Abstract
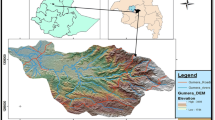
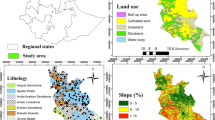
Soil properties are an outcome of the interplay between different soil forming factors and processes of which topography or altitude plays an important role. A study was conducted in the mid-Himalayan region to verify the impact of altitude on different soil properties. Geo-referenced soil samples were collected from 0–20 cm depth from the agricultural fields with an altitudinal variation of 760 m to 1170 m above mean sea level (amsl). Soils of the area were dominantly gravely sandy loam texture; moderately to highly acidic in reaction with low soluble salts and very high soil organic carbon (SOC) content. Soil fertility of the region was high in available phosphorous (P), relatively medium to high in available nitrogen (N), whereas, potassium (K) content was in medium range. Among the micronutrients, deficiencies were recorded for boron (B) and manganese (Mn), whereas, zinc (Zn), iron (Fe) and copper (Cu) content were high. It was observed that altitude had little/variable control over pH, EC, P, Cu, Mn, S and Fe distribution, whereas increasing trend of SOC, Zn, B, K and N content with altitude could be attributed to management practices and the effect of soil erosion and deposition at different altitude. The study indicated that the chemical and physical properties of soils were selectively affected by the altitudinal variations and are an important base for initiating scientific management of soil resources in the area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolghasem, A., Reyhane, A., Noram, I. and Bin, R. (2014) Influence of slope aspects and depth on soil properties in a cultivated ecosystem. Faculty of Range Land and Watershed Management Gorgan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Gorgan, Iran.
Babalola, O., Babaji, G.A. & Mustapha, S. (1998) Soil management for sustainable agriculture and environmental harmony. Pro. (24) Annual Conference of the Soil Sci. Soci. of Nigeria Held at the Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University, Bauchi.
Baetens, J.M., Verbist, K., Cornelis, W. M., Gabriels, D. and Soto, G. (2009) On the influence of coarse fragments on soil water retention. Water Resour. Res., v.45(7).
Bhattacharyya, T., Pal, D. K., Mandal, C. and Velayutham, M. (2000) Organic carbon stock in Indian soils and their geographical distribution. Curr. Sci., v.79, pp.655–660.
Brady, N.C. and Weil, R.R. (2007) Nature and properties of soil. Pearson Education, Inc. and Dorling Kindersley Publishing; v.56, 857p.
Burt, R. (2014) Soil Survey Staff. Soil Survey Field and Laboratory Methods Manual.Soil Survey Investigations Report 51(2.0) Soil Survey Staff (Ed.). U.S. Department of Agri. Natural Resources Conservation Service.
Catt, J.A. (1991). HD Foth, Fundamentals of Soil Science, John Wiley & Sons, New York, Chichester, etc., 360p.
Das, A., Krishnaswami, S., Sarin, M.M. and Pande, K. (2005) Chemical weathering in the Krisna Basin and Western Ghats of the Deccan Traps, India: rates of basalt weathering and their controls. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.69(8), pp.2067–2084.
Dimri, B.M., Jha, M.N. and Gupta, M.K. (2006) Soil potassium changes at different altitudes and seasons in upper Yamuna Forests of Garhwal Himalayas. Indian Forester, v.132(5), pp.609–614.
Fernández-Romero, M. L., Lozano-García, B., & Parras-Alcántara, L. (2014). Topography and land use change effects on the soil organic carbon stock of forest soils in Mediterranean natural areas. Agricult., Ecosyst. Environ., v.195, pp.1–9.
Gairola, S., Sharma, C. M., Ghildiyal, S. K. and Suyal, S. (2012) Chemical properties of soils in relation to forest composition in moist temperate valley slopes of Garhwal Himalaya, India. Environmentalist, v.32(4), pp.512–523.
Gisilanbe, S.A., Philip, H.J., Solomon, R.I. and Okorie, E.E. (2017) Variation in soil physical and chemical properties as affected by three slope positions and their management implications in Ganye, North-Eastern Nigeria. Asian Jour. Soil Sci. Plant Nutri., v.2(3), pp.1–13.
Gregorich, E.G., Greer, K.J., Anderson, D.W. and Liang, B.C. (1998) Carbon distribution and losses: Erosion and deposition effects. Soil Tillage Res., v.47, pp.291–302.
Grobler, L., Bloem, A. A. and Claassens, A. S. (1999) A critical soil sulphur level for maize (Zea mays L.) grown in a glasshouse. South African Jour. Plant and Soil, v.16(4), pp.204–206.
Hendershot, W.H., Courchesne, F. and Schemenauer, R.S. (1992) Soil acidification along a topographic gradient on round top Mountain, Quebec, Canada. Water, Air, and Soil Poll., v.61(3–4), pp.235–242. http://agropedia.iitk.ac.in/content/present-scenario-agriculture-uttarakhandhttp://sap.ipni.net/article/uttarakhand
Huang, Y.L., Yang, S., Long, G.X., Zhao, Z.K., Li, X.F. and Gu, M.H. (2016). Manganese toxicity in sugarcane plantlets grown on acidic soils of southern China. PloS One, v.11(3): e0148956.
Jackson, M.L. (1973) Soil Chemical Analysis, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, p.498.
Khan, F., Ahmad, W., Bhatti, A.U., Khattak, R.A. and Shafiq, M. (2004) Effect of soil erosion on chemical properties of some soil series in NWFP. Sci, Tech, Develop., v.23(4), pp.31–35.
