Abstract
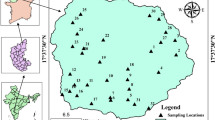
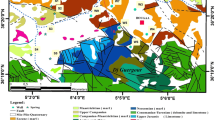
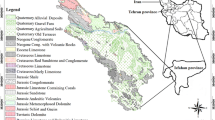
Major hydrochemical ionic concentrations in groundwater has been analyzed during dry and wet periods (pre-monsoon and post-monsoon periods, respectively) in a semi-arid Sanganer block, Jaipur district, Rajasthan, India. The standard methods were utilized for evaluating its appropriateness for irrigation and drinking uses. Results indicate that groundwater is moderately alkaline and predominantly Ca-Na-HCO3-type. About 38.8, 33.3, 33.3 and 22.2% samples for TDS, Cl−, NO3− and F− concentrations, respectively, have exceeded the guidelines of drinking water standards in the dry period whereas in the wet period, about 44.4, 33.3, 44.4 and 16.6%, respectively. The EC, SAR, RSC, Na%, KR, and MAR parameters indicate that the majority of samples are unsuitable for irrigation. Gibbs diagram suggests that the hydrochemistry is dominatingly impacted by the evaporation mechanism. Chloro-alkaline indices adapted show that the study area mostly belong to the discharge areas. The corrosivity ratio indicates that only PVC pipes could be utilized in an area of 280 km2 for the groundwater based water supply. Further percentage of pollution index shows that groundwater is adversely impacted partially by the anthropogenic activities. But the Na++K+ vs. Cl− plot illustrates that the combined Na+−K+ contribution is from the silicate weathering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, Z., Mapoma, H.W.T., Su, C., Aziz, S.Z., Ma, Y. and Abbas, N. (2018) Spatial analysis of groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation in Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.190(7), Art.391.
Ayers, R.S. and Westcot, D.W. (1985) Water quality for agriculture. FAO Immigration and Drain. Paper no. 29(1), pp.1–109.
Bachmat, Y. (1994) Groundwater contamination and control. Marcel Dekker Inc. New York.
Balasubramanian, A. (1986) Hydrogeological investigation in the Tambraparani River basin, Tamil Nadu. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Mysore, India.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) (2012) Indian Standards Specification for drinking water. IS: 10500: 2012, 2nd Rev., BIS, New Delhi.
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) (2000) Project on beneficiation of ground water quality with reference to fluoride problems. CGWB Report, Western Region, Jaipur, 14p.
David, M.D. and Gentry, L.E. (2000) Anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen and phosphorous and riverine export for Illinois, USA. Jour. Environ. Qual., v.29, pp.494–508.
Davis, S.N. and Deloiest, R.J.M. (1966) Hydrogeology. Wiley, New York, 463p.
Durfor, C.N. and Becker, E. (1964) Public water supplies of the 100 largest cities in the United States Water Supply. Paper No. 1812, pp.343–346.
Gibbs, R.J. (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, v.170, pp.1088–1090.
Hem, J.D. (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters. 3rd edn. USGS Water Supply Paper No.2254, pp.117–120.
Hem, J.D. (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters. Book 2254, 3rd edn. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, 263p.
Joshi, D.M., Kumar, A. and Agrawal, N. (2009) Assessment of the irrigation water quality of river Ganga in Haridwar district, India. Jour. Chem., v.2(2), pp.285–292.
Keesari, T., Kulkarni, U.K., Deodhar, A., Ramanjaneyulu, P.S., Sanjukta, A.K. and Kumar, U.S. (2014) Geochemical characterization of ground-water from an arid region in India. Environ. Earth Sci., v.71, pp.4869–4888.
Kelly, W.P. (1963) Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Science, v.95(4), pp.355–391.
Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Esmaeili, A. and Rastmanesh, F. (2010) The source of fluoride toxicity in Muteh area, Isfahan, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci., v.61, pp.777–786.
Kumar, K.S., Chandrasekhar, N., Seralathanp Godson Price S. and Magesh, N.S. (2012) Hydrogeochemical study of shallow carbonate aquifers, Rameswaram Island, India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.184(7), pp.4127–4138.
McCarthy, M.F. (2004) Should be restrict chloride rather than sodium? Med. Hypothesis, v.63, pp.138 148.
Mondal, N. C. and Singh, V. P. (2011) Hydrochemical analysis of salinization for a tannery belt in Southern India. Jour. Hydrol., v.405(3–4), pp.235–247.
Mondal, N.C., Adike, S., Singh, V.S., Ahmed, S. and Jayakumar, K.V. (2017) Determining shallow aquifer vulnerability by the DRASTIC model and hydrochemistry in granitic terrain, Southern India. Jour. Earth Sci., v. 126(6), pp.1–23.
Mondal, N.C., Prasad, R.K., Saxena, V.K., Singh, Y. and Singh, V.S. (2009) Appraisal of highly fluoride zones in groundwater of Kurmapalli watershed, Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh (India). Environ. Earth Sci., v.59(1), pp.63–73.
