Abstract
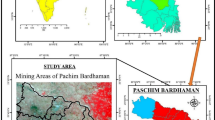
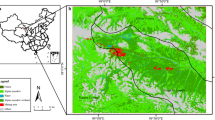
Surface mining is the dominant driver of land use land cover (LULC) change in the Raniganj coalfield region in West Bengal, India. Owing to its multifaceted consequences on soil, water, and landholders, assessment of spatio-temporal changes in mining areas has become important. The oldest coal mine of India, Raniganj coalfield has been producing superior quality non-coking coal for the last 246 years. To reduce the cost per unit production of coal, the mining authority prefers the opencast method over underground mining. The mushrooming growth of opencast mines in this coalfield causing huge waste dumps, depletion of vegetated surface, changing slope and drainage pattern, soil erosion, and degradation of environmental quality. With this background, the present study examines the spatio-temporal changes and evolution of opencast mines using multi-temporal Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) and Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) datasets of 1991, 2001 and 2014. Further, the study assessed the dynamics of mining patches and their characteristics through spatial metrics analysis. The LULC maps reveal good agreement with in-situ observation as verified by overall accuracy (≥ 85%) and Kappa (≥ 0.75) statistics. The study showed that mining areas have increased rapidly during the period and the growth has occurred by depleting the forest, sparse vegetation, and agricultural land. It is also noteworthy that the rate of growth in mining areas was comparatively higher during 2001–2014 than in 1991–2001. The change of dynamics of LULC revealed that more than 70% of the active mines was excavated after 2001. It is also observed that patch parameters, i.e. area, perimeter, shape, and density of the mining patches have changed with time that certainly establishes the dynamic nature of mining patches. The unprecedented growth of mining areas during the last decade has been a serious matter of concern from the ecological perspective of the area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari, K., Sadhu, K., Chakroborty, B., Gangopadhyay, A. (2013) Effect of mining on geochemistry of groundwater in Permo-carboniferous Gondwana coalfields: Raniganj Basin, India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.82, pp.392–402.
Agarwal. (1991) Global warming in an unequal World. International Sustainable Development, v.1, pp.98–104.
Bhattacharya, A., Bhattacharya, D. N. and Mallick, D. K. (1997) Land subsidence hazards in Raniganj coalfield — A case study. Geol. Surv. India Spec. Publ., v.48(2), Kolkata, pp.55–67.
Buczyñska A (2020) Remote sensing and GIS technologies in land reclamation and landscape planning processes on post-mining areas in the Polish and world literature. AIP Conference Proceedings 2209, 040002. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0000009
Charou, E., Stefouli, M., Dimitrakopoulos, D., Vasiliou, E., Mavrantza, O. D. (2010) Using remote sensing to assess impact of mining activities on land and water resources. Mine Water Environ., v.29, pp.45–52.
Chatterjee, R. S., Bannerjee, D., Roy, J., Bhattacharya, A. K. (1994) Landsat TM data processing techniques for identifying and delineating environmental impacts of coal mining. ITC Jour., v.2, pp.155–162.
Community Issues in Coal Belts, Environics Trust (2016) Raniganj-Jharia, pp.1–18
Crist, E. P., Cicone, R. C. (1984) Application of the tasselled cap concept to simulated Thematic Mapper data. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, v.50, pp.343–352.
Dasgupta, S., Dutta, S. (2005) Study on stabilization of inaccessible waterlogged void beneath a run talkies, Raniganj. Mine Tech., v.26, pp.42–48.
Dhar, B. B. (1996) Keynote address on status of mine fires — trends and challenges. In Seminar on Prevention and Control of Mine and Industrial Fires — Trends and Challenges, Kolkata, 21–22 December, pp. 1–8.
Gangopadhyay, P.K., Lahiri-Dutt, K., Saha, K., (2006) Application of remote sensing to identify coalfires in the Raniganj coal belt, India. Internat. Jour Applied Earth Observ. Geoinfo, v.8, pp.188–195.
Goswami, S. (2015) Impact of coal mining on environment: A study of Raniganj and Jharia coal field in India. IAFOR Jour. Arts Humanities v.3, pp.1–15.
Guerra, M.B.B., Teaney, B.T., Mount, B.J., Asunskis, D.J., Jordan, B.T., Barker, R.J., Santos, E.E., Schaefer, C.E.G.R. (2017) Post-catastrophe analysis of the Fundão Tailings Dam Failure in the Doce River system, Southeast Brazil: Potentially Toxic elements in affected soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. v.228, pp.1–12.
Guha, A., Vinod Kumar, K. (2012) Structural controls on coal fire distributions — remote sensingbased investigation in the Raniganj coalfield, West Bengal. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.79, pp.467–475.
Haack, B., Jampoler, S. (1995) Colour composite comparisons for agricultural assessments. Internat. Jour. Remote Sens., v.16, pp.1589–1598.
Herold, M., Couclelis, H., Clarke, K. C. (2005) The role of spatial metrics in the analysis and modeling of urban land use change. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst., v.29, pp.369–399.
