P. (1964) Fluvial processes in geomorphology. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco, 52p.
Limaye, A.B., Lazarus, E. D., Li, Y., Schwenk, J. (2021) River sinuosity describes a continuum between randomness and ordered growth. Geology, v.49(12), pp.1506–1510. doi:https://doi.org/10.1130/G49153.1
Majumdar, S., Das (Pan), N. (2014) Spatio-temporal shift of right bank of the Gumti River, Amarpur Town, Tripura and its impact. In: Singh, M. et al. (Eds.), Landscape Ecology and Water Management: Proceedings of IGU Rohtak Conference, 2. Advances in Geographical and Environmental Sciences.
Nagarajan, R., Marathe, G. T., Collins, W. G. (1993) Technical note Identification of flood prone regions of Rapti river using temporal remotely-sensed data, Internat. Jour. Rem. Sens., v.14:7, pp.1297–1303. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169308953957
Pareta, K., Pareta, U. (2019) Hydro-geomorphological mapping of Rapti River basin (India) using ALOS PALSAR (DEM), GRACE/GLDAS & Landsat-8 remote sensing data. Amer. Jour. Geophys., Geochem. Geosyst., v.5(3), pp.104–118.
Patel, A., Singh, M.M., Singh, S.K., Kushwaha, K., Singh, R. (2022) AHP and TOPSIS based sub-watershed prioritization and tectonic analysis of Ami River Basin, Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.98(3), pp.423–430. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-1995-0
Rahman, M.R. (2010) Impact of river bank erosion hazard in the Jamuna floodplain areas in Bangladesh. Jour. Sci. Found., v.8(1&2), pp.55–65. doi:https://doi.org/10.3329/jsf.v8i1-2.14627
Rana, N.K., Kumar, R., Kumar, D. (2009) Nature of Channel Shifting of a Foothills-Fed River in The Alluvial Setting: A case Study of River Rapti Basin. Indian Jour. Geomorph., v.13 & 14, pp.83–98.
Rana, N.K. (2015) Delimitation of Channel Migration Zones in the Rapti River Basin, Middle Ganga Plains. National Geographical Jour. India, v.61(1), pp.99–112.
RSAC, UP, Lucknow, Flood Reports. https://rsac.up.gov.in/
Schumm, S.A. (1969) River metamorphosis. Jour. Hydraulics Div., v.95(1), pp.255–274.
Schümm, S.A., Lichty, R.W. (1963) Channel widening and flood plain construction along Cimarron River in southwestern Kansas. USGS Prof. Pap., 352-D, pp.71–88.
Schumm, S.A. (1963) Sinuosity of Alluvial Rivers on the Great Plains. Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer., v.74(9), pp.1089–1100. doi:https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1963)74[1089:SOAROT]2.0.CO;2
Singh, D.S. (2009) Rivers of Ganga Plain: Boon/Bane Rivers of Ganga Plain. Earth Sci India. https://www.earthscienceindia.info.
Singh, D.S., Awasthi, A. (2011) Natural hazards in the Ghaghara River area, Ganga Plain, India. Natural Hazards, v.57(2), pp.213–225. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9605-7
Singh, D.S., Prajapati, S.K., Singh, P., Singh, K., Kumar, D. (2015) Climatically induced levee break and flood risk management of the Gorakhpur region, Rapti River Basin, Ganga Plain, Indian. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.85(1), pp.79–86.
Singh, I.B. (1996) Geological evolution of Ganga Plain-an overview. Jour. Palaeontol. Soc. India, v.41, pp.825–252.
Sinha, R., Tandon, S.K., Gibling, M.R., Bhattacharjee, P.S., Dasgupta, A.S. (2005) Late Quaternary geology and alluvial stratigraphy of the Ganga basin. Himalayan Geol., v.26(1), pp.223–240.
Sinha, R., Friend, P.F. (1994) River systems and their sediment flux, Indo-Gangetic Plains, northern Bihar, India. Sediment, v.41, pp.27–52.
Thakur, P.K., Laha, C., Aggarwal, S.P. (2012) River bank erosion hazard study of river Ganga, upstream of Farakka barrage using remote sensing and GIS. Natural Hazards, v.61, pp.967–987. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-9944-z
Winterbottom, S.J. (2000) Medium and short-term channel planform changes on the rivers Tay and Tummel, Scotland. Geomorphology, v.34, pp.195–208.
Yadav, S.K., Singh, S.K. (2021) Morpho-tectonic assessment of Central Northern escarpment of Peninsular India, based on tectonically sensitive geomorphic indices. Physical Geography, pp.1–31. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/02723646.2021.1899478
Youdeowei, P.O. (1997) Bank collapse and erosion at the upper reaches of the Ekole creek in the Niger delta area of Nigeria. Bull. Internat. Assoc. Eng. Geol., v.55(1), pp.167–172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rathore, V.K.S., Verma, P.K., Singh, A.K. et al. Channel Dynamics of a Middle Reach of Rapti River, Eastern Indo-Gangetic Plain, India. J Geol Soc India 99, 995–1005 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2420-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2420-z