Abstract
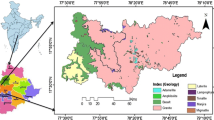
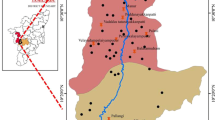
Fresh and pure water has an important role to play for healthy life. Currently, in many studies higher concentrations of contaminants like calcium, sodium, nitrate, lead, chromium, arsenic, fluoride etc. have been reported that makes the water unfit for its direct consumption. Sources and release mechanism of many such pollutants is still not known. These sources can be anthropogenic or geogenic. This paper deals with one of such contaminants namely fluoride and emphasizes on its release from various minerals viz. Gypsum, fluorite, tourmaline, actinolite, plagioclase, biotite, quartz, kayanite, epidote and orthoclase under different pH environment. It has been noted that maximum fluoride has been released from the fluorite at all pH environment (acidic, normal and alkaline) of water while minimal fluoride was released from kayanite. However, orthoclase, tourmaline and biotite can release fluoride in considerable amount. The attempts were also made to compare the release of fluoride from modern sand (Ganga sediments) with ancient sand (from sandy aquifer) under different pH condition. Outcome of studies shows that maximum fluoride released from the sand at the pH range of 6.1 to 8.2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adimalla, N. and Li, P. (2019) Occurrence, health risks, and geochemical mechanisms of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of the rock-dominant semi-arid region, Telangana State. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An Internat. Jour., v.25, pp.81–103. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1480353
Chakraborti, D., Rahman, M. M., Chatterjee, A., Das, D., Das, B., Nayak, B., Pal, A., Chowdhury, U.K., Ahmed, S., Biswas, B.K., Sengupta, M.K., Lodh, D., Samanta, G., Chakraborty, S., Roy, M.M., Dutta, R.N., Saha, K.C., Mukherjee, S.C., Pati, S. and Kar, P.B. (2016), Fate of Over 480 Million Inhabitants Living in Arsenic and Fluoride Endemic Indian Districts: Magnitude, Health, Socio-Economic Effects And Mitigation Approaches. Jour. Trace Elem. Med. Biol., v.38, pp.33–45.
Choubsia, S.L. (1999) Some observations on endemic fluorosis in domestic animals in Southern Rajasthan (India). Vet. Res. Comm., v.23, pp.457–465.
Farooqi, A., Masudaa, H. and Firdous, N. (2007) Toxic Fluoride and Arsenic Contaminated Groundwater in the Lahore and Kasur Districts, Punjab, Pakistan and Possible Contaminant Source. Environ. Pollut., v.145(3), pp.839–849
Fawell, J., Bailey, K., Chilton, J., Dahi, E., Fewtrell, L., Magara, Y. (2015) Fluoride in Drinking-Water. London: Published on behalf of the World Health Organization by IWA Publishing, Alliance House, 12 Caxton Street, London SW1H 0QS, UK.
Gleick, Peter H., (1993) Water. In: Crisis: A Guide to the World’s Fresh Water Oxford University Press.
Kumar, S. and Saxena, A. (2011) Chemical Weathering of the Indo-Gangetic Alluvium with Special Reference to Release of Fluoride in the Groundwater, Unnao District, Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.77, pp.459–477
Li, P., Li, X., He, Li, Y., Li, G. Xiang, (2019) Occurrence And Health Implication Of Fluoride In Groundwater of Loess Aquifer in The Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study of Tongchuan, Northwest China. Exposure and Health, v.1, pp.95–107
Li, P., Qian, H.J., Wu, Chen, Zhang, Y., Zhang, H. (2014) Occurrence And Hydrogeochemistry of Fluoride in Alluvial Aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ. Earth Sci., v.71, pp.3133–3145.
Meij, R. (1995) The Distribution of Trace Elements during the Combustion of Coal. In: Swain, DJ, Goodarzi, F. (Eds.), Environmental Aspects of Trace Elements in Coal. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell Ma USA, Chapter 7, pp.111–127.
Mukherjee, I. and Singh, U.K. (2019) Fluoride Abundance and their Release Mechanisms in Groundwater along, with Associated Human Health Risks in A Geologically Heterogeneous Semi Arid Region of East India. Microchemical Jour. (Elsevier), v.152, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104304.
Naseem, S., Rafique, T., Bashir, E., Bhanger, M.I., Laghari, A. and Usmani, T.H. (2010) Lithological Influences On Occurrence Of High-Fluoride Groundwater in Nagar Parkar Area, Thar Desert, Pakistan., Chemosphere, v.78, pp.1313–1321.
