Abstract
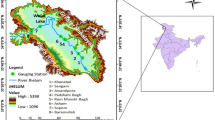
Flooding is a widespread, frequent and most disastrous natural hazard around the globe. Flood frequency analysis is a necessary step for floodplain zoning and planning of the dams, bridges, culverts, embankments and anti-erosion structures along or across a river. In the Rapti river basin, the flood frequency analysis has been performed using the annual maxima series of discharges recorded at Jalkundi and Birdghat (Gorakhpur) gauge and discharge (G/D) sites with the help of Log Pearson Type-III (LP-III) and Gumbel Extreme Value -1 (EV1) methods. The flood discharges at 25, 50, 100, 200, 500 and 1000 year return periods are lower at Birdghat than those at Jalkundi. Such a reverse scenario indicates storage of flood waters in the Rapti floodplain near and upstream of Birdghat G/D site. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) and Anderson-Darling (A–D) tests have been applied on the annual maxima series of discharge data to identify the appropriate curve fitting models, namely LP-III and EV1. The goodness-of-fit analysis shows that the LP-III method is more appropriate for flood frequency analysis than the EV1 at above mentioned G/D sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang, A.H-S., Tang, W. (2007) Probability concepts in engineering: emphasis on applications to civil and environmental engineering. John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Barker, V.R., (1977) Stream channel response to floods with examples from central Texas. Geog. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.88, pp.1057–1070.
Bhat, M.S., Alam, A., Ahmad, B., Kotlia, B.S., Farooq, H., Taloor, A.K., Ahmad, S. (2019) Flood frequency analysis of river Jhelum in Kashmir basin. Quat. Internat., v.507, pp.288–294, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2018.09.039.
Chandra, S., Rhodes, E., Richards, K. (2007) Luminescence dating of late quaternary fluvial sediments in the Rapti basin, north-central Gangetic plains. Quat. Internat., v.159, pp.47–56.
Dhital, M.R. (2015) Geology of the Nepal Himalaya-regional perspective of the classic collided orogen. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02496-7.
Garde, R.J. (1998) Floods and flood control: engineering approach. In: V.S. Kale (Ed.), Flood studies in India. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.41, pp.173–193.
Hydrological Records of Nepal (1998) Stream Flow Summary, HMG of Nepal, Kathmandu.
Kale, V.S. (2003) Geomorphic effects of monsoon floods on Indian rivers. Nat. Hazards, v.28, pp.65–84, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021121815395.
Kale, V.S., Gupta, A. (2010) Introduction to geomorphology. Universities Press (India) Pvt. Ltd., India.
Kamal, V., Mukherjee, S., Singh, P., Sen, R., Vishwakarma, C.A., Sajadi, P., Asthana, H., Rena, V. (2017) Flood frequency analysis of Ganga river at Haridwar and Garhmukteshwar. Appl. Water Sci., v.7, pp.1979–1986, doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0378-3.
Kulshrestha, S.M. (1997) Drought management in India and potential contribution of climate prediction. JointCOLA/CARE Technical Report No.1, Centre for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies/Centre for the Application of Research on the Environment, Maryland, p.105.
Kumar, A., Ram, L.C. (1995) Semi-Quantitative precipitation forecast for Rapti catchment by synoptic analogue method. Mausam, v.46, pp.97–99.
Kumar, R. (2019) Flood inundation and hazard mapping of 2017 floods in the Rapti River basin using Sentinel-1A synthetic aperture radar images. In: P. Kumar, M. Rani, P.C. Pandey, H. Sajjad, B. Chaudhary (Eds.), Applications and Challenges of Geospatial Technology. Springer, pp.77–98.
Kumar, R., Singh, R., Gautam, H., Pandey, M.K. (2018) Flood hazard assessment of August 20, 2016 floods in Satna district, Madhya Pradesh, India. Remot. Sens. Appl. Soc. and Env., v.11, pp. 104–118, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2018.06.001.
Mohindra, R., Parkash, B., Prasad, J. (1992) Historical geomorphology and pedology of the Gandakmegafan, middle Gangetic plains, India. Ear.Surf. Proc. and Landf., v.17, pp. 643–662.
National Water Development Authority (2019) Detailed Project Report (DPR) BurhiGandak-Noon-Baya-Ganga intra-state link of Bihar (Chapter III Hydrology). http://nwda.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/DPR_BG_N_BG_Ch_3.pdf. Accessed 28 March, 2019.
Nazemi, A.R., Elshorbagy, A., Pingale, S. (2011) Uncertainties in the estimation of future annual extreme daily rainfall for the city of Saskatoon under climate change effects. Proc. 20th Canadian Hydrotech. Conf., CSCE.
Ponce, V.M. (1989) Engineering Hydrology, Principles and Practices. Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Singh, D.S., Prajapati, S.K., Singh, P., Singh, K., Kumar, D. (2015) Climatically induced levee break and flood risk management of the Gorakhpur region, Rapti river basin, Ganga plain, India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.85, pp.79–86.
Singh, O. and Kumar, M. (2013) Flood events, fatalities and damages in India from 1978 to 2006. Nat. Hazards, v.69, pp.1815–1834.
Singo, L.R., Kundu, P.M., Odiyo, J.O., Mathivha, F.I., Nkuna, T.R. (2013) Flood frequency analysis of annual maximum stream flows for Luvuvhu river catchment, Limpopo province, South Africa. http://univendspace.univen.ac.za/handle/11602/1262. Accessed on 13 June 2019.
Sivasami, K.S. (2002) Environmental effect due to floods and reservoirs. In: V. Subramanian (Ed.), Environmental hazard in South Asia. Capital, New Delhi, pp. 65–82.
Srivastava, R.C. (1975) Conservation of flood water and its planning in Rapti basin. Uttar Bhar. Bhoog. Patri., v.11, pp.37–46.
USGSEE (2015) EarthExplorer Web Portal. http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ Accessed 23 October 2015.
Ward, R.C. (1978) Floods — a geographical perspective. The Macmillian Press, London.
Yadav, R. (1998) Best fitted distribution of estimation of future flood for Rapti river systems in eastern Uttar Pradesh. Indian Jour. Engg. Mat. Sci., v.5, pp.22–27.
Yadav, R.P. (1999) Floods in eastern U.P. Radha Publication, New Delhi-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R. Flood Frequency Analysis of the Rapti River Basin using Log Pearson Type-III and Gumbel Extreme Value-1 Methods. J Geol Soc India 94, 480–484 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1344-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1344-0