Abstract
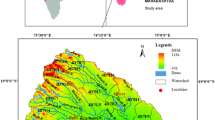
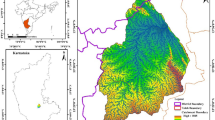
In order to address current global water shortages, geovisualization tools such as remote sensing and geographic information systems aid planners and decision makers in generating more effective and correct judgments for the execution of water harvesting activities for the maximum utilization of rainwater. Keeping in view, a weighted sum approach technique was used to infer hydrological behavior and priorities at watershed level in the Harohar sub-basin of middle Gangetic plains. It was observed that monsoon rainfall (1.7 mm year−1) and post-monsoon rainfall (0.6 mm year−1) has been declined whereas pre-monsoon rainfall (1.5 mm year−1) has significantly increased over the period 1985–2019. Furthermore, morphometric, slope, hydrological, geomorphological, and lithological variations results revealed that 56.30% of areas are prioritized as very high, followed by high (30.5%), and only 2–7% of areas fall under very low to low priority for construction of rain water harvesting structures. Water harvesting facilities such as farm ponds, check dams, tanks, aharpynes, and conservation ditches might be offered in prioritized locations for optimum utilization of surface runoff and ground water recharge. Based on the above scientific findings, this study may be helpful in water resource planning at the basin/watershed level across the globe
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aher, P.D., Adinarayana, J. and Gorantiwar, S.D. (2014) Quantification of morphometric characterization and prioritization for management planning in semi-arid tropics of India: a remote sensing and GIS approach. Jour. Hydrol, v.511, pp.850–860. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.02.028
Akram, J., Khanday, M.Y. and Rais, S. (2011) Watershed prioritization using morphometric and landuse/landcover parameters: a remote sensing and GIS approach. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.78, pp.63–75.
Adham, A., Riksen, M., Ouessar, M. and Ritsema, C.J. (2016) A Methodology to Assess and Evaluate Rainwater Harvesting Techniques in (Semi-) Arid regions. Water, v.8, pp.198.
Aayog NITI (2018) Composite Water Management Index: a tool for water management, http://www.niti.gov.in/writereaddata/files/document_publication/2018-05-18-Water-Index-Report_vS8-compressed.pdf
Biswas, S., Sudhakar, S. and Desai, V.R. (1999) Prioritization of sub-watershed based on morphometric analysis of drainage basin: a remote sensing and GIS approach. Jour. Indian Soc. Rem. Sens., v.27(3), pp. 155–166.
Gajbhiye, S., Mishra, S.K. and Pandey, A. (2014) Prioritizing erosion-prone area through morphometric analysis: an RS and GIS perspective. Appl. Water Sci., v.4(1), pp.51–61.
Hajam, R.A., Hamid, A. and Bhat, S. (2013) Application of morphometric analysis for geo-hydrological studies using geo-spatial technology–a case study of Vishav Drainage Basin. Hydrol. Curr. Res, v.4(157), pp.2. doi:https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7587.1000157
Horton, R.E. (1932) Drainage basin characteristics. Trans. Amer. Geophys Union, v.13, pp.350–361.
Horton, R.E. (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.56(3), pp.275–370.
Hamed, K.H. and Rao, A.R. (1998) A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. Jour. Hydrol, v.204(1–4), pp.182–196.
Javed, A., Khanday, M.Y. and Rais, S. (2011) Watershed prioritization using morphometric and land use/land cover parameters: A remote sensing and GIS based approach. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.78(1), pp.63–75. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-011-0068-6.
Jothimani, M., Abebe, A. and Dawit, Z.(2020) Mapping of soil erosion-prone sub-watersheds through drainage morphometric analysis and weighted sum approach: a case study of the Kulfo River basin, Rift valley, Arba Minch, Southern Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ, v.6, pp.2377–2389. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00820-y
Jeet, P., Singh, D.K, Sarangi, A., Mali, S.S. and Singh, A.K. (2021) Delineation of potential water harvesting site for agriculture water planning in Betwa basin of India using geospatial and Analytical Hierarchical Process technique. Geocarto Internat., pp.1–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.2000647.
Kandpal, H., Kumar, A., Reddy, C.P. and Malik, A. (2017) Watershed prioritization based on morphometric parameters using remote sensing and geographical information system. Indian Jour. Ecol, v.44, pp.433–437.
Kumar, A., Darmora, A. and Sharma, S. (2012) Comparative assessment of hydrologic behaviour of two mountainous watersheds using morphometric analysis. Jour. Hydrol, v.35(3&4), pp.76–87. doi:https://doi.org/10.5958/j.0975-6914.35.3X.008
Kumar, D., Singh, D. S., Prajapati, S. K., Khan, I., Gautam, P. K. and Vishawakarma, B. (2018) Morphometric Parameters and Neotectonics of Kalyani River Basin, Ganga Plain: A Remote Sensing and GIS Approach. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.91, pp.679–686. doihttps://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0923-9
Kushwaha, N.L., Elbeltagi, A., Mehan, S., Malik, A. and Yousuf, A. (2022) Comparative study on morphometric analysis and RUSLE-based approaches for micro-watershed prioritization using remote sensing and GIS. Arab. Jour. Geosci., v.15(7), pp.18. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09837-2
Malik, A., Kumar, A., Kushwaha, D.P., Kisi, O., InanSalih, Q.S., Al-Ansari, N. and Yaseen, Z.M. (2019a) The implementation of a hybrid model for hilly sub-watershed prioritization using morphometric variables: case study in India. Water, v.11(6), pp.1138. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061138
Malik, A., Kumar A. and Kandpal, H. (2019b) Morphometric analysis and prioritization of sub-watersheds in a hilly watershed using weighted sum approach. Arab. Jour. Geosci., v.12(118), pp.1–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4310-7
Malik, A., Kumar, A. and Kandpal, H. (2019) Morphometric analysis and prioritization of sub-watersheds in a hilly watershed using weighted sum approach. Arab. Jour. Geosci, v.12(4), pp.118.