IEA (2018) World Energy Outlook, International Energy Agency, https://coal.nic.in/content/production-and-supplies
Joshi, P.K., Kumar, M., Midha, N., Vijayanand, Paliwal, A. (2006) Assessing areas deforested by coal mining activities through satellite remote sensing images and GIS in parts of Korba, Chattisgarh. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sens., v.34, pp.415–421.
Julea, A., Méger, N., Bolon, P., Rigotti, C., Doin, M.P., Lasserre, C., Trouvé, E., Lazarescu, V.N. (2011) Unsupervised spatiotemporal mining of satellite image time series using grouped frequent sequential patterns. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote Sens., v.49, pp.1417–1430.
Kauth, R.J., Thomos, G.S. (1976) The tasseled cap- agraphic description of the spectral-temporal development of agricultural crops as seen by Landsat. Proceedings, Symposiumon Machine Processing of Remotely Sensed Data, West Lafayette, IN: LARS, pp.41–51.
Latifovic, R., Fytas, K., Chen, J., Paraszczak, J. (2005) Assessing land cover change resulting from large surface mining development. Internat. Jour. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinfo., v.7, pp.29–48.
Li, Liang-jun, Wu, Yan-bin (2008) Application of remote-sensing-image fusion to the monitoring of mining induced subsidence. Jour. China Univ. Mining and Tech., v.18, pp.531–536.
Li, Z., Ma, Z., van der Kuijp, T.J., Yuan, Z, Huang, L. (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ., v.468–469, pp.843–853.
Li, N., Yan, C.Z., Xie, J.L. (2015) Remote sensing monitoring recent rapid increase of coal mining activity of an important energy base in northern China, a case study of Mu Us Sandy Land. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, v.94, pp.129–135.
Manna, A., Maiti, R. (2014) Opencast Coal Mining Induced Defaced Topography of Raniganj Coalfield in India — Remote Sensing and GIS Based Analysis. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sens., v.42, pp.755–764.
Manna, A., Maiti, R. (2016) Alteration of Surface Water Hydrology by Opencast Mining in the Raniganj Coalfield Area, India. Mine Water Environ., v.35, pp.156–167.
Ministry of Coal, Govt. of India, (2018) https://coal.nic.in/sites/upload_files/coal/files/coalupload/Activites-moc-2018-19.pdf
Moreno-de las Heras, M., Merino-Martin, L., Nicolau, J.M. (2009) Effect of vegetation cover on the hydrology of reclaimed mining soils under Mediterranean-Continental climate. Catena, v.77, pp.39–47.
Nascimento FS, Gastauer M, Souza-Filho PWM, Nascimento Jr WR, Santos DC, Costa MF (2020) Land Cover Changes in Open-Cast Mining Complexes Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens., v.12, pp.611. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040611
National Remote Sensing Centre Technical Manual (2012) National Land Use Land Cover Mapping using Multi-temporal Satellite Data. (2nd Cycle). pp.1–78.
Paterson, J.C.K. (1910) Bengal District Gazetteers: Burdwan, Bengal Secretariat Book Depot., Calcutta.
Rathore, C.S., Wright, R. (1993) Monitoring environmental impacts of surface coal mining. Internat. Jour. Remote Sens., v.14, pp.1021–1042.
Rigina, O. (2002) Environmental impact assessment of the mining and concentration activities in the Kola Peninsula, Russia by multidate remote sensing. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.75, pp.11–31.
Rudke, A.P., de Souza, V.A.S., dos Santosm, A.M., Xavier, A.C.F., Filho, O.C.R., Martins, J.A. (2020) Impact of mining activities on areas of environmental protection in the southwest of the Amazon: A GIS- and remote sensing-based assessment. Jour. Environ. Managmt., v.263, pp.110392.
Singh, R. P., Yadav, R. N. (1995) Prediction of subsidence due to coal mining in Raniganj coalfield, West Bengal, India. Engg. Geol., v.39, pp.103–111.
Tan, K. L., Wan, Y. Q., Wang, X. F., Sun, S.X., Chen, X. L. (2012) The exploration method of coal resources based on remote sensing technology, Geology in China. v.39, pp.218–227.
Xu, J., Zhao, H., Yin, P., Jia, D., Li, G. (2018) Remote sensing classification method of vegetation dynamics based on time series Landsat image: a case of opencast mining area in China. Jour. Image. Video Proc., v.113, pp.1–10.
Zhang M, Wang J, Feng Y (2019) Temporal and spatial change of land use in a large-scale opencast coal mine area: A complex network approach. Land Use Policy, v.86, pp.375–386. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.05.020
Zhu, D., Chen, T., Zhen, N., Niu, R. (2020) Monitoring the effects of open-pit mining on the eco-environment using a moving window-based remote sensing ecological index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., pp.1–13. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08054-2
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the EarthExplorer (EE) user interface, developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for providing satellite data sets used in this study. We are grateful to the Department of Remote Sensing and GIS, Vidyasagar University for infrastructural support required accomplishing this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patra, T., Dutta, D., Kundu, A. et al. Evolution of Opencast Mines in the Raniganj Coalfield (India): An Assessment through Multi-temporal Satellite Data. J Geol Soc India 98, 387–394 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-1990-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-1990-5