Abstract
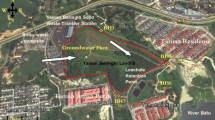
Non-engineered landfill sites pose substantial environmental threats, especially on air, biodiversity, soil fertility, human health. In addition, they have significant threats to groundwater resources. As a result, areas lying close to these landfills have a higher chance of groundwater contamination because of the leachate originating from these sites. Therefore, physico-chemical, heavy metal and organic pollutants were examined to study the effects of leachate seepage on groundwater quality collected in and around the Bandhwari sanitary landfill site. The study results revealed that parameters such as TDS, total hardness, COD, cations, anions, and heavy metals (Cd and Pb) exceeded the BIS limits and WHO limits. It depicts that contaminant from the landfill site have made their way into the groundwater, adversely affecting the quality of groundwater of the vicinal area, despite the existing quartzite geological setup and deep aquifers. The concentration of COD in groundwater samples around landfill ranged between 08–152 mg/L, and COD in leachate samples ranged between 14000–14800 mg/L. The concentration of BOD in groundwater samples ranged between 1.0–30 mg/L, and BOD for leachate samples ranged between 6771–7617 mg/L. The samples analysed for organochlorine, carbanates and organo-phosphorus pesticides shows that pesticides concentration is within the acceptable limit of 0.001 µg/L.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agamuthu, P (2013) Landfilling in developing countries. Waste Management & Research 31:1–2. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0734242X12469169.
APHA, A.W.A. (2012). Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. In: E.W. Rice, R.B. Baird, A.D. Eaton and L.S. Clesceri(Eds.), Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association
BIS. I.S. (2012) Indian Standard Drinking Water Specification. IS 10500:2012, New Delhi. Bureau of Indian Standards.
CGWB (2005). Ground water management studies of Gurgon and parts of Faridabad districts of Haryana state.
CGWB (2019). Aquifer mapping and management plan for sustainability of ground water resources in Haryana state.
Gosain, R, Srivastava, S.K., Singh, C.K. (2018). Conference on Water — Technological Innovation and Solution, INC-IAH & CAWTM MRIIRS Faridabad.
Guerrero, L.A., Maas, G., Hogland, W. (2013) Solid waste management challenges for cities in developing countries. Waste Management, v.33, pp.220–232.
Iqbal, N. (2016) At half the height of Qutub Minar, meet Delhi’s garbage high-rises. The Indian Express. 30 May.
Joshi, R., Ahmed, S. (2016) Status and challenges of municipal solid waste management in India: A review. Cogent Environmental Science, Volume 2.
Kumar, A. (2013) Existing situation of Municipal solid waste management in NCT of Delhi, India. Internat. Jour. Social Sci., v.1, pp.6–17.
Maheshwari, R., Gupta, S., Das, K. (2015) Impact of Landfill Waste on Health: An overview. IOSR Jour. Environ. Sci., Toxicol. Food Tech., v.1, pp.17–23.
Mohiddin, S.K. (2018) Groundwater Contamination at Solid Waste landfills of Delhi, Swastik Publications, New Delhi
Nagarajan, R, Thirumalaisamy, S, Elango, L (2012) Impact of leachate on groundwater pollution due to non-engineered municipal solid waste landfill sites of erode city, Tamil Nadu, India. Iranian Jour. Environ. Health Sci. Engg., v.9, pp.1–12.
NCR Planning Board (2002) Draft report of Master Plan of NCR, 2021
Srivastava, S.K. (2021) Hydro Chemical Behaviour of Contaminants. Internat. Jour. Scienti. Res. Develop., v.8, pp.123–128.
Vrijheid, M. (2000). Health effects of residence near hazardous waste landfill sites: a review of epidemiologic literature. Environ. Health Perspect., v.108(suppl 1), pp.101–112.
WHO (1996). Guidelines for drinking water quality: Health criteria and other supporting information, Geneva: World Health organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, S.K., Mohiddin, S.K., Prakash, D. et al. Impact of Leachate Percolation on Groundwater Quality near the Bandhwari Landfill Site Gurugram, India. J Geol Soc India 99, 120–128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2274-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2274-4