Piekos, R. and Paslawska, S. (1998), Leaching Characteristics of Fluoride from Coal Fly Ash, Fluoride, v.31(4), pp.188–192 [https://www.fluorideresearch.org/314/files/FJ1998_v31_n4_p188-192.pdf]
Rao, R., Rao, N.V., Suryaprakasa, K. and Schuiling, R.D. (1993) Fluorine Distribution in Waters of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol., v.21, pp.84–89
Rasool A. Farooqi, Xio, T., Ali, W., Noor, S.O., Abiola, S., Nasim, (2018) A Review of Global Outlook on Fluoride Contamination in Ground Water with Prominence on the Pakistan Current Situation, Environ. Geochem. Health, v.40, pp.1265–1281.
Read, H.H. (2005) Rutley’s Elements of Mineralogy, Twenty-seventh Edition 482p.
Saxena, A., Kumar, S. and Goel, P. (2014) Source mineral for the release of Arsenic in the groundwater of Karanda block, Ghazipur district, Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.84, pp.590–596.
Saxena, V.K. and Ahmed, S. (2001) Dissolution of ûuoride in Groundwater: A Water-Rock Interaction Study. Environ. Geol., v.40, pp.1084–1087.
Shaji, E., Bindu, Viju J. and Thambi, D.S. (2007), High Fluoride in Ground-water of Palghat District, Kerala. Curr. Sci., v.92(2), pp.240–245.
Shortt, H. E., McRobert, G.R. and Bernard, T.W. (1937) Endemic ûuorosis in the Madras Presidency. Indian Jour. Medical Res., v.25(2), pp.553–568.
Shukla, S., and Saxena, A. (2018) Global Status of Nitrate Contamination in Groundwater: Its Occurrence, Health Impacts, and Mitigation Measures, Handbook of Environmental Materials Management, Springer International Publishing, pp.16–17.
Shukla, S. and Saxena, A. (2020) Sources and Leaching of Nitrate Contamination in Groundwater. Curr. Sci., v.118(6), pp. 883–891. doi: https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v118/i6/883-891.
Shusheela, A.K. (2002) Fluorosis in Developing countries: Remedial measures and Approaches. Proc. Indian Nal. Sci. Acad. (PINSA), B68 No.5, pp.389-400 [https://insa.nic.in/writereaddata/UpLoadedFiles/PINSA/Vol68B_2002_5_Art02.pdf]
Singh, P. (2010) Geochemistry and Provenance of Stream Sediments of the Ganga River and its major tributaries in the Himalayan region, India. Chemical Geol., v.269, pp.220–236.
Srivastava, R.P. (1968) Systematic Geological Mapping in Parts of Ajmer, Bhilwara and Udaipur Districts, Rajasthan included in Topo-Sheet Nos. 45 K/1 & 5. Geol. Surv. India, Progress Report for the field-season 1966–67 (GSI WRO 630), pp.1–18.
Tahaikt, M, Haddou, A. Ait, Habbani, R. El, Amor, Z., Elhannouni, F., Taky, M., Kharif, M., Boughriba, A, Hafsi, M., Elmidaoui, A., (2008) Comparison of The Performances of Three Commercial Membranes in ûuoride Removal By Nanoûltration, Continuous Operations. Desalination (Elsevier) v.225(1–3), pp.209–219. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.07.007
Teotia, S.P.S., Teotia, M., Singh, D.P., Rathour, R.S., Singh, C.V., Tomar, N.P.S., Nath, M. and Singh, N.P. (1984) Endemic ûuorosis: Change To Deeper Bore Wells as A Practical Community-Acceptable Approach to its Eradication. Fluoride, v.17, pp.48–52.
Vardhan, C.M.V. and Karthikeyan, J. (2011) Removal of Fluoride from Water Using Low-Cost Materials, Fifteenth International Water Technology Conference, Alexandria, Egypt, pp.1-14.
Water Quality Report by Jal Shakti Mission (2019) [website: https://ejalshakti.gov.in/IMISReports/Reports/TargetAchievement/rpt_WQM_WaterQualityTestingInLabs_S.aspx?Rep=0&RP=Y&APP=IMIS]
Wenzel, W.W. and Blum, Weh (1992) Fluoride speciation and mobility in Fluoride contaminated soil and minerals. Soil Sci., v.153, pp.357–364.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P., Saxena, A. Release of Fluoride in Groundwater from Various Rock Forming Minerals and Sandy Aquifer of Central Ganga Basin, India. J Geol Soc India 98, 133–138 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-1939-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-1939-8