Kitundu, K.M.B. and Mrema, J.P. (2006) The Status of Zn, Cu, Mil, and Fe in the Soils and Tea Leaves of Kibena Tea Estates, Njombe, Tanzania. Tanzania Jour. Agricult. Sci., v.7(1), pp.34–41.
Kjeldahl, J. (1883) New Method for the Determination of Nitrogen. Chemical News, v.48(1240), pp.101–102.
Majji, A. K., Reddy, G. O. and Sarkar, D. (2012) Acid Soils of India: Their Extent and Spatial Variability (No. 145). National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning (NBSS & LUP).
Mandal, D., Singh, R., Dhyani, S.K. and Dhyani, B.L. (2010) Landscape and land use effects on soil resources in a Himalayan watershed. Catena, v.81, pp.203–208.
Marschner, H. (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. 2nd. Edn. Academic Press.
Mathew, M. M., Majule, A. E., Marchant, R. and Sinclair, F. (2016) Variability of soil micronutrients concentration along the slopes of Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci., pp.1–7.
Nuga, B.O., Eluwa, N.C., Akinbola, G.E. and Wokocha, C.C. (2006). Characterization and classification of soils along a toposequence in Ikwuano Local Government area of Abia State. Agricult. Jour., v.1(4), pp.192–197.
Ollinger, S., Smith, M., Martin, M., Hallett, R., Goodale, C. and Aber, J. (2002). Regional variation in foliar chemistry and N cycling among forests of diverse history and composition. Ecology, v.83, pp.339–355.
Partap, T. (2011) Hill agriculture: challenges and opportunities. Indian Jour. Agricult. Econ., v.66, pp.1–20.
Ritchie, J.C., McCarty, G.W., Venteris, E.R. and Kaspar, T.C. (2007) Soil and soil organic carbon redistribution on the landscape. Geomorphology, v.89, pp.163–171.
Roy, T., Kumar, S., Lekh, C., Kadam, D. M., Bihari, B., Shrimali, S. S., Bishnoi, R., Maurya, U. K., Singh, M., Muruganandam, M., Singh, L., Sharma, S. K., Kumar R. and Mallik, A. (2019) Impact of Pusa hydrogel application on yield and productivity of rainfed wheat in North West Himalayan region. Curr. Sci., v.116(7), pp.1246–1251.
Sarkar, A.N. and Wynjones, R.G. (1982) Effect of rhizosphere pH on the availability and uptake of Fe, Mn and Zn. Plant and Soil, v.66(3), pp.361–372.
Schwanghart, W. and Jarmer, T. (2011) Linking spatial patterns of soil organic carbon to topography—a case study from south-eastern Spain. Geomorphology, v.126, pp.252–263.
Seibert, J., Stendahl, J. and Sørensen, R. (2007) Topographical influences on soil properties in boreal forests. Geoderma, v.141, pp.139–148.
Seybold, C.A., Herrick, J.E. and Brejda, J.J. (1999) Soil resilience, a fundamental component of soil quality. Soil Science, v.164, pp.224–234.
Sierra, J., Noël, C., Dufour, L., Ozier-Lafontaine, H., Welcker, C. and Desfontaines, L. (2003) Mineral nutrition and growth of tropical maize as affected by soil acidity. Plant and Soil, v.252(2), pp.215–226.
Singh, D., Chhonkar, P.K. & Dwivedi, B.S. (2015). Manual on Soil, Plant and Water Analysis. Westville Publishing House, New Delhi. 210p.
Soil Survey Staff (1998) Keys to Soil Taxonomy, Eighth edition. US Department of Agriculture Natural Resource Conservation Service, Washington DC. 326p.
Sojka, R.E. and Upchurch, D.R. (1999) Reservations regarding the soil quality concept. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Jour., v.63, pp.1039–1054.
Sun, W., Zhu, H. and Guo, S. (2015) Soil organic carbon as a function of land use and topography on the Loess Plateau of China. Ecological Engg., v.83, pp.249–257.
Sun, W.Y., Shao, Q.Q., Liu, J.Y. and Zhai, J. (2014). Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena, v.121, pp.151–163.
Vladychenskiy, A.S. (2005) Genesis of soils and factors of the soil formation. Environment structure and function: Earth system. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Department of Soil Science, Moscow, Russia; http://www.eolss.net/EolsssampleAllChapter.aspx
Walkley, A. and Black, I.A. (1934) An examination of the Degtareff method for determining soil organic matter and proposal modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, v.37, pp.29–38.
Waqar, A, Munir, H. Z., Sukhdev, S. M., Abid, N. and Saifullah, N. (2012). Boron deficiency in soils and crops: A Review. In: Crop Plant. InTech.
Webb, A.A. and Dowling, A.J. (1990) Characterization of basaltic clay soils (Vertisols) from the Oxford Land System in Central Queensland. Australian Jour. Soil Res., v.28(6), pp.841–856.
Yimer, F., Ledin, S. and Abdelkadir, A. (2006) Soil property variations in relation to topographic aspect and vegetation community in the southeastern highlands of Ethiopia. Forest Ecology & Management, v.232, pp.90–99.
Acknowledgements
The senior author and the entire team is thankful to Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, for providing funding through Farmer’s FIRST Program and to the Director, ICAR-Indian Institute of Soil & Water Conservation, Dehradun for providing infrastructural facilities for carrying out the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurya, U.K., Roy, T., Bihari, B. et al. Impact of Altitude on Soil Physico-chemical Properties in a Topo-Sequence in Mid Himalayan Watershed: A Case Study from Dehradun District, Uttarakhand. J Geol Soc India 99, 421–429 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2326-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2326-9