Abstract
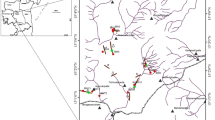
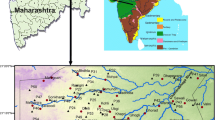
Exploration of groundwater resources in basaltic hard-rock terrain has always remained a challenging task for hydrogeologists as the potential groundwater zones/recharge pockets in such areas are associated with differential weathering, anisotropy, heterogeneities, fractured and fissured geological features etc. The thickness of the weathered/fractured layer overlying the compact rocks in such terrain plays a vital role in groundwater prospects. Paucity of water in the semi-arid trap covered areas of north Maharashtra necessitated to locate sources of groundwater almost all over the region. This has driven hydrogeologists to determine the role of dykes in the occurrence, movement and storage of groundwater. The study area is situated in Nandurbar district of Maharashtra bordering Narmada-Tapi rift zone. Two-dimensional (2D) electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) was used to generate subsurface resistivity models for delineating the availability of groundwater in the dyke-infested basaltic region of Nandurbar. The available dug well/borehole lithology suggests that the top layer is comprised of red bole, laterite or black soil followed by weathered/fractured rock. Results from the 2D inverted models of resistivity variation with depth suggest the occurrence of aquifers mostly in weathered/fractured zones within the traps or beneath it. The resistivity models suggest that the northern part of the study area represents a promising aquifer zone with reasonable thickness of weathered formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeoti, L., Alile, O.M. and Uchegbulam, O. (2010) Geophysical investigation of saline water intrusion into freshwater aquifers: A case study of Oniru, Lagos State. Sci. Res. Essays, v.5, pp.248–259.
Auden, J.B., (1949) Dykes in western India. Trans. Natl. Inst. Sci., India, v.3, pp.123–157.
Babar, M. and Muley, R. (2018) Investigation of Sub-surface Geology through Integrated Approach of Geological and Geophysical Studies in the Part of South-eastern Maharashtra, India. Amer. Jour. Water Res., v.6(3), pp.123–136. doi:https://doi.org/10.12691/ajwr-6-3-3
Babiker, M. and Gudmundsson, A. (2004) The effects of dykes and faults on groundwater flow in an arid land: The Red Sea Hills, Sudan. Jour. Hydrol., v.297, pp.256–273.
Banham, S. and Pringle, J.K. (2011) Geophysical and intrusive site investigations to detect an abandoned coal-mine access shaft, Apedale, Staffordshire, UK. Near Surface Geophys. doi:https://doi.org/10.3997/1873-0604.2011028.
Carrier, A., Fischanger, F., Gance, J., Cocchiararo, G., Morelli, G. and Lupi, M. (2019) Deep electrical resistivity tomography for the prospection of low- to medium-enthalpy geothermal resources. Geophys. Jour. Int., v.219, pp.2056–2072.
CGWB, (2013) Groundwater Information, Nandurbar district, Maharashtra. Technical report No. 1797/DBR/2013.
Dahlin, T. (2000) Electrode charge-up effects in DC resistivity data acquisition using multi electrode arrays. Geophys. Prospect., v.48(1), pp.181–187.
Deshpande, G.G. (1998) Geology of Maharashtra. Geological Society of India, Bangalore.
Duraiswami, R.A. (2005) Dykes as potential groundwater reservoirs in semiarid areas of Sakri Taluka, District Dhule of Maharashtra. Gondwana Geol. Magazine, v.20(1), pp.1–9.
Gemail, Kh. (2015) Application of 2D resistivity profiling for mapping and interpretation of geology in a till aquitard near Luck Lake, Southern Saskatchewan, Canada. Environ. Earth Sci., v.73, pp.923–935.
Geological Survey of India (GSI), (2001) District Resource Map — Dhule-Nandurbar District, Maharashtra. Geol. Surv. India, Kolkata.
Gupta, G., Patil, J.D., Maiti, S., Erram, V.C., Pawar, N.J., Mahajan, S.H. and Suryawanshi, R.A. (2015) Electrical resistivity imaging for aquifer mapping over Chikotra river basin, Kolhapur District, Maharashtra. Environ. Earth Sci., v.73, pp.8125–8143.
Gupta, G., Erram, V.C. and Kumar, S. (2012) Temporal geoelectric behavior of dyke aquifers in northern Deccan Volcanic Province, India. Jour. Earth System Sci., v.121(3), pp.723–732.
Hasan, M., Shang, Y., Akhter, G. and Khan, M. (2017) Geophysical Investigation of Fresh-Saline Water Interface: A Case Study from South Punjab, Pakistan. Ground Water. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12527.
Kumar, D., Thiagarajan, S. and Rai, S.N. (2011) Deciphering Geothermal Resources in Deccan Trap Region using Electrical Resistivity Tomography Technique. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.78, pp.541–548.
Loke, M.H. and Barker, R.D. (1996) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections using a quasi-Newton method. Geophys. Prospect., v. 44, pp.131–152.
Loke, M.H. (2011) Electrical imaging surveys for environmental and engineering studies- a practical guide to 2-D and 3-D surveys, Penang, Malaysia. https://www.geoelectrical.com/coursenotes.zip.
Maiti, S., Erram, V.C., Gupta, G., Tiwari, R.K., Kulkarni, U.D. and Sangpal, R.R. (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality: A fusion of geochemical and geophysical information via Bayesian Neural Networks. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.185(4), pp.3445–3465.
Melluso, L., Sethna, S.F., Morra, V., Khateeb, A. and Javeri, P. (1999) Petrology of the mafic dyke swarm of the Tapti River in the Nandurbar area (Deccan Volcanic Province). Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.43, pp.735–755.