Mondal, N.C., Singh, V.P., Singh, VS. and Saxena, V.K. (2010) Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry. Jour. Hydrol., v.1–2, pp.100–111.
Mondal, N.C., Tiwari, K.K., Sharma, K.C. and Ahmed, S. (2016) A diagnosis of groundwater quality from a semiarid region in Rajasthan, India. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.9(9), pp.1–22, art.602.
Nagaiah, E., Sonkamble, S., Mondal, N.C. and Ahmed, S. (2017) Natural zeolites enhance groundwater quality: evidences from Deccan basalts in India. Environ. Earth Sci., v.76, pp.536 1–17.
Pacheco, F. and Van der Weijden, C.H. (1996) Contributions of water-rock interactions to the composition of groundwaters in areas with a sizeable anthropogenic input: a case study of the water of the Fundao area, Central Portugal. Water Resour. Res., v.32, pp.3553–3570.
Pant, R.R., Zhang, F., Rehman, F.U., Wang, G., Ye, M., Zeng, C. and Tang, H. (2018) Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal. Sci. Total Environ, v.1, pp.770–782.
Piper, A.M. (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, v.25(6), pp.914–928.
Rafique, T., Naseem, S., Usman, T.H., Basir, E., Khan, F.A. and Bhanger, M.I. (2009) Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high fluoride groundwater in the Nagar Parkar area Sindh, Pakistan. Jour. Hazardous Materials, v.171, pp.424–430.
Rajesh, R., Brindha, K. and Elango, L. (2015) Groundwater quality and its hydrochemical characteristics in a shallow weathered rock aquifer of southern India. Water Quality, Exposure and Health, v.7(4), pp.515–524.
Rao, N.S. (2009) Fluoride in groundwater, Varaha river basin Visakhapatnam district Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.152(1–4), pp.47–60.
Richards, L.A. (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Agricultural Handbook 60, USDA and IBH publishing Co. Ltd., New Delhi, India, pp.8–99.
Ryzner, J.W. (1944) A new index for determining amount of calcium carbonate scale formed by water. Jour. Amer. WW Assocn., v.36, pp.472–486.
Sarwade, D.V., Nandakumar, M.V., Kesari, M.P., Mondal, N.C., Singh, V.S. and Bhoop Singh (2007) Evaluation of seawater ingress into an Indian Attoll. Environ. Earth Sci., v.52(2), pp.1475–1483.
Schoeller, H. (1967) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Method and techniques of groundwater investigation and development Water Research Series — 33, UNESCO, pp.44–52.
Sharma, D.A., Rishi, M.S. and Keesari, T. (2017) Evaluation of groundwater quality and suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in southwest Punjab, India using hydrochemical approach. Applied Water Science, v.7, pp.3137–3150.
Soumya, B.S., Sekhar, M., Riotte, J., Banerjee, A. and Braun, J.J. (2013) Characterization of groundwater chemistry under the influence of lithologic and anthropogenic factors along a climatic gradient in Upper Cauvery basin, South India. Environ. Earth Sci., v.69(7), pp.2311–2335.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Chidambaram, S., Prasanna, M.V., Vasanthavihar, M., John, P. and Anandhan, P. (2008) Identification of major sources controlling groundwater chemistry from a hard rock terrain-a case study from Mettur taluk, Salem district, Tamil Nadu, India. Jour. Earth System Sci., v. 117, pp.49–58.
Stallard, R. and Edmond, J.M. (1983) Geochemistry of the Amazon. 2. The influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.88, pp.9671–9688.
Subba Rao, N., Surya Rao, P., Venktram Reddy, G, Nagamani, M., Vidyasagar, G. and Satyanarayan, N.L.V. (2012) Chemical characteristics of groundwater and assessment of groundwater quality in Varaha river basin, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.184, pp.5189–5214.
Szaboles, I. and Darab, C. (1964) The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate content of soils. In: Proc. 8th International Congress of ISSS. Trans II, pp.803–812.
Todd, D.K. (1980) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley International Edition, John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York.
Trivedy, R.K. and Goel, P.K. (1984) Chemical and biological methods for water pollution studies. Environ Publication, Karad, Maharashtra, India.
Wilcox, L.V. (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. US Dept Agri Curcular 969, Washington DC, p.19.
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva.
Acknowledgements
Prof. V.M. Tiwari, Director of CSIR-NGRI, Hyderabad has encouraged and permitted to publish this article (Ref. No.: NGRI/Lib/2018/Pub-106). This work is a part of the first author’s Ph.D. Thesis [Ref. No.: 31/023(0240)/2018-ERR-I, dated: 13-07-2018]. The anonymous reviewer has given his critical and constructive comments to improve the article. The authors are thankful to them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, A., Tiwari, K.K. & Mondal, N.C. Hydrochemical Characterization for Groundwater Suitability in a Semi-Arid Area in Sanganer Block, Jaipur District, Rajasthan. J Geol Soc India 96, 399–409 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1569-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1569-y