Mallick, J., Singh, C.K., Al-Wadi, H., Ahmed, M., Rahman, A., Shashtri, S. and Mukherjee, S. (2015) Geospatial and geostatistical approach for groundwater potential zone delineation. Hydrol. Proces., v.29(3), pp.395–418. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10153
Meshram, S.G. and Sharma, S.K. (2018) Hydrologic modeling. In: V.P. Singhet al. (Eds.), Hydrologic modeling, water science and technology library 81, Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd, doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5801-131
Miller, V.C. (1953) A quantitative geomorphic study of drainage basin characteristics in the Clinch Mountain area, Virginia and Tennessee.
Project NR 389042, Tech. Rept. 3. Columbia University, Department of Geology, ONR, Geography Branch, New York.
Ozdemir, H. and Bird, D. (2009) Evaluation of morphometric parameters of drainage networks derived from topographic maps and DEM in point of floods. Environ. Geol., v.56, pp.1405–1415.
Patel, D.P., Dholakia, M.B., Naresh, N. and Srivastava, P.K. (2012) Water harvesting structure positioning by using geo-visualization concept and prioritization of mini-watersheds through morphometric analysis in the lower tapi basin. Jour. Indian Soc. Rem. Sens, v.40, pp.299–312.
Rai, P.K., Mohan, K., Mishra, S., Ahmad, A. and Mishra, V.N. (2017) A GIS based approach in drainage morphometric analysis of Kanhar River Basin, India. Appl. Water Sci., v.7(1), pp.217–232
Rashid, M., Lone, M.A. and Romshoo, S.A. (2011) Geospatial tools for assessing land degradation in Budgam district, Kashmir Himalaya, India. Jour. Earth Syst. Sci., v.120(3), pp.423–433.
Ratnam, K.N., Srivastava, Y., Rao, V. V., Amminedu, E., and Murthy, K. (2005) Check dam positioning by prioritization of micro-watersheds using SYI model and morphometric analysis–remote sensing and GIS perspective. Jour. Indian Soc. Rem. Sens., v.33, pp.25–38.
Schumm, S.A. (1956) Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.67, pp.597–646.
Sharma, S.K., Rajput, G.S., Tignath, S. and Pandey, R.P. (2010) Morphometric analysis of and prioritization of watershed using GIS. Jour. Indian Water Res. Soc., v.30(2), pp.33–39.
Strahler, A.N. (1964) Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basin and channel networks. In: Chow, V.T. (Ed.), Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw Hill Book Company, New York, pp.4–39.
Sen, P.K. (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. JASA, v.63(324), pp.1379–1389.
Singh, P., Gupta, A. and Singh, M. (2014) Hydrological inferences from watershed analysis for water resource management using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Egypt. Jour. Rem. Sens. Space Sci., v.17, pp.111–121.
Singh, A.P, Arya, A.K. and Singh, D.S. (2020) Morphometric Analysis of Ghaghara River Basin, India, Using SRTM Data and GIS. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.95, pp.169–178. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1406-3
Srinivasa Vittala, S., Govindaiah, S. and Honne Gowda, H. (2004) Morphometric analysis of sub-watersheds in the pavagada area of Tumkur district, South India using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Jour. Indian Soc. Rem. Sens., v.32, pp.351. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030860
Theil, H. (1950) A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis. Indagationesmathematicae, v.12(85), pp.173.
Thomas, J., Joseph, S., Thrivikramji, K.P. and Abe, G. (2011) Morphometric analysis of the drainage system and its hydrological implications in the rain shadow regions, Kerala, India. Jour. Geographical Sci., v.21(6), pp.1077.
Vieceli, N., Bortolin, T.A., Mendes, L.A., Bacarim, G., Cemin, G. and Schneider, V.E. (2015) Morphometric evaluation of watersheds in Caxias do Sul City, Brazil, using SRTM (DEM) data and GIS. Environ. Earth Sci., v.73(9), pp.5677–5685.
Water, U. N. (2018). 2018 UN World Water Development Report, Nature-based Solutions for Water.http://repo.floodalliance.net/jspui/bitstream/44111/2726/1/Screen%20Shot%202018-03-23%20at%2009.52.12.png
Yadav, S.K., Singh, S.K., Gupta, M. and Srivastava, P.K. (2014) Morphometric analysis of upper tons basin from northern foreland of peninsular India using CARTOSAT satellite and GIS. Geocarto Internat., v.1, pp.20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, A., Upadhyaya, A., Jeet, P. et al. Morphometric Analysis and Prioritization of Watershed for Water Management using Weighted Sum Approach and Geospatial Tools: A Case Study of Harohar Sub-basin, India. J Geol Soc India 99, 859–867 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2393-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2393-y