Mondal, N.C., Singh, V.P. and Ahmed, S. (2013) Delineating shallow saline groundwater zones from southern India using geophysical indicators. Environ. Monit. Assess., v. 185, pp.4869–4886.
Nadagouda, B.V., Lakkundi, T.K., Ugarkar, A.G. and Puranik, S.C. (2012) Geo-Electrical Approach for Groundwater Prospecting in Deccan Trap Terrain around Mudalgi Village, Gokak Taluk, Belgaum District, Karnataka. Int. Jour. Earth Sci. Engg., v.5(3), pp.457–462.
Nilsen, K.H., Sydnes, M., Gudmundsson, A. and Larsen, B.T. (2003) How dykes affect groundwater transport in the northern part of the Oslo Graben. Geophys. Res. Abstracts, v.5, pp.09684.
Pakhmode, V., Kulkarni, H. and Deolankar, S.B. (2003) Hydrological-drainage analysis in watershed-programme planning: a case from the Deccan basalt, India. Hydrogeol. Jour., v. 11, pp.595–604.
Park, Y.H., Doh, S.J. and Yun, S.T. (2007) Geoelectric resistivity sounding of riverside alluvial aquifer in an agricultural area at Buyeo, Geum River watershed, Korea: An application to groundwater contamination study. Environ. Geol., v.53, pp.849–859.
Pawar, N.J., Pawar, J.B., Supekar, A., Karmalkar, N.R., Kumar, S. and Erram, V.C. (2008) Deccan dykes as discrete and prospective aquifers in parts of Narmada Tapi zone, Dhule District, Maharashtra. In: Srivastava, R.K., Sivaji, Ch., Chalapati Rao, N.V. (Eds.), Indian Dykes, GSI Special Volume Narosa Publishing House Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi India, pp.189–198.
Patil, S.K. and Rao, D.R.K. (2002) Palaeomagnetic and rock magnetic studies on the dykes of Goa, west coast of Indian Precambrian Shield. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.133, pp.111–125.
Peacock, J.R., Mangan, M.T., McPhee, D. and Wannamaker, P.E. (2016) Three dimensional electrical resistivity model of the hydrothermal system in Long Valley Caldera, California, from magnetotellurics. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.43(15), pp.7953–7962.
Rai, S.N., Thiagarajan, S. and Ratnakumari, Y. (2011) Exploration of groundwater in the basaltic Deccan traps terrain in Katol taluk, Nagpur district, India. Curr. Sci., v.101(9), pp.1198–1205.
Rai, S.N., Thiagarajan, S., Ratnakumari, Y., Anand Rao, V. and Manglik, A. (2013) Delineation of aquifers in basaltic hard rock terrain using vertical electrical soundings data. Jour. Earth Syst. Sci., v.122(1), pp.29–41.
Ratnakumari, Y., Rai, S.N., Thiagarajan, S. and Kumar, D. (2012) 2D Electrical resistivity imaging for delineation of deeper aquifers in a part of the Chandrabhaga River basin, Nagpur District, Maharashtra, India. Curr. Sci., v.102(1), pp.61–69.
Sethna, S.F., Khateeb, A. and Javeri, P. (1996) Petrology of basic intrusives in Deccan Volcanic Province south of Tapti Valley and their comparison with those along West Coast. Gondwana Geol. Magz., v.2, pp.225–232.
Shailaja, G., Kadam, A.K., Gupta, G., Umrikar, B.N. and Pawar, N.J. (2018) Integrated geophysical, geospatial and MCDA techniques for delineation of groundwater potential zones in a semi-arid hard-rock aquifer region, Maharashtra, India. Hydrogeol. Jour. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1883-2
Shailaja, G., Gupta, G., Suneetha, N. and Laxminarayana, N. (2019) Assessment of aquifer zones and its protection via second-order geoelectric indices in parts of drought-prone region of Deccan Volcanic Province, Maharashtra, India. Jour. Earth Syst. Sci., v.128, pp.78. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1104-y
Singh, R.P. and Jamal, A. (2002) Dykes as groundwater loci in parts of Nashik District, Maharashtra. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.59(2), pp.143–146.
Suneetha, N., Gupta, G., Tahama, K. and Erram, V.C. (2020) Two-dimensional modelling of electrical resistivity imaging data for assessment of saline water ingress in coastal aquifers of Sindhudurg district, Maharashtra, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00725-w
Suneetha, N., Gupta, G., Rambabu, S., Tahama, K. and Erram, V.C. (2021) Evaluation of water quality and its suitability for drinking and irrigational purpose in parts of coastal Sindhudurg district, Maharashtra, India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.97, pp.173–185. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1649-7
Tahama, K., Gupta, G., Baride, M.V., Patil, J.B. and Baride, A. (2019) Evaluation of Groundwater Potential and Aquifer Protective Capacity of the Overburden Units in Trap Covered Dhule District, Maharashtra. Bull. Pure Appl. Sci., v.38F(2), pp.246–265. doi:https://doi.org/10.5958/2320-3234.2019.00019.2
Thiagarajan, S., Rai, S.N., Kumar, D. and Manglik, A. (2018) Delineation of groundwater resources using electrical resistivity tomography. Arab. Jour. Geosci., v. 11. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3562-y
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Director, IIG, for the kind permission to publish this paper. The authors are thankful to Shri B.I. Panchal for drafting the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahama, K., Gupta, G., Erram, V.C. et al. Electrical Resistivity Imaging in Parts of Nandurbar District, Deccan Volcanic Province, Maharashtra, India. J Geol Soc India 98, 305–313 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-1981-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-